![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
When does the nutritive suck rhythm develop? |
35-36 wks |
Either 28-33 wks or 35-36 |
|
|
Describe 4 differences between nutritive (N) and non nutritive suck (NNS) |
N: for nutrition NNS: state regulation/exploration N: initially continuous bursts then shorter suck bursts NNS: short suck bursts w/ brief pauses eg. Maggie in Simpsons N: 1 Suck /sec NNS: 2 sucks/sec N: suck/swallow 1:1 NNS: suck/swallow 8:1 |
|
|
|
Which reflex is debated to have dvpd at term? |
Cough - new research suggests neonates have apnoeac event to protect airway |
Has major role in airway protection |
|
|
What does penetration mean ;) |
When food/drink gets to the level of vocal folds |
|
|
|
What does aspiration mean? |
When food/drink enters the airway, below level of vocal folds |
|
|
|
At what age does World Health Organisation recommend weaning? |
6 months |
|
|
|
Name 2 treatments for reflux |
Anti reflux meds & Nissen fundoplication |
|
|
|
In the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Innitiative (IDDSI) what are the 5 levels of drink thickness? |
Thin, Slightly Thick, Mildly Thick, Moderately Thick, Extremely Thick |
|
|
|
What does a Moderately Thick drink equate to on the modified food scale? |
Liquidised |
|
|
|
What does an extremely thick drink equate to on modified food scale? |
Pureed |
|
|
|
Which cranial nerve innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles |
Hypoglossal (12) |
|
|
|
Which cranial nerve responsible for taste and touch of posterior 1/3 tongue |
Glossopharyngeal (9) |
|
|
|
What are 4 key principles of ethics? |
Beneficience- acting in the best interest Non-maleficience- avoiding deliberate harm Autonomy-respect for clients wishes & ability to make decisions for themselves. Justice- fair distribution of resources (Beauchamp & Childress, 2001) |
|
|
|
Name 5 types of consent |
Implied Expressed Restricted Unaltered Refused |
|
|
|
True or False- intervention without consent is considered to be assault? |
True |
|
|
|
Which statement is not from BMA guidance on consent. A) make a free choice (no pressure)B) understand, in broad terms, what consequence would be of not receiving proposed treatment.C) retain the informatiom for at least 45 minutes. |
C Person also needs to: Understand what the medical treatment is, it's purpose and why being proposed. Understand main benefits, risks and alternatives Retain information long enough to make an effective decision (thus have to ask repeatedly if have any short term memory diffs) |
|
|
|
What is Gillick (Fraser) Competence |
A child under age 16 can give consent if have sufficient understanding and intelligence to make their own decision on the matter. (Example of requesting contraceptive pill). |
|
|
|
What's the age of legal consent? |
16 yrs |
|
|
|
At what age can you refuse treatment without needing parents' consent? |
18 yrs + |
|
|
|
Describe Mendelsohn Manouevre + what it's for |
Compensatory Technique. Swallow and palate your larynx. When your larynx is elevated, hold it in position for several secs. Works on poor laryngeal elevation, keeping the cricophartngeal sphincter open for longer, |
|
|
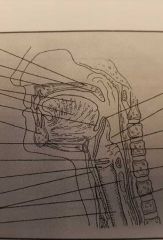
|
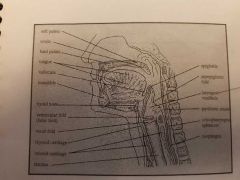
|
|
|

|
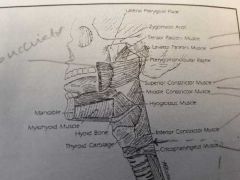
|
|
|
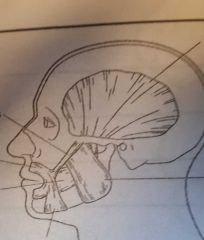
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
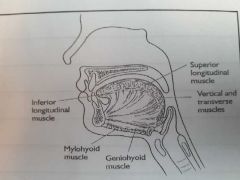
|
|
|
|
What's the respiratory rate of a pre-term infant |
40-60 breaths per min |
|
|
|
What's the respiratory rate of full term infant? |
30-40 breaths/min |
|
|
|
What's respiratory rate of an infant 1-4 yrs? |
25-30 breaths /min |
|
|
|
What's the respiratory rate of adult? |
12-16 breaths /min |
|
|
|
How is O2 saturation measured? |
Quant of O2 in blood ready for exchange at tissue level. % |
|
|
|
Which of these O2 sats indicate hypoxia? < 90, 92-95, < 95 |
< 90 Pre-term infants: 92-95, term infants > 95, infants with cardio often < 95 |
|
|
|
Name the 12 Limiting Factors |
1. Exaggerated jaw movement (high tone) eg. Open mouth, gross jaw gradation 2. Jaw thrust (high tone) eg. Forceful & sudden jaw drop 3. Jaw retraction (high tone) 4.Exaggerated tongue protrusion (low tone) 5. Tongue thrust (high tone) 6. Tongue retraction (pulled: high tone, falls into pharynx: low tone), 7. Tonic bite reflex (high tone) 8. Jaw clenching (high tone) 9. Jaw anchoring (low tone) 10. Lip retraction (high tone) 11. Lip pursing (high tone) 12. Low tone lips |
|
|
|
What's blue dye test and name disadv and advantages |
Used with trachee patients, where they swallow blue dye and then SLT suctions trachee to see if blue dye has entered airway. Disadv: only shows gross aspiration so cld get "false negative" eg. trace, subjective, doesn't tell you when / why aspiration occured, pts have died from blue dye poisoning Adv: simple, available, low cost, indicates gross aspiration |
|
|
|
What's Oximetry and advs and disadvs? |
Monitors o2 saturation of capillary blood flow. Normal sats = 99-100%. Advs: portable, non-invasive, info on swallow breath co-ord, monitors 1 aspect of response to feeding, can show readiness for ax eg. If desat when handled then bad sign Disadv: research not correlated desats to aspiration, affected by movement, affected by skin pigmentation, need to use over period time. |
|
|
|
What is Scintintigraphy and what can it measure? |
Assesses movement of a radoinuclide bolus through oral, pharyngeal and oesophageal stages of the swallow. Quantifies bolus residue if pharynx and amount aspirated. Also records GOR. Can use with vffs and to see lungs ability to clear penetrated material over time. Disadv: lower spec images of anatomy, can't be used diagnostically without other tool. |
|

