![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
how do we calculate average speed? |
speed (m/s) = total distance travelled (m) ÷ time taken (s) |
|
|
Distance Time graphs: -what does line sloping up show? -what does lime sloping down show? -what does gradient show? -What does flat gradient show? |
-moving away from starting point -going back to starting point -gives speed at that time -Stop |
|
|
Velocity? Acceleration? |
objects speed in a given direction Change in velocity |
|
|
how do you calculate acceleration? |
acceleration (m/s²) = change in velocity* (m/s) ÷ time taken (s) * final velocity - original velocity |
|
|
Velocity Time Graphs : -What does the gradient show? -What does steep line show? -What does flat line show? -What does area under graph show? |
-objects acceleration -greater acceleration -steady speed -distance travelled |
|
|
Resultant force? What happens if there is no resultant force? |
Difference between the force casuing motion and drag forces Object is stationary/constant velocity |
|
|
When does fuel consumption increase in vehicles? |
When drag forces increase because larger forward force is needed to overcome drag = more energy needed from engine to provide large force |
|
|
How do we calculate acceleration? |
change in speed / time taken= Acceleration m/s² |
|
|
Streamlined objects? |
Have small cross-sectional areas and smooth surfaces = reduces drag |
|
|
How do we calculate total stopping distance? |
Thinking distance + braking distance |
|
|
Reaction time? |
Time taken for a driver to react to a hazard |
|
|
How do we calculate thinking distance? |
speed × time it takes for driver to react and brake |
|
|
What increases thinking distance? |
If driver is: - distracted or tired - taken alcohol or drugs (including some medication) |
|
|
Braking distance? |
Distance travelled when brakes are applied and car is slowing down |
|
|
What increases breaking distance? |
-Wet or icy roads -Worn down tyres -Brakes in bad condition |
|
|
What is aquaplanning? What happens if treads are worn out? |
When water from wet road is channeled out by tyre through the treads. Water will not be channeled out and car will slide over layer of water and cannot be controlled |
|
|
What happens to drag forces as object moves faster? |
They increase |
|
|
How do we calculate weight? |
Weight (N) = mass (kg) × gravity (N/kg) |
|
|
When dpes a skydiver reach their terminal Velocity? |
When drag forces increase and match his weight |
|
|
Extension? |
Difference between original length and the stretched length |
|
|
What is the extension like when an elastic object is stretched? |
Extension is proportional to the force applied up to a limit Above the limit extension is no longer proportipnal |
|
|
What is the work done (when elastic object is stretched/squashed) stored as? |
Elastic Potential Energy |
|
|
How is kinetic energy transferred to surroundings from a moving object? Examples? (2) |
As a result of frictional forces -Friction between car tyres and rpad surface -Air resistance |
|
|
How can energy transfer from moving objects be useful? |
-Regenerative brakes slow down car using engine. Car's kinetic energy is used to charge battery. -Car crumple zones designed to distort and absorb kinetic energy during car crash |
|
|
How can kinetic energy be stored? |
Flywheels - heavy, fast spinning wheels store energy for short periods |
|
|
How is work done calculated? |
Work (J) = force (N) × distance moved in the direction of the force (m) |
|
|
How do we calculate Gravitational Potential energy? |
GPE (J)= mass (kg) × gravity (N/kg) × height (m) |
|
|
What is the gravity on earth? |
9.8 N/kg (usually rounded up to 10) |
|
|
How is kinetic energy calculated? |
KE (J) = 1/2 × mass (kg) × velocity² (m/s)² |
|
|
What happens to the kinetic energy of an object when: a) its mass doubles b) if the speed doubles |
a) KE doubles b) KE increases fourfold |
|
|
What is power? |
Power measures how quickly work is done or energy transferred. |
|
|
How is power calculated? (2) |
power (W) = Energy transferred (J) ÷ time (s)
power (w) = [Force (N)×distance (m)] ÷ time (s) |
|
|
How do we calculate momentum? |
Momentum = mass (kg) × velocity (m/s) |
|
|
Momentum is conserved. Before and after collisions it is the same. See Diagram |
|
|
|
What happens to the momentum before and after if a stationary object explodes in two parts? |
