![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. The first college of Pharmacy in the US was located in
|
Philadelphia
|
|
|
2. Official monographs on recognized, therapeutically active drug substances appear in the
|
USP (United States Pharmacopeia)
|
|
|
3. The NDA is
|
The final step a developer takes in seeking FDA approval for a new drug.
|
|
|
4. The IND:
|
Requires a proposed new drug to be relatively safe and potentially useful.
|
|
|
6. The first Federal Law in the US designed to regulate the purity of drug products manufactured domestically was
|
B. The Food and Drug Act of 1906
|
|
|
7. The Kefauver-Harris Amendment to the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act of 1938
|
A. Became law in 1962
B. Implemented the IND process C. Required proof of both safety and efficacy |
|
|
8. The clinical phase of the FDA approval process for a new drug takes approximately
|
5 years
|
|
|
9. The dosage form most cited, but almost never used in drug therapy is the
|
Pill
|
|
|
requirements of a drug dosage form
|
F. The therapeutic and non-therapeutic ingredients must be compatible
G. The dosage form must lend itself to efficient administration H. The container must be clearly labeled |
|
|
12. Schedule 1 drugs have
|
D. No accepted medical use and high potential for abuse
|
|
|
1. A thermodynamic study can give the following type of information on a reaction
|
B. The energy that may be released or consumed by the reaction
|
|
|
3. A reaction that is spontaneous at all temperatures is ... enthalpy and entropy wise
|
B. A decrease in enthalpy and an increase in entropy
|
|
|
The first federal law in the US to regulate drug products manufactured domestically?
|
Food and drug act 1906
|
|
|
Drug approval process consists of?
|
manufacturing standards
cant be introduced until FDA approved adequate clinical studies demonstrate efficacy |
|
|
Supercritical fluid
|
when temperature and pressure of liquid goes beyond crit. point, polar and nonpolar are completly miscible
|
|
|
Boyles law of Pressure
|
PV=nRT
P=atm V=litres R-0.082 T=temp in kalvin n-moles |
|
|
Eutectics
|
minimum temp. at which two components of mixture will melt at certain compostion
|
|
|
Solvate vs. Hydrate
|
solvate is crystals
if solvent is water then its a hydrate |
|
|
Lyotropic vs Thermotropic crystal formation
|
lyo: caused by water
thermo: caused by heat |
|
|
surface tension
|
force pulling molecules of interface together, results contractions of liquid surface
|
|
|
Amorphous Solids are?
|
supercooled liquids
glass, plastics like crystals but random |
|
|
Extensive vs. Intensive Properties
|
extensive additive
intensive not |
|
|
Physical vs. Chemical change
|
P: identity does not change
C: identity does change |
|
|
3 main bond types
|
Ionic
Covalent Hydrogen- FON |
|
|
Melting point and solubility relationship?
|
higher melting point less solubility
|
|
|
Van Der Walls Forces are?
|
Debye (dipole induced)
London (both induced) Keesom- Dipole (polarity) |
|
|
Iodine (I2) is dissolved in aqueous solution of potassium iodide (KI). What types of intermolecular forces are involved before and after the dissolution?
|
a
|
|
|
Solid state,
solution state diffusion exothermic process feasibility |
read it somewhere else
|
|
|
Open system, closed, isolated
|
everything exchanged
energy nothing |
|
|
Isothermal
Adiabatic |
process carried out w/o change in temp.
process carried out w/o change in heat content |
|
|
Federal food and drug act 1906
|
required drugs marketed interstate to comply with their claimed standards of strength and quality
|
|
|
Federal food , drug, and cosmetic act 1938
|
prohibits the distribution and use of any new drug/drug product w/o the proir filing of NDA
|
|
|
Kefauver/ Harris amendments 1962
|
requires IND (investivational new drug application) filing w/ FDA before drug clinically tested on humans
only after safety and efficacy proved can file NDA |
|
|
Durham-Humphrey Amendment 1951
|
RX's for legend drugs may not be refilled, w/o consent of prescriber, created 'legend' drugs and OTC drugs
|
|
|
Comprehensive Drug abuse Preevention and control act
|
1970 created 5 schedules for the classification and control of drugs with abuse potential
|
|
|
CFR vs. FR
|
FR is federal register where regulations first published for public comment.
once finalized go into CFR (code of federal regulations) |
|
|
Title 21 CFR req.s?
|
8 volumes with regs. issued under FDA.
