![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mucosa is comprised of 2 layers, name them.
|
1. epithelium
2. lamina propria (CT) |
|
|
Name the 3 types of mucosa in the oral cavity.
|
1. lining
2. masticatory 3. special |
|
|
Which types of mucosa in the mouth are keratinized?
|
masticatory and special
|
|
|
T or F: special mucosa is both keratinized and non-keratinized?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: masticatory mucosa can be para-keratinized or ortho-keratinized?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: basal lamina and basement membrane are synonymous?
|
True
|
|
|
______________ cells produce the lamina lucida of the basal lamina.
|
epithelial
|
|
|
Major component of lamina lucida.
|
laminin
|
|
|
Lamina densa is composed of type __ collagen.
|
IV
|
|
|
epithelial cells attach to lamina lucida via __________ and ____________.
|
hemidesmosomes; anchoring filaments
|
|
|
lamina propria attaches to lamina densa via _______________.
|
type VII collagen (anchoring fibrils)
|
|
|
Type __ collagen anchors lamina propria to lamina densa via type __ collagen fibrils.
|
I; VII
|
|
|
Rete pegs are part of the (epithelium/lamina propria)?
|
epithelium
|
|
|
Papillary layer is a (LP/epithelial) layer?
|
LP
|
|
|
Which layer is deep to the papillary layer?
|
reticular layer
|
|
|
T or F: the reticular layer is composed of large, mesh like collagen fibers and connects the LP to tissue beneath?
|
True
|
|
|
Rete pegs will be longer in (keratinized/non-keratinized) tissue?
|
keratinized
|
|
What are a-c?
|
a- epithelium
b- basal lamina c- lamina propria |
|
|
Capillary network of oral mucosa are found within the (papillae/rete pegs)?
|
papillae
|
|
|
Number of capillary loops in oral mucosa is (greater/less) than in the skin?
|
greater
|
|
|
In the cheek, each papilla has (one/multiple) capillary loops while the tongue papillae have (one/multiple) loops?
|
one;multiple
|
|
|
Blood flow in the oral mucosa is greatest where?
|
the gingiva
|
|
|
Blood flow in the oral mucosa is (greater/less) than the skin?
|
greater
|
|
|
The pink color of the oral mucosa is due to ______________?
|
increased number of capillaries
|
|
|
T or F: In the oral mucosa, there are no arteriovenous shunts, but there are numbers anastomoses between the arterioles and capillaries?
|
True
|
|
|
What contributes to quick healing in the oral mucosa?
|
Large available blood flow (lots of capillaries)
|
|
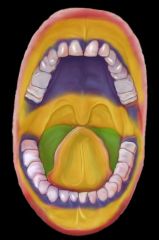
In this picture, what do the colors represent? (be specific)
|
Yellow - lining mucosa (non-keratinized)
Blue- Masticatory mucosa (keratinized) Green - Special mucosa (can be keratinized or non-keratinized) |
|
|
Where is special mucosa found?
|
dorsal surface of tongue
|
|
|
The ventral surface of the tongue has what type of mucosa?
|
lining
|
|
|
Gingiva is comprised of what type of mucosa?
|
masticatory
|
|
|
The soft palate is ___________ mucosa, while the hard palate is ___________ mucosa?
|
lining;masticatory
|
|
|
name 4 locations of lining mucosa?
|
1. ventral tongue
2. cheeks 3. soft palate 4. lips |
|
|
Lining mucosa will have (many/few) CT papillae?
|
few
|
|
|
What holds mucosa to the underlying muscle?
|
submucosa
|
|
|
T or F: Lining mucosa has no keratinocytes?
|
False, they get larger as they move towards the surface
|
|
|
Lining mucosa has a _______ appearance?
|
frothy
|
|
|
Cells in the lining mucosa have _________ filled sacs which push cytoplasmic components to the (center/periphery) of the cell?
