![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is meant by a physiological range?
|
Range of values acceptable for certain chemicals to sustain life
|
|
|
# What is the physiological range for blood pH? For blood Sodium ion?
|
Blood: 7.35-7.45pH
Na: 135-145mEq/L |
|
|
What is negative feedback?
|
Product shuts down the reaction pathway, something makes process goes in other direction
|
|
|
Why water good solvent?
|
polar
|
|
|
molality
|
mol/kg
|
|
|
Major elements of human body
|
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sodium, Phosphorous, Sulfur
SPOCHS |
|
|
water necessary for life
|
great solvent, bio rxns take place liquid form
|
|
|
inorganic ions required for life why
|
because they give charges, electric potentials can be created
|
|
|
hydrogen ions needed in required conc. cuz
|
changes organic molecules from polar to non
effects protein conformations |
|
|
what use hydrogen ion gradient?
|
electron transport chain
|
|
|
how does pH affect solubility of drug?
|
can make it into ion which is polar and soluble or the other way
|
|
|
three types of RNA
|
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, ncRNA 'non-coding'
|
|
|
Why is calcium used for so many physiological process?
|
so abundant
|
|
|
why different muscle look diff?
|
different purposes
|
|
|
Ficks law of diffusion?
|
high concentration to low concentration, speed of diffusion depends on gradient
|
|
|
surface area/lipid solubility
affect lipid solubility? |
SA: more increases
lipid solubility: more increases lipid sol. affected by pH |
|
|
osmolality of blood and extra cellular fluid (ECF)?
|
275--299 mOsm/kg
|
|
|
osmolality of 300 mM glucose? Of 150 mM NaCl? Of 100 mM CaCl2?
|
300 for all
|
|
|
thiomersal? how work
|
causes enzymes be nonfunc. since Hg binds to thiol group in active site
|
|
|
How polar molecules cross membrane
|
transport proteins
|
|
|
func. of integrin? cadherin?
|
integrins: glycoprotein that attach cell to outside matrix
Cadherin: adhesion molecules, connect cell to cell |
|
|
SGLUT? GLUT? func.
|
SGLUT in intestine, symport, 1 glu. 2 Na, secondary active trans., ACTIVE
GLUT transport glucose across membrane, FACILITATED DIFFUSION |
|
|
sodium, potassium pump func.
|
create gradient, 3 Na out, 2 K in, cleaves ATP
|
|
|
Receptor function
|
recieve signals and perform task for signal
|
|
|
Membrane transports?
|
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion--> Vmax against gradient active transport secondary active endo/exocytosis |
|
|
glucose against gradient why?
|
sodium cotrans. intestine kidney
|
|
|
nucleus func?
|
holds genetic info
rRNA, mRNA formed |
|
|
ribosome
|
organelles that perform protein syn.
bound on ER (rough) for secretion |
|
|
glycosylation occurs?
|
mostly rough ER, not really anywhere else
|
|
|
what happens in mito. why inner out mems.
|
Krebs, electron transport chain, cuz
|
|
|
lysosome?
|
disgests shit, acidic internal environment, storage
|
|
|
peroxisome
|
off ER w/ enyzmes that degrades fatties and other shit and makes H2O2
|
|
|
proteasome
|
large protein complex that kill other proteins by proteolysis
|
|
|
dinitrophenol does
azide |
decreases proton gradient
metabolic poison that binds irreveriblly to heme cofactor (bad for repiratory) |
|
|
transcription factor?
|
it makes RNA
|
|
|
rough ER makes what
|
secreted and membrane proteins
|
|
|
golgi does?
|
glycosilation, phosphorlation, and forms secretory vesicles
|
|
|
dyneins and kinesins
|
intracellur transport
|
|
|
4 basic tissue types?
|
Connective
Epithelial Muscle Nervous |
|
|
Cell membrane important cuz?
|
gradients
semipermeable |
|
|
protein gylcosylation occurs where?
|
Rough ER
Golgi |
|
|
2nd ary messenger is?
|
causes cascade of events, like cAMP and GDP,
inducer never enters cell |
|
|
Different methods of transport are?
|
Diffusion
Facilitated Active Secondary active |
|
|
Symport
Antiport |
same
opposite |
|
|
Receptor mediated endocytosis works how?
|
i dont want to tell you
|
|
|
Henderson Hasselbach is?
|
pH= pKa + log -A/HA
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton fibers are?
|
microfiliments-->actin
intermediate filaments-->keritin microtubules-->tubulin (flagella) motile |
|
|
Which cytoskeletal filaments are associated with the centrioles?
|
microtubules, important for cell division
|
|
|
Basic features of connective tissue
|
connects shit?
anchor structure strength communication nutrition lotta matrix |
|
|
fibroblasts produce?
|
collagen
elastic fibers reticular fibers |
|
|
loose connective tissue contains what cells?
|
fibroblasts
macrophages mast cells |
|
|
what makes cartilage?
|
chondrocytes
|
|
|
what makes bone?
|
osteoblasts and cytes
|
|
|
connective tissue that covers bone? cartilage?
|
periosteum
perichondrium |
|
|
adipocyte?
