![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Alaska Current
|
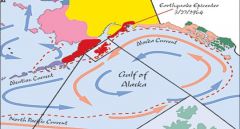
- Warm-water eddy current
- Resulting from the northward diversion of a portion of the North Pacific Current when it meets the west coast of the North American continent |
|
|
Aleutian current
(subarctic current) |
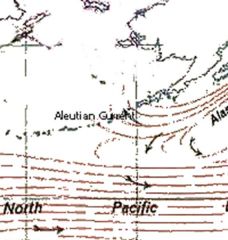
- Eastward flowing ocean current which lies north of the North Pacific Current
- Northern branch of the Kuroshio Current which moves northeast then east - As it approaches the coast of North America it divides to form the northward-flowing Alaska current and the southward-flowing California Current |
|
|
Davidson Current
|
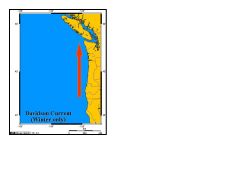
- Weak and narrow
- Countercurrent of the Pacific Ocean running north along the western coast of the United States from northern California to Washington to at least latitude 48° N - Prevails during the winter months, generally from September through February |
|
|
California Current
|
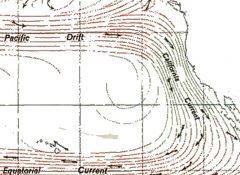
- Cold current
- Moves south along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia, and ending off southern Baja California - Part of the North Pacific Gyre |
|
|
Cromwell current
(Pacific Equatorial Undercurrent) (Equatorial Undercurrent) |
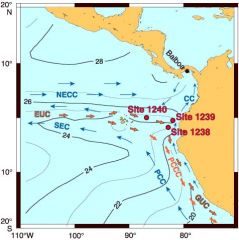
- A submarine river: particular ocean current that is, in effect, a river flowing under the surface of an ocean
- 250 miles (400 km) wide and flows to the east - hidden 300 feet (100 m) under the surface of the Pacific Ocean at the Equator - Relatively narrow in depth compared to other ocean currents at only 100 feet deep |
|
|
East Australian Current
|
- Warm current
- Results in a current vortex in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand - Also acts to transport tropical marine fauna to habitats in sub-tropical regions along the south east Australian coast |
|
|
Equatorial Counter Current
|
- Warm current
- Significant current in the Pacific, Atlantic and Indian Oceans - Flows west-to-east at approximately five degrees north - Result from the need to balance the movement of water to the west of each ocean, caused by the westerly flowing North and South Equatorial currents |
|
|
Humboldt Current
(Peru Current) |
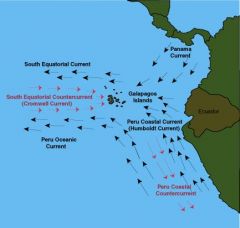
- Cold Current
- One of the major upwelling systems of the world |
|
|
Kamchatka Current
(Oyayisho current) |
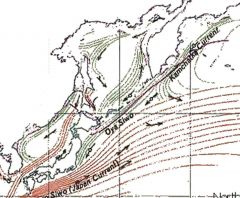
- Cold-water current
- Flowing south-westward from the Bering Strait, along the Siberian Pacific coast and the Kamchatka Peninsula - A portion of this current then becomes the Oyashio Current while the remainder joins the warmer North Pacific Current |
|
|
Kuroshio Current
(Japanese 黒潮) |
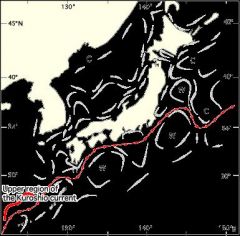
- Warm current
- World's second-largest - Found in the western Pacific Ocean off the east coast of Taiwan and flowing northeastward past Japan, where it merges with the easterly drift of the North Pacific Current - Transports warm, tropical water northward towards the polar region |
|
|
Tsushima Current
|
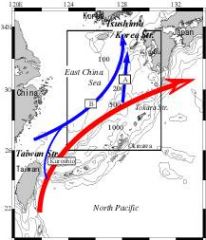
- Branch into the Sea of Japan
|
|
|
North Pacific Current
(North Pacific Drift) |

- Slow warm water current
- Flows west-to-east between 40 and 50 degrees north in the Pacific Ocean - Forms the northern part of the North Pacific Subpolar Gyre - Formed by the collision of the Kuroshio Current and the Oyashio Current |
|
|
Oyashio Current
|
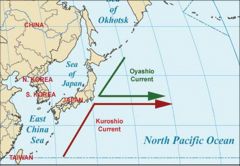
- Cold subarctic ocean current
- Flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean - Has an important impact on the climate of the Russian Far East, mainly in Kamchatka and Chukotka - During glacial periods the current cannot flow |