Federal Register issued each workday by superintendent of docs., GPO, contains proposed and final legal notices issued by federal agencies |
|
|
Main drug discovery resources
|
Natural Resources
Synthetic Semi-Synthetic |
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? Random
|
Random-tests numerous compounds or natural substances for bio activity
|
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? NonRandom
|
Bioassays-test agents against controls for effects
Disease spec. animal models-bioassays invivo, great and expensive High Throughput screening- a system able to examine 15000 compounds a week using 10-20 bioassays (shit ton) |
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? Molecular mod
|
chemical alteration of a known and previously characterised chemical compound for the purpose of enhancing its usfulness as a drug
|
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? Mechanism Based
|
molecular mod to design drug that interferes with specific biochemical path of disease process
|
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? Molecular Graphics
|
Use of computer graphics to represent / manipulate to fit simulated structure of receptor
|
|
|
Methods of drug discovery? Pharmocogenisis
|
study of effect of genes, how genes effect if you get screwed by drugs or they actually help
|
|
|
Drug Nomenclatures? 4
|
Empirical Formula--> dont know this go home
Systematic chem name-->bullshit long as chemical name nonproprietary name--> generic, aka ampicillin code number assigned by USAN councel--> code assigned before nonproprietory name, prefix(sponsor) numbers after ie. SQ 14225 (captoprol) by squib |
|
|
Responsibility of pharacuetics
|
characterized bio activity, evaluate chem properties to ensure stable and useful pharm. product
|
|
|
info in IND?
|
Safety eval-animals
clinical data drug id and manufacturing instructions outline of proposed clinical studies routes of admin approximate num. patients estimate length of treatment environmental impact? no one cares |
|
|
Steps of drug approval
|
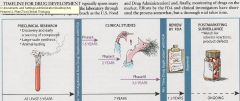
|
|
|
Bioequivalents
|
pharmaceutically equivalent when administered to same individuals w/ same dosage regimen--> comparable bioavailiblilty
|
|
|
Bioavailability
|
extent and rate of absorbtion from a dosage form refected by a time concentration curve of the administered drug in systemic circulation
|
|
|
therapeutic equivalent
|
Pharmceutical equivalent provides same therapeutic effect as measured by control of a disease or disease symptom
|
|
|
MEC
|
minimum effective concentration
avaerage blood serum conc. representing the minumum conc. that can produce the drugs desired effect |
|
|
MTC
|
minimum toxic concentration
serum conc. above level expected to produce dose related toxic effects |
|
|
MED
|
median effective dose
amount that will produce desired intensity of effect in 50% of induvuduals tested |
|
|
MTD
|
median toxic dose
amount that will produce a toxic effect in 50% ppl tested |
|
|
generic vs. reference drug product
|
generic less time develop
G uses same active excipient G bioequivalent to reference G contain different crap excipients (dont matter) |
|
|
Orange Book
A and B |
A- drugs therapeutically equivalent to pharmaceutically equivalent product
B- not therapeutically equivalent to pharmaceutically equivalent product |
|
|
Orange Book
AA and AB |
AA- drugs not presenting bioequivalence problems
AB- products meet necessary bioequivilence reqs. |
|
|
Pharmacuetical reasons for dosage design
|
safe and convient delivery of amount
|
|
|
Considerations for dosage design
|
nature of illness
therapuetic situation method of treatment route of admin age anticipated condition of patient |
|
|
Oral route perks? cons?
|
P-natural, uncomplicated, convenient, safe
C- slow response, chance irreg. aborb, possible destruction by acid/enzyme |
|
|
Rectal perks? cons?