|
connective tissue
lots of lipid storage, irregular shape |
|
|
epithelial tissue?
top is called? bottom is called? |
rapid regen/ growth
top-->apical bottom-->basal connected to basement basement membrane--> secreted by cells |
|
|
types of epithelial tissue?
ex of each |
simple squamous
strat. squamous cuboidal columnar |
|
|
Desmosome do and have?
adherens junctions |
intermediate filament
connect cells |
|
|
Desmosomes have
hemidesmosomes different how? Adherins junction? |
cadherins
hemi: anchor to basement, use integrins adherins: use cadherins and integrins link actin filments between cells |
|
|
tight junctions use?
gap junctions? |
occludin and claudin
gap: connexin --> let communicate |
|
|
body membranes are?
where is each? parietal vs. visceral |
cutaneous
mucous serous synovial p vs. v -->p lines cavity wall v covers organs |
|
|
Epidermis is what type of tissue?
how about dermis layers? |
stratified squamous
dermis--> papillary is losse connective reticular is dense irregular connective |
|
|
4 layers of epidermis? sometimes 5
|
Basal
Spinosum Granulosum Lucidium(only in thick) Corneum |
|
|
dermis function?
|
structural support
vascularization of area |
|
|
Keratinocytes do? and where
melanocytes? langerhans? merkels? |
produce keratin (produced at basal layer)
M: make melanin, color L: phagocytes M:sensory receptors |
|
|
what proteins form dermis?
what makes them? |
collagen, elastin, reticular
made by fibroblasts |
|
|
mast cells? why important
|
immflammitory effects
release histamine, heparin |
|
|
sudoriferous gland?
arrector pilli muscle |
sweat gland, temp reg.
muscle that gives you goose bumps (attached to hair follicles) |
|
|
sensory receptors in skin?
what they do? |
merkel
meissners pacinian ruffinis end organs free nerve endings afferent |
|
|
Osteoblast
Osteocyte Osteoclast |
make bone
mature bone cell, sits there in lacunae bone absorption, group of macrophages fused |
|
|
Canaliculi
central canal osteon osteoid |
canals
big canal contains canal and shit protein mixture secreted by blasts, mostly collogen |
|
|
periostuim
endostium hydroxyapatite osteoprotegrin |
connective tissue around bone
connective tissue inside bone what makes bone hard stops osteoclast formation from macs (stimulated by estrogen) |
|
|
RANK
RANKL produced where? |
RANK is cytosine receptor osteoclasts (monocytes)
RANKL is protein that binds to it and stim. osteoclast formation |
|
|
Bone fluid is?
|
Collagen, Ca binding proteins, proteogylcans, hydroxyapatate
|
|
|
What has highest free [Ca++]?
|
Blood Plasma
|
|
|
Physiological effects of PTH?
|
released when low Ca in blood,
Bone-decrease blast, inc clast Kidney- Ca retension, PO4 excretion Overall- inc Ca, Decr PO4 |
|
|
Physiological effects of calitriol?
Physiological effects of calcitonin? \Physiological effects of PTH? |

|
|
|
Which hormone increases calcitriol?
which hormone uses G proteins? which hormone acts as DNA binding receptor? |
PTH and hypophosphitimea
G: PTH, calctonin DNA: calcatriol |
|
|
Which hormone decreases phosphate levels?
What cell does calcitonin act on mainly? |
PTH and calcitonin
acts on osteoclasts |
|
|
Effects of glucocorticoids
what do bisphosphates do? |
cortisol-->cause bone lose
stim. absorb inhibit syn. inhibit Ca. reaborb in kidney destroy osteoclasts |
|
|
Muscle types, what diff?
|
Skeletal-->bone, multinuke, striated, voluntary/invol
Smooth-->walls of hollow organs, skin, BV, eyes, glands, one nuke, involuntary Cardiac-->heart, single nuke, striated, involuntary, intercalated disks |
|
|
resting membrane potential
threshold potential |
-70mV or -50--90
-50mV |
|
|
thick
thin filaments made of protein spans entire sarcomere |
myosin
tropomyosin, troponin, actin titin |
|
|
how action potenial take place
|
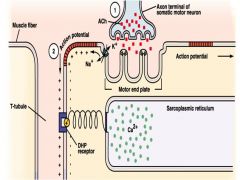
|
|
|
Where does the myofiber action potential begin?
|
at neuromuscular junction
|
|
|
Movement of which ion is mainly responsible for the resting membrane potential?
Movement of what ion causes the depolarization phase of the action potential? repolarization phase of the action potential? |
K
Na K |
|
|
what does calcium bind to
what does myosin bind to? |
troponin
actin |
|
|
cholinergic agonists do?
antagonists? curare? neostigmine? |
contract
prevent contractions C: compeditive inhibitor Neo: inhibits AcH breakdown |
|
|
botox does?
|
blocks release of AcH at neuromuscluar junction
|
|
|
Myasthenis gravis
muscular dystrophy |
autoimmune disorder caused by antibodies that block AcH receptors, treat with cholenesterase inhibitor
X linked genetic disease, degeneration of muscle, Duchenne most common, cuz dystrophin not allow actin bind extracellularness |

