![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the purpose of hemostasis?
|
Maintain blood flow through vessels
Stop blood loss following vascular injury |
|
|
What are the key components of hemostasis?
|
Vasculature: endothelium, subendothelium
Coagulation proteins Platelets Fibrinolysis/inhibitors |
|
|
What are the stages of hemostasis?
|
Primary hemostasis
Secondary hemostasis |
|
|
What occurs in primary hemostasis?
|
1. Endothelium is disrupted
2. Platelets stick to the exposed collagen 3.Platelet plug is formed This is an unstable compound...it this is where it stopped, you'd only have hemostasis for minutes to hours. |
|
|
What occurs in secondary hemostasis?
|
Enzymatic activation of coagulation proteins to form a stable cap above the platelet plug; fibrin clot forms
|
|
|
What are the different stages of hemostasis?
|
1. Primary hemostasis
2. Secondary hemostasis 3. Termination/attenuation 4. Fibrinolysis/remodeling |
|
|
What happens in termination/attenuation?
|
Arrest hemostasis; contains size of clot
|
|
|
What happens in fibrinolysis/remodeling of clots?
|
Fibrinolytic system is activated-->clot removal
Vascular remodeling |
|
|
What is the definition of plasma?
|
Blood from which he cellular components have been removed
Where the clotting factors reside. |
|
|
What is the definition of serum?
|
Plasma from which the clotting factors have been removed
Antibodies are still here. |
|
|
What are coagulation factors?
|
Proteins needed to complete the series of steps which result in the formation of a fibrin clot
Most coagulation factors are proteases Also, most coagulation factors are zymogens that are activated by a protease (the coagulation factor upstream) |
|
|
What is a zymogen?
|
An inactive form a protein that is able to be activated by the activity of a protease.
|
|
|
What are some examples of anticoagulents?
|
Protein S: innate cofactor
Heparin |
|
|
What are examples of procoagulents?
|
Tissue factor
|
|
|
What are some examples of trombolytic/fibrinolytic substances?
|
Plasmin
|
|
|
What are some examples of antifibrinolytic substances?
|
Tranexamic acid
|
|
|
What are the key components in primary hemostasis?
|
Vessel wall/subendothelium
Platelets Von Wilebrand factor |
|
|
What are the activating factors in hemostasis?
|
Tissue factor
Collagen Von Wilebrand Factor |
|
|
What is the first response to vessel inury?
|
Transient vasoconstriction
Allows for procoagulents to act at the site of injury |
|
|
What are some of the different activities that platelets can perform?
|
Receptors for plasma proteins, subendothelium
Secretory function: can release granules Synthetic functions: thromboxane |
|
|
What are the activities of thromboxane?
|
Activates platelet clotting
|
|
|
What different cellular components interact in platelet adhesion?
|
Platelet glycoprotein Ib adheres to vWF
|
|
|
What are the steps of platelet activity?
|
Adhesion
Activation Aggregation |
|
|
What occurs during platelet activation?
|
Shape change: discoid-->spherical
Release of granules |
|
|
What occurs during platelet aggregation?
|
Exposure of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa which results in cross-linking of adjacent platelets via fibrinogen
|
|
|
What is Von Wilebrand factor?
|
Large, multimeric protein held together by disulfide bond synthesized by endothelium and megakaryocytes
Carrier of factor VIII in plasma |
|
|
How does Von Willebrand factor work?
|
It's a glue for platelets
|
|
|
What is the initiator of secondary hemostasis?
|
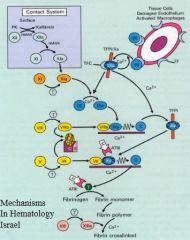
Tissue factor
|
|
|
What clotting factor does tissue factor interact with?
|
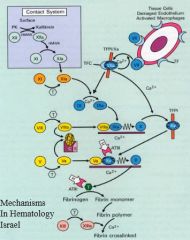
Tissue factor VIIa
|
|
|
When tissue factor VIIa is activated, what does it then go and cleave?
