![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
|
Scalar quantities have magnitude only. Vector quantities have a magnitude and a direction. Vector quantities may be represented by an arrow. (length = magnitude, direction = directions of quantity |
|
|
What is a force?
|
A force is a push or pull that acts on an object due to the interaction with another object. All forces are either contact forces or non contact forces. It is a vector quantity
|
|
|
Examples of contact forces?
|
Friction Air resistance Tensions Normal contact force |
|
|
Examples of non-contact forces?
|
Gravitational force Electrostatic force Magnetic force |
|
|
Label the forces acting on a plane. |
Thrust ( pushes in desired direction) Drag ( opposite to thrust) Lift Weight (downwards) |
|
|
What is weight?
|
Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity. The weight of an object depends on the gravitational field strength at the point where the object is. It is measured using a calibrated spring-balance ( a newtonmeter) W = m g weight, W, in netwons, N mass, m, in kilograms, kg gravitational field strength, g, in newtons per kilogram, N/kg |
|
|
What is a resultant force?
|
A single force that has the same effect as a number forces acting on the same object. Can be measured by drawing a parallelogram, draw a bisecting line then measure with a ruler or using cosine rule ( a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2bccosA ) |
|
|
What is the moment of a force?
|
Moment of a force is the turning effect of a force. M = F d moment of a force, M, in newton-metres, Nm force, F, in newtons, N distance, d, is the perpendicular distance from the pivot to the line of action of the force, in metres, m |
|
|
What happens if the resultant force of a moving object is 0?
|
Constant velocity in a straight line.
|
|
|
As an aircraft moves along the runway to take off its acceleration decreases even though the force from the engines is contant. Why?
|
As speed increases air resistance increases thus reducing the resultant force.
|
|
|
What is the centre of mass?
|
Centre of mass is the point at which the total mass seems to act/ appears to be concentrated
|
|
|
How can an object be made more stable (relate to centre of mass)?
|
Wider, larger base Lower centre of mass Line of action of the weight must fall inside of the object so there is is no resultant moment. |
|
|
What is the difference between distance and displacement?
|
Distance is how far an object moves. It is a scalar quantity (doesn't involve direction). Displacement is the distance an object moves, measured in a straight line from start point to finish point and the direction of that line. It is a vector quantity |
|
|
What is the difference between speed and velocity.
|
Speed is a scalar quantity (does not have a direction) Velocity is the speed of an object in a given direction. It is a vector quantity |
|
|
Typical speed for sound in air, a walker, a runner and cyclist?
|
sound in air = 330m/s walking = 1.5m/s running = 3m/s cycling = 6m/s |
|
|
What are the SUVAT equations
|
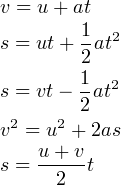
S = displacement (m) U = initial velocity (m/s) V = final velocity (m/s) A = acceleration (m/s^2) T = time (s) |
|
|
How to read distance-time or displacement-time graph?
|
Gradient = speed or velocity Diagonal line = Constant speed/velocity Upwards curve = Acceleration Downwards curve = Deceleration Flat line = no movement Note: distance-time graphs cannot move back down on the y axis but displacement-time graphs can. |
|
|
How to read a velocity time graph?
|
Gradient = acceleration Upwards diagonal line = (positive) acceleration Downwards diagonal line = decceleration Flat line = constant velocity Area underneath = distance |
|
|
Equation for acceleration?
|
acceleration = change in velocity/ time |
|
|
What is the relationship falling objects have with gravity?
|
An object falling freely under gravity has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s^2. An object falling through a liquid initialy accelerates due to the force of gravity. |
|
|
What is Hooks Law?
|
The extension of the spring is directly proportional to the force applied, as long as the spring extension limit has not been exceeded. F = k e F is force measured in N k is the spring constant measured in N/m e is extension measured in m |
|
|
How can we carry a stretch test?
|
Clamp a spring at its upper end and hang an empty weight hanger from the other end to keep the spring straight. Measure the original length of the spring with a metre rule. Use a fiduciary mark to improve accuracy and reduce parallax errors. Add weight to the hanger in a sensible increments. For each weight added measure the extension of the spring by measuring the new length and subtract the original. Repeat and add more weight. Plot a graph of force against extension of the spring. On this graph if Force is on the x axis and Extensions is on the y axis, spring constant is the reciprocal of the gradient (1/gradient) |
|
|
What are stopping distances? What is it made up of?
|
Stopping distance is the total time a driver takes to stop. It is made up of thinking distance + braking distance. Thinking distance is the drivers reaction time. It is affected by …. - Fatigue - Drinking - Drugs - Using a phone Braking distance is the how for the driver travels under the breaking force. It is affected by …. - The age of the car - The mass of the car - The weather - The road - The quality of the tires |
|
|
What is the equation of momentum?
|
Momentum is held by all moving forces. p = mv p is momentum measured in kg/s m is mass measured in kg v is velocity measured in v |
|
|
What is the relationship force has with momentum?
|
Force = change in momentum/time F = m(v- u)/t F is momentum measured in N m is mass measured in M v is terminal velocity measured in m/s u is initial velocity measured in m/s t is time measured in s The force is greater if the momentum changes in less time. |
|
|
What is the law of conservation of momentum?
|

In a closed system the total momentum before an event equals the total momentum after an event. When two objects push each other apart, they move with different speeds if they have unequal objects and with equal and opposite momentum, so their total momentum is zero. Before an explosion momentum is zero. After an explosion pieces fly off in different direction so momentum cancels out. |
|
|
How do safety measures reduce impact forces? Give examples.
|
By increasing the time taken for momentum to change. Air bags work as compressing air decreases your velocity over a longer period of time rather than hitting the dashboard. Seat belts stop a person being flung forward if the car stops suddenly. The car seatbelt will instead stretch slightly increasing the impact time and reducing the impact force. |
|
|
Describe the resultant forces on a sky diver.
|
As the diver drops air resistance is minimal, the strongest force is weight. This causes constant acceleration. Gradually air resistance increases slowing the rate of acceleration. This leads to constant velocity as the forces are balanced. As the parachute opens air resistance increases further which causes a deceleration. The forces eventually balance and reach a terminal velocity. |
|
|
Describe the equation for pressure on a flat surface.
|
p = F/A p is pressure measured in Pascals N/m^2 F is force measured in N A is area measured in m/s |
|
|
How do you convert from mm^2 to m^2
|
Multiply by 1,000,000. This is as you need to square the initial multiplier (1,000) |
|
|
Why is pressure greater, deeper underwater? Why do objects sink?
|
Because of the weight exerted by the mass of the water above. Objects sinks if its weight is greater than the upthrust on it when it is fully immersed. |
|
|
Describe atmospheric pressure.
|
Air molecules collide with surfaces and create pressure on them. Atmospheric pressure decreases with higher altitude because there is less air above a given altitude than there is at a lower altitude. |