|
perfered for drug destroyed by stomach or intestines
patients that are vomiting or coma half drug miss first pass metab. C: inconvieent, irregular absorb, |
|
|
Parentral routes
SQ, IM, IV , ID |
P: rapid absorb
blood levels predictable small dose good for uncouncious patients C: sterility req. costly to admin. not reversible, easy overdose |
|
|
Epicutaneous route
|
P:prolonged local action with minimal absorption,
C:creams ointments pastes, messy and shit, iritation to skin |
|
|
Ocular, Oral(great), Nasal
|
P: local drug treament, sterile form created with comfort in mind
C: preparations can be adsorbed systemically |
|
|
Factors influence bioavailibility
|
physiological factors and patient characteristics
drug substance , physiochemical properties pharmaceutical ingredients and dosage form characteristics |
|
|
Differences in 4 types absorption
|
Passive
Filtration Specialized trans Facilitated |
|
|
factors of drug dissolution
|
drugs acid base or salt forms may result in differences in dissolution rate
|
|
|
factors of drug dissolution
|
crystal, amaphorous
surface area and state of hydration |
|
|
factors of drug stability
|
oxidative decomp
hydrolysis temp. relative humidity (tolerable levels) evironment of light and air packaging |
|
|
factors effect drug absorption
|
drug solubility
physical form dissolution itself particle size and surface area |
|
|
recognize the different conditions of GI tract
|
pH
enzymes that kinda shit membrane perm. |
|
|
Exothermic
Endothermic delta H's? what about |
exo:H less than zero (losing heat)
endo: H greater than 0 all at constant T of course |
|
|
Strong electrolyte groups?
|
Inorganic acids
inorganic bases most salts |
|
|
Weak electrolytes groups?
|
organic acids and bases
inorganic compounds some salts complex ions ex. Cu(NH3)4 2+ |
|
|
Molarity
Normality Molality Mole Fraction |
g/L
N--> gram EQUIVALENT / L m--> g / 1000g X--> ratio of solute to, solute and solvent mix |
|
|
ppm
ppb |
(mass A/ all the shit together) 10 to the 6
for ppb same only 10 to the 9 |
|
|
Atomic Number
Atomic Weight |
did you really even answer that? Go home
|
|
|
Normality
|
(Mw/valence) / L
|
|
|
Add 20 gram of NaCl into 80 gram of water. What will be the molefraction of each?
|
figure it out
|
|
|
Ideal solution
Non-ideal solution |
Ideal solutions are formed by mixing substances with similar properties
gas: absence of attractive forces solution: uniformity of forces |
|
|
What is the partial pressure of propellants 11 and 12 in the 50:50 weight mixture and what is the total vapor pressure of this mixture?
P11o(137.4 g/mol) at 21 oC = 13.4 psi P12o(120.9 g/mol) at 21 oC = 84.9 psi |
6.27
45.17 51.44 |
|
|
solution pressure laws
Henrys Raoults |
Henry’s law -solute
psolute= ksolute Xsolute Raoult’s law- solvent psolvent= psolventoXsolvent |
|
|
Colligative properties
|
Vapor pressure depression
boiling point elevation freezing point depression osmotic pressure |
|
|
Vapor Pressure Depression depends on
|
mole fraction of solute
(p1o -p1)/ p1o= Δp/ p10= X2= n2/(n1+ n2) delta p is lowering of vapor pressure |
|
|
Boiling point elevation
|
ΔT = K x m
m molality K constant T in celcius |
|
|
The molal elevation constant of a drug is 0.5 oC kg mole -1. What will be the boiling point elevation of a 0.30 m aqueous solution of that drug?
|
0.15
|
|
|
Freezing point depression
|
ΔT = i x K x m
i = Van't Hoff factor --> 1 for nonelectrolytes, for strong electrolyes i is ions in solute formula K = constant m is molality |
|
|
Van't Hoff Equation!
electrolyte vs. non |
i is the number of particles per unit molecule of a solute which are released into solution
Electrolyte HCl= 2 H2SO4 =3 H3PO4 =4 CaCl2 =3 |
|
|
Ethylene glycol [C2H5(OH)2] is used as antifreeze. Knowing that the normal freezing point of water is 0 oC and the cryoscopic constant of water is 1.86 oC kg mole-1, calculate the freezing point depression of a 35 wt/wt% EG in water?
