![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Plate Tectonics |
Plate tectonics are the theory of platetectonics refers to the movements of Earth’s plates. uAs platetectonics operate over time, the size, shape and locationof the world’s continents and oceans slowly change. |
|
|
The Earth’s tectonic plates and the Pacific ring of fireexplain the relationship between the occurrence of volcanoes and earthquakesaround the world. |
Most of the earths volcanoes and earthquakes heavy populate the area around the Pacific Ocean, the pacific ring of fire. The volcanoes and earthquakes are mostly situated on these because these are where a lot of the worlds tectonic plates meet. |
|
|
Diagram of Constructive and Destructive tectonic plates |
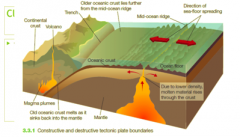
|
|
|
Geomorphic Process |
Plate tectonics, chemical weathering and physical weathering (such as erosion, transportation and deposition) are the major geomorphic processes. The processes vary according to rock type and climate, and operate at speeds ranging from slow to fast. |
|
|
Rock Cycle |
Geomorphic processes are part of the rock cycle, which continually recycles earth's materials. As new crust is created, older crust is subducted back into the mantle to be melted once again. |
|
|
Litosphere |
The part of the land that is moving is the Earth's surface called the Litosphere |
|
|
Upper Mantle |
Made up of the earth's crust and a part of the upper mantle |
|
|
Name the Tectonic Plates |
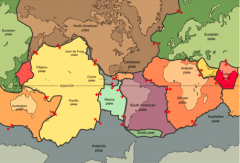
|
|
|
Three types of plate boundaries |
Convergent, Divergent and Transform |
|
|
What are convergent boundaries? |
Two tectonic plates that push together Sometimes one will move under the other (subduction) They can form volcanoes and mountains There can be also areas of high volcanic activity |
|
|
What are divergent boundaries? |
Where two plates are pushed apart The area on land where the boundary occurs is called a rift New land is formed by magma pushing up from the mantle and cooling as it reaches the surface |
|
|
What are transform boundaries? |
Where two plates slide past each other Often called faults Can be areas where earthquakes often occur |
|
|
What is a volcano? |
A volcano is an openingin the surface of the Earth’s crust through which molten magma, solid materialssuch as ash, and gas can escape. |
|
|
Three types of natural hazards? |
Atmospheric - (cyclones, floods, droughts, fires and tornadoes) Geomorphic (volcano, earthquakes, tsunamis, avalanches and landslides) Biological ( epidemics and famine) |
|

What type of Volcano is this? |
Cinder cone volcano - simplest type of volcano that ejects gas and lava from a single vent in a crater to form a steep circular or oval cone of cinders |
|

What type of volcano is this? |
Composite/Stratovolcanoes - 2.usuallysymmetrical steep-sided cones made up of alternating layers of lava flows, andsolid material ejected under pressure from the volcano (e.g. ash, bombs,cinders). |
|

What type of volcano is this? |
Shieldvolcanoes – usually composed of very fluid lava that forms volcanoes that arevery broad at the base and with gentle slopes.
|
|
|
What is a hot spot? |
Hotspotvolcanoes form above a mantle plume, a column of unusually hot magma that risesfrom very deep within the Earth. |
|
|
What is a intrusive volcano? |
When magma is forcedto the surface only a small amount of the mass actually reaches that level. |
|
|
What is extrusive volcanoes? |
Extrusivevolcanic landforms are lavaflows and volcanic cones as built by the accumulation of ashes,cinders and other pyroclastic products of volcanic explosions. |
|
|
Where did the worst earthquake in the world occur? |
China 830,000 deaths |
|
|
Highest on the Richter scale? |
Chilli - M9.5 |
|
|
What is a hypocentre? |
Theunderground point or region of an earthquake |
|
|
What is an epicentre? |
Thepoint directly about the hydrocentre on the ground |
|
|
What is an interplate earthquake? |
Interplateearthquakes occur at plate boundaries when plates collide or move laterallyalong each other |
|
|
What is an intraplate earthquake? |
Intraplateearthquakes occur in the middle of plate, along fault lines |
|
|
Types of landslides? |
flow, topple, slump, slide, creep, fall |
|
|
What is an earthquake? |
Suddenrelease of energy in the earths crust creating vibrations |

