![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
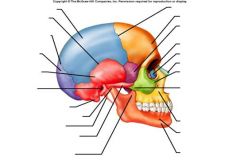
Find the following:
Frontal bone Parietal bone Occipital bone Mandible Sphenoid Bone Temporal bone
|
|
|
|
Squamous |
Roof and part of posterior wall of EAM |
|
|
Mastoid |
Projects down to form mastoid process - a location - |
|
|
Tympanic |
Floor, anterior wall, part of posterior wall of EAM |
|
|
Petrous |
Houses IE and contains IAC |
|
|
Mastoid process is... |
Petrous |
|
|
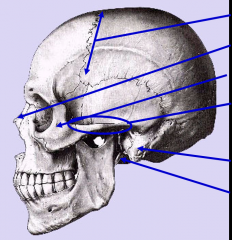
Coronal suture Nasal bone Zygomatic bone Zygomatic arch External auditory meatus Mastoid process Styloid process |
|

|
styloid process (S) mastoid process (M) external auditory meatus (E)Is surrounded by tympanicpart mandibular fossa (F) zygomatic process (Z) squamous part (Sq) |
|

|
27 = Pinna 29 = EAM 31 = TM |
|
|
Cartilage of the auricle is covered by what? |
perichondrium & skin
|
|
|
Auricle is connected to... |
Skull & scalp by 3 extrinsic muscles When muscles are well developed, they can move the ear |
|
|
The TM is ________ shaped |
concave |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
Perichondrium |
the fibrous membrane of connective tissue covering the surface of cartilage except at the endings of joints |
|
|
The sound collector frequency for the pinna is around what frequency? |
5000 Hz |
|
|
________ frequencies pass around pinna |
low
|
|
|
What characteristics of the pinna make this structure act as a resonator for high-freq sounds? |
the convolutions and depressions |
|
|
HI freq patterns change with changes in sound source, providing what cues? |
Horizontal and localization cues |
|
|
Which localization is better: horizontal or vertical? |
Horizontal |
|
|
EAM or ear canal |
**EAM is tunnel into temporal bone from concha to TM **Slight s-shape **About 2.5 cm (1”) in length & 7 mm in diameter **Outer 1/3rd cartilaginous **Inner 2/3 osseous ** Migration of epithelial cells deposits old, dirty cerumen at canal opening **sensory innervation via Arnold's n of CN X and mandibular n. of CN V |
|
|
Osseous portion of EAM |
Skin overlying osseous portion highly sensitive to touch |
|
|
Cartilaginous portion of EAM |
*Skin overlying cartilaginous portion thicker than over osseous portion *contains hair follicies, sebaceous glands, and ceruminous glands |
|
|
You can get a standing wave phenomenon @ what freq? |
@ 4-6K Hz |
|
|
What are the issues with standing waves? |
Can lead to sound cancellation Null points each ¼ wavelength (6dB down points)lOccur under phones commonly @6000-8000 Hz Due to standing waves in soundfield, warble tones used to obtain thresholds |
|
|
What is the adult ear canal resonance? |
~2000-5000 Hz *Primary peak of 17 dB @ 2700 Hz *Secondary peak of 12-14 dB at 4000-5000 Hz |
|
|
Exact resonance varies; but how many times a wavelength does EAM resonate best at? |
@ 4x the wavelength |
|
|
Do you lose or gain resonance because of HA(s)? |
You lose resonance |
|
|
Microtia |
Small pinna; underdeveloped pinaa |
|
|
Atresia |
absence of ear canal |
|
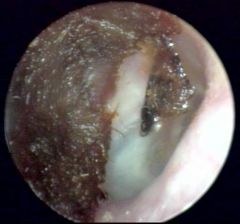
This shows |
cerumen |
|
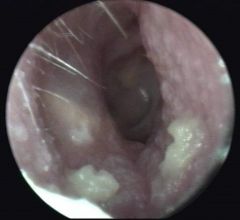
this shows |
otitis externa, which is painful on lobule; use cotton or medication to get it out |