It is zero before and after because each part of the momentum is same in opposite directions |
|
|
Static electricity? (4) |
When different materials are rubbed together electrons transfer. Some materials gain electrons and some lose electrons. Objects with same charge repel Objects with same charge attract |
|
|
How can a gold leaf electroscope with a negative charge be used to investigate charge on other materials? |
If negatively charged object comes close the gold leaf rises more If positively charged object comes close the gold leaf rises less |
|
|
What is electrostatic induction? |
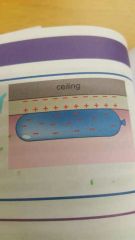
negatively charged object stick to uncharged objects because it redistributes the electrons leaving it with a positive charge |
|
|
How can the dangers of electrostatic discharge be reduced? |
A lightening conductor attracts lightening strikes which travels down the metal rod to flow safely away. |
|
|
Series circuit? What is the current like? What is the potential difference/voltage like? |
Loop of conductors Current is same throughout Potential difference is shared between components in proportion to their resistance |
|
|
Parallel circuits? Current? Voltage/Potential Difference? |
Components connected in more than one loop Current divides at junctions and the total current flowing out is same as current that flowed in Potential difference across each loop is the same as the potential difference from the cell. |
|
|
What type of materials do electric currents flow through more easily? |
Low resistance materials |
|
|
How do we calculate resistance? |
resistance (Ω) = voltage (V) ÷ current (A) |
|
|
What increases a wire's resistance? Why? |
If the wire is longer or thinner. Electrons are more likely to collide with the nuclei in the material |
|
|
Ohm's law? |
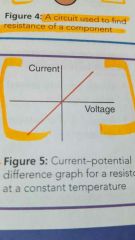
In ohmic materials the voltage is proportional to current and resistance is constant |
|
|
This is the circuit used to measure resistance: (Need to know this) |
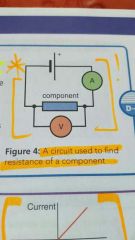
|
|
|
What are the 4 different non-ohmic devices? |
Filament light bulb Diodes Light dependent resistor Thermistor |
|
|
What happens when the current in a filament bulb increases? |
Its resistance increases |
|
|
Diode? |
Allows current to flow in one direction |
|
|
Light Dependent Resistor? Thermistor? |
-Smaller resistance when light shines on it -smaller resistance when heated |
|
|
This is the graph of current when filament bulb and diode is put in place: |
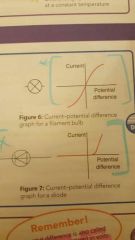
|
|
|
How do diodes, LDRs, Thermistors and light emitting diodes work? |
They are made from semiconductor materials so the electrons gain enough energy when the material is heated or light shines on to be able to flow through it. |
|
|
What happens when a cell in a series circuit is connected the opposite way? |
It's potential difference is negative |
|
|
How do we calculate voltage across a single component in a circuit? |
Voltage (V) = current × resistance |
|
|
What are the two types of currents? |
Alternating Current Direct Current |
|
|
Direct Current? (d.c.) |
current flows only in one direction |
|
|
Alternating current? (a.c.) |
Current constantly changes direction |
|
|
What is the name of the device used to measure a.c. and d.c. currents? |
Oscilloscope |
|
|
On the oscilloscope what does the amplitude of the trace and number of squares between the peaks of the trace show? |
-Maximum potential difference supplied (V) -Time per cycle (s) |
|
|
How do we calculate the frequency of the supplied voltage? |
Frequency (Hertz) = 1/time per cycle (s) |
|

Name the three wires in this three pin plug: |
Blue = Nuetral Wire Yellow+Green = Earth Wire Brown = Live wire |
|
|
Double insulated Appliances? Wires they consist of? |
Appliances with a plastic outer vase and no touchable metal parts -Live wire -Neutral wire |
|
|
What happens when there is a fault in the appliance and the equipment becomes live? |
Current flows through the earth wire and blows the fuse |
|
|
Purpose of the fuse? How? |
Protects appliance and flex from overheating If current is too large fuse melts and breaks the circuit |
|
|
What are the mistakes when wiring a plug? (4) |
-connecting wires to wrong pin -not gripping cable tightly under the cable grip -not attaching wires firmly to pins -too much bare wire exposed |

