![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Match the dz the the following descriptions:
- irreversible airway dilation - destruction of aveolar parenchyma - episodic, reversible airway narrowing - bronchiolar and aveolar airspace fibroblasts - productive cough >3mos, >2ys |
Bronchiectasis
Emphysema Asthma BOOP Chronic Bronchitis |
|
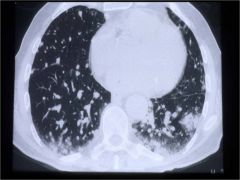
Describe what is seen, and name the dz.
|
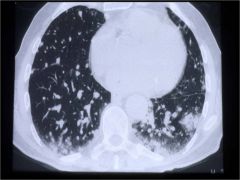
Patchy (focal) airspace infiltrates
BOOP |
|
|
Pt presents with:
- acute onset of cough, fever, dyspnea, and malaise - multiple patchy airspace infiltrates - Patchy fibromyxoid plugs in distal bronchioles and aveoli, +/- endogenous lipid pneunomia ...what txt is most appropriate? What is the name of the disease if we know the cause? if we don't? Are any of these Sx/signs specific? Even in combination? |
Corticosteroids (60-70% will respond)
Bronchiolitis Obliterans/Organizing Pneumonia (BOOP) Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (COP) No. Nope. |
|
|
Why are thin-walled aveoli necessary?
|
If the walls are too thick gas-exchange won't work.
|
|
|
What are the two types of bronchiectasis?
Which is seen in CF pts? Kartangener (primary ciliary dyskinesia syndrome)? What is seen on Xray? Pathology? |
obstructive
non-obstructive, post-inflammatory both are the non-obstructive variety airway dilation which extends to the periphery Dilation of bronchi, with a degree of inflammation and scarring. - organization = fibrosis |
|
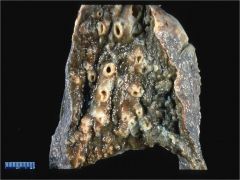
What dz is seen here?
|
Bronchiectasis
|
|
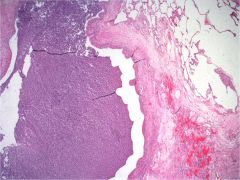
What is seen here? What is in the airway?
|
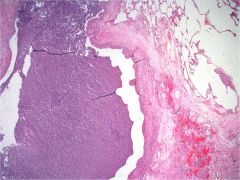
Bronchiectasis;
muco-purulent debris in airway lumen (all of the purple mush on the left) |
|
|
Could anything that obstructed outflow for long enough cause bronchiectasis?
|
yes.
|
|
|
Missing Dynein arms causes are implicated in which dz?
|
primary ciliary dyskinesia
|
|
|
What is the general pathogenesis of Bronchiectasis?
|
impaired mucus flow --> microbial colonization --> microbial products --> 1) mucus hypersecretion 2) structural damage ---> back to even more impair mucus flow
...**vicious cycle** |
|
|
Is Bronchiectasis reversible?
|
No, irreversible.
|
|
|
Edema, smooth muscle thickening, BM thickening, mucous cell hyperplasia, increased submucosal eosinophils, and thickened intralumenal mucus...
...this describes the pathogenesis of which diz? |
asthma
|
|
|
Is Wheezing expiratory or inspiratory? Strider?
Does Radiograph help Dx asthma? Tiss biopsy? |
expiratory
inspiratory No, we do neither. |
|
|
What do we call it when a pt dies of asthma?
|
status asthmaticus
|
|
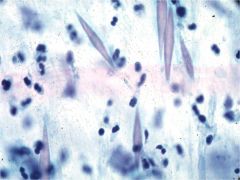
What are seen here? What dz are they seen in?
|
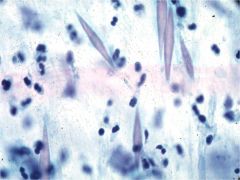
Charcot-Leyden crystals
- related to the granules in eosinophils Asthmatics (typically extrinsics) |
|
|
Are the pathologic criterion for chronic bronchitis the relevant ones for making the Dx?
What are the units of "productive cough"? Are X-rays specific in Chronic bronchitis? |
No; it is a clinical Dx.
productive cough more than 3months at least two times a year. for more than 2 years. Cups of mucin per day. No. |
|
|
In which dz might you find mucous cellular and glandular hyperplasia; along with possible submucosal chronic inflammation and/or respiratory bronchiolitis?
|
chronic bronchitis.
|
|
|
Most pts with Chronic bronchitis have what characteristic?
|
They're smokers.
|
|
|
What are the two main causes of Emphysema?
More in the upper lobe suggest which? Lower lobe? |
Smoking
a1-antitrypsin deficiency. centrilobular type: the one more common in smokers panlobular type: more common in late cigarette smokers or those with a1-antitrypsin def. |
|
|
In which dz do you see:
- septal destruction w/ dilation of distal airspaces - increased elastase activity |
emphysema
|
|
|
If you stabbed an emphysema pt in the lung, would their lung collapse like a normals? Why?
|
no.
Default elasticity of the lung has be lost. |
|
|
____ is due to too much elastase.
|
Emphysema
|
|
|
Does smoking elevate elastase? how about lower antielastase actv (like a1-antitrypsin)?
|
It can do both.
|
|
|
COP (Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia) is a term that should be reserved for which sort of BOOP?
|
ideopathic (i.e. we don't know the cause)
|
|
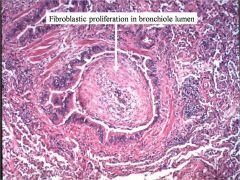
Dz?
|
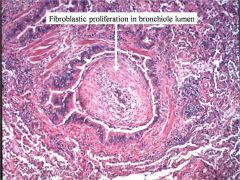
BOOP (Bronchiolitis obliterans)
|
|
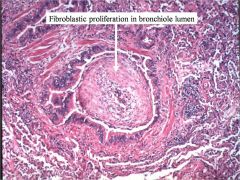
Dz?
|
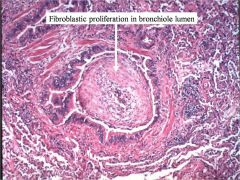
BOOP (Bronchiolitis obliterans)
|