|
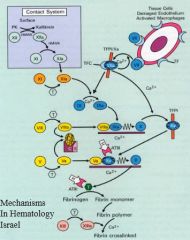
IXa
Xa |
|
|
What is the activity of factor X?
|
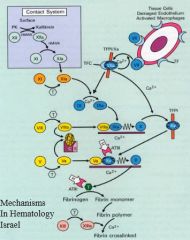
Activation of prothrombin/tissue factor 2-->thrombin
|
|
|
What is the activity of factor II/thrombin?
|
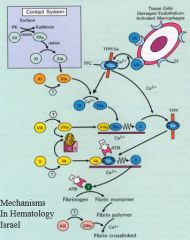
The key component of secondary hemostasis
It converts fibrinogen (soluble) into fibrin (insoluble) |
|
|
What are the proteases activated by thrombin? How does this work?
|
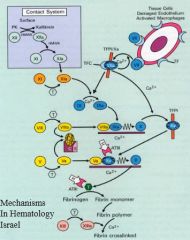
XI
VIII: cofactor V: cofactor Amplification |
|
|
What are the activities of factor V and VIII in coagulation?
|
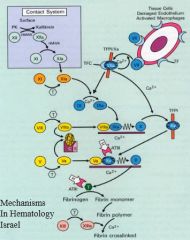
Cofactors: they greatly enhance the activity of the proteases they bind to
|
|
|
Factor VIII binds to what protease? What does this do?
|
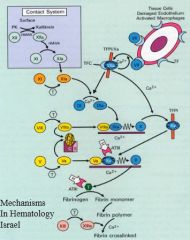
IX
Greatly enhances activity |
|
|
Factor V binds to what protease? What does this do?
|
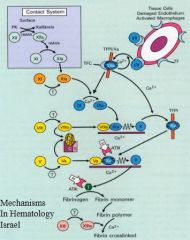
V
Greatly enhances activity |
|
|
What is the effect of missing factor VII or tissue factor?
|
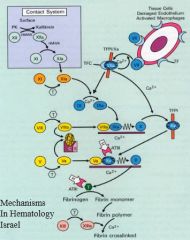
Incomptible with life.
|
|
|
What disease is caused by missing factor VIII?
|
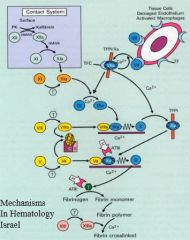
Hemophilia
|
|
|
What is the name of the molecule that blocks the binding of tissue factor to VIIa?
|
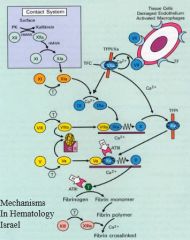
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor
Binds to VIIa to stop the initiation of the extrinsic pathway |
|
|
What is the name of the molecule that blocks thrombin?
|
Antithrombin III
It also blocks Xa |
|
|
What are the activities of protein C/S?
|
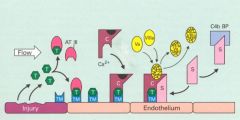
Regulation of the activated clotting factors.
Lysis of Va, VIIIa |
|
|
What is the activity of plasmin?
|
Cleaves fibrin to dissolve clots.
|
|
|
What is D Dimer?
|
It's a degradation product of fibrin breakdown.
We can measure this to see if someone has a DVT, PE, or DIC |
|
|
What are the two main assays that we do to assess coagulation?
|
Prothrombin time
activated partial thromboplastin time They look at secondary hemostasis |
|
|
What pathway is assessed by prothrombin time?
|
Extrinsic pathway
|
|
|
What factors are captured by prothombin time?
|
VII
X V II Fibrinogen |
|
|
What factors are measured by activated partial thromboplastin time?
|
HMWK
PreKal XII XI IX VII X V III Fibrinogen |
|
|
What is the INR?
|
(Patient prothrombin time/Control prothrombin time)*ANR
|

