![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
OCD is described using what 2 words? |
Obsession- thoughts Compulsion- behaviour |
|
|
What is OCD? |
Repetitive behaviour accompanied by obsessive thinking |
|
|
The DSM symptoms for OCD |
- recurrent obsessions and compulsions - recognition by the individual - everyday life is disrupted by behaviour |
|
|
E.gs of OCD |
Trichotillomania- compulsive hair pulling Hoarding disorder |
|
|
Emotional characteristics of OCD |
Distressed Anxiety Frustration Embarrassment |
|
|
Behavioural characteristics of OCD |
Checking Avoidance Mental acts e.g praying |
|
|
Cognitive characteristics of OCD |
Irrational and intrusive Fear Obsessional thoughts |
|
|
Physical Symptoms of OCD |
Trembling Shaking Sweating Tiredness Loss of appetite Chest pains Tension |
|
|
OCD cycle |
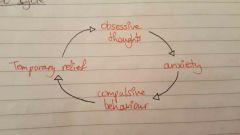
|
|
|
Genetic Explanations for OCD |
Predisposition may be inherited MZ= identical (high concordance rate) DZ= non-identical (low concordance rate) |
|
|
What does concordance rate mean? |
The presence of the same trait in a pair of twins |
|
|
Is MZ always 100%? Why? |
Because there are environmental effects acting |
|
|
What study is there to prove that MZ twins have a higher concordance rate? |
Nestadt et al (2000) did a meta-analysis of 14 other studies and found that on average MZ twins are 2x more likely to develop the disorder |
|
|
What is the COMT gene useful for? |
It helps reduce the action of dopamine high dopamine= less likely to develop OCD |
|
|
Neural Explanations for OCD |
Focuses on neurotransmitters as well as brain structures |
|
|
Develop points about the 2 neurotransmitters involved in OCD |
Serotonin- regulates mood Low level= mood disorder e.g depression More serotonin= happier and more relaxed Dopamine- regulates mood Low levels= good High levels= symptoms of OCD |
|
|
What 2 brain structures affect OCD with a research that supports them |
Basal Ganglia- involved in many things including the co-ordination of movement Max et al (1994) found that when basal ganglia is disconnected from the frontal cortex during surgery, OCD symptoms are reduced Orbitofrontal cortex- region which converts sensory information into thoughts and actions Increased activity in that region prevents patients from stopping their behaviour |
|
|
Evaluation of genetic/neural explanations |
-OCD is not entirely genetic - neuro-imaging studies show that some people with brain impairments involving the basal ganglia show no signs of OCD - ignore other factors e.g cognitions and learning aren't taken into account of |
|
|
Biological approach to treating OCD |
Drug therapy: SSRI= anti-depressant Works on serotonin system in the brain |
|
|
How does the SSRI prevent reabsorption and breakdown of serotonin? |
1) Serotonin is released by the presynaptic neuron (gives) and travels across a synapse 2) The neurotransmitter chemically conveys the signal from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron (takes) and then it's absorbed by the presynaptic neuron where it is broken down and re-used |
|
|
What drug is usually administered. Give details about it |
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
Typical dose= 20mg a day (may be increased if its not benefiting patient
Takes up to 3-4 months of daily use to see a reduction in symptoms |
|
|
Strengths of drug therapy/ biological approach |
- evidence for the effectiveness Soomro et al (2009) - symptoms decline around 70% of patients taking SSRIs - cost effective - compared to therapies, SSRIs are non-disruptive to patients lives - less time consuming |
|
|
Limitations of drug therapy/ biological approach |
- body can built tolerance so dosage would need to he increased - patient can give up because of time taking to see a change (to prevent this doctor should warn patient) - can get addicted - side effects e.g sleep, headaches (can cause patient to take more medicine) |