|
-16.1 C
|
|
|
Tonicity
Hyper Iso Hypo |
Hyper water out
Iso same Hypo water in |
|
|
Osmotic pressure is?
|
pressure created to equilibrate solutions through semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
Osmotic pressure formula?
|
pi = m RT
Morse equation R= 0.082 L atm/mol deg T= absolute temp, aka kalvin m = moles note: pi should be for 1 L |
|
|
A solution containing 10.0 g of sucrose dissolved in 100 g of water has a boiling point of 100.149 oC. What is the molecular weight of sucrose? Kbfor water is about 0.51 oC m-1
|
342
|
|
|
Vapor pressure lowering
|
Δp = 0.018 p1o m
in aq 0.018 p1o = 0.43 @ 25 oC = 0.083 @ 0 oC |
|
|
Degree of dissociation variable? formula?
|
alpha
alpha = (i -1)/(v-1) can also be simplified but i dont have those symbols |
|
|
Activity and Activity Coefficient
|
A: effective conc. of ions
A. co: effective stoichiometric ion conc. AC<1 interionic interactions AC>1 more water molecule for interaction |
|
|
Ionic Strength
|
u= 1/2 (c1 z1(squared) + c2 z2(squared) ...)
c is conc. of ion z is valence |
|
|
A buffer contains 0.3 mole of K2HPO4and 0.1 mole of KH2PO4per liter of solution. What is the ionic strength of the solution?
|
1
|
|
|
Debye-Huckel Theory
|
to do with activity and valence and ionic strength
factor A is 0.51 |
|
|
What is the milliosmolalityof a 0.120 msolution of potassium bromide? What is osmotic pressure in atmosphere?
|
223 cuz 1.86 not 2
|
|
|
Brownsted Lowry Theory
Lewis Acid and Bases |
Proton donor and acceptor
L: acid electron pair acceptor, bases is pair donor |
|
|
Amphoter
|
can act as acid and base
|
|
|
pH of a Weak Acid
|
x = √(KaCa) = [H3O+]
Ca= original acid concentration x = concentration of the Ac-or H3O+at equilibrium |
|
|
Acidity of a Weak Acid
|
Ka= x2/Ca
|
|
|
Buffer Capacity
|
Buffer Capacity=number of moles of OH-or H3O+ added//////
(pH change) ×(volume of buffer in L) |
|
|
Approximate Buffer Capacity
|
β= ΔB/ΔpH
ΔB=increment of base added other is prolly change in pH morons |
|
|
Buffer Capacity Equation
|
β= 2.3 C Ka[H3O+]/(Ka+ [H3O+])2
C is total acid and salt conc. |
|
|
Prepare a buffer solution of pH 5.00 having a capacity of 0.02.
acetic acid with pKa of 4.76 would be ideal |
β= 2.3 C Ka[H3O+]/(Ka+ [H3O+])2
|
|
|
Acidic buffers
Basic Buffers |
pH = pKa + log ([salt]/[acid])
pH = pKw-pKb+ log ([base]/[salt]) |
|
|
Change in entropy
|
ΔS= Q/T
Q amount of heat added to sys. T- temp kalvin |
|
|
When entropy gen. most heat?
|
low temp.
|
|
|
Gibbs Free Energy
|
ΔG = ΔH -T ΔS
|
|
|
Free Energy, Temperature
|
If ΔS and ΔH have opposite signs, spontaneity is not temperature dependent, happens or not If ΔS and ΔH have similar signs, the spontaneity will be temperature dependent
|
|
|
Internal Energy, Heat and Work
|
Internal Energy: Total energy of a system
Heat: Transfer of energy due to the change in temperature Work: Transfer of energy due to the other factors |
|
|
1stLaw thermodynamics
|
ΔU = Q -W
change in energy = heat added - work done |
|
|
Iso-volumetric system
|
Volume of the system remains same before and after the process
ΔU = Q |
|
|
Isobaric/ Adiabatic systems
|
Pressure of the system remains same before and after the process
ΔU = Q –(P ×ΔV) ΔU = -W in adiabatic |

