![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
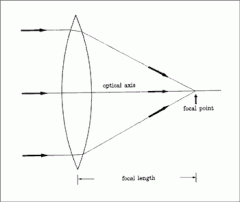
Converging Lens |
|
|
|
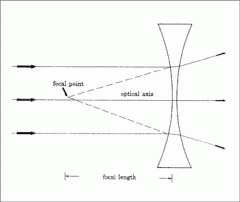
Diverging Lens |
|
|
|
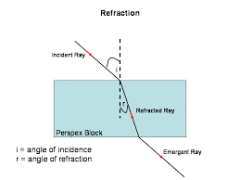
Refraction |
-When radiation waves slow down they bend towards the normal. -Light enters glass it slows to 2/3s its speed in air. -If wave hits boundary at 90° no change - slows -When light hits new medium some light pass through some is reflected. |
|
|
Refraction diagram |
|
|
|
Converging lens rules |
-Incident ray = parallel to axis. Refraction through lens and focal point. -Incident ray = Through focal point before lens. Refraction through lens. Travels parallel to the axis. -Incident ray = passing through lens centre. Carries on in same direction. |
|
|
Diverging lens rules |
-Incident ray = Parallel to axis. Refracts through lens and travels inline with focal point. -Incident ray = Passing towards focal focal point. Refracts through lens and travels parallel to the axis. -Incident ray = Passing through lens centre. carries on in same direction. |
|
|
Object placed at 2F |
Image: Real Inverted Same size as object Appears at 2F |
|
|
Object placed between F and 2F |
Image:
Real Inverted Bigger than object Appears beyond 2F |
|
|
Object placed nearer than F |
Image:
Virtual Same orientation as object Bigger than object Appears on the same side of lens as the object |
|
|
Powerful Lens makes = _________ focal length
|
Short
|
|
|
Lens Equation |
1/F = 1/U +1/V
F = Focal Length U = Object Distance V = Image Distance |