|
fluid;periphery
|
|
|
Fluid filled cells in the lining mucosa act as __________ to underlying cells?
|
cushion
|
|
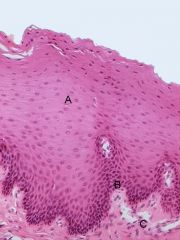
Name the fingerlike projections depicted at 'A'
|
desmosomes
|
|
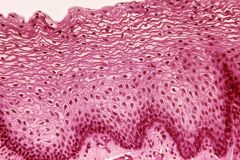
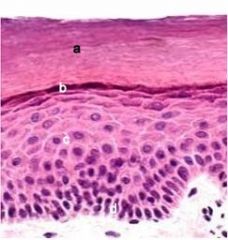
Name the type of mucosa.
|
lining (note the white, "frothy" cells at top)
|
|
|
Name two places where masticatory mucosa is found?
|
gingiva and hard palate
|
|
|
T or F: thickness of masticatory mucosa is indicative of attrition?
|
True
|
|
|
______ papillae in masticatory mucosa are tall and thin.
|
CT
|
|
|
___________ usually underlies masticatory mucosa.
|
bone
|
|
|
Name the two forms of masticatory mucosa.
|
1. orthokeratinized stratified squamous
2. parakeratinized stratified squamous |
|
|
Is orthokeratinized or parakeratinized more common?
|
ortho
|
|
|
Where is parakeratinized mucosa found?
|
non-attached free gingiva
|
|
|
masticatory mucosa will have (small/large) rete pegs?
|
large
|
|
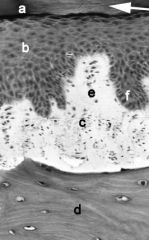
What type of mucosa? What are a-f?
|
masticatory
a- cornified layer b- epithelium c- lamina propria d- underlying bone e- CT papilla f- rete peg |
|
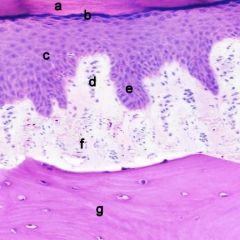
What are a-g? specific type of mucosa?
|
a- cornified layer
b- granular layer c- epithelium d- CT papilla e- rete peg f- lamina propria g- bone orthokeratinized mucosa (has a granular layer, parakeratinized does not) |
|
|
Name the 4 layers of orthokeratinized epithelium?
|
1. stratum corneum
2. stratum granulosum 3. stratum spinosum 4. stratum basale |
|
|
Cells in the stratum corneum are (dead/alive)?
|
dead
|
|
|
T or F: Cells in the stratum corneum have a nucleus?
|
False
|
|
|
Cells in the stratum corneum are filled with ____________?
|
lipid
|
|
|
Thickness of the stratum corneum is dependent on _____________ _______?
|
mechanical stress
|
|
|
Stratum corneum is compose of flattened __________?
|
squames
|
|
|
Stratum granulosum is __ to __ cells deep.
|
2-4
|
|
|
Cells in the stratum granulosum are filled with ___________, which contribues to their dark _______?
|
keratohyalin granules; color
|
|
name the strata.
|
a- stratum corneum
b- stratum granulosum c- stratum spinosum d- stratum basale |
|
|
T or F: Dead cells in parakeratinized mucosa retain their nuclei and do NOT comprise a stratum corneum?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: There is a granular (stratum granulosum) layer in parakeratinized mucosa?
|
False
|
|
|
If a nuclei is shrunken and degenerated, it is ___________? This occurs in ____________ mucosa?
|
pyknotic;parakeratinized
|
|
|
T or F: there is no submucosa under specialized mucosa
|
True
|
|
|
Papillae in specialized mucosa have two possible functions, what are they?
|
mechanical, taste
|
|
|
T or F: special mucosa can be covered by keratinized or non-keratinized stratified squamous?
|
True
|
|
|
Name the four types of lingual papillae?
|
filiform, fungiform, circumvallate, foliate
|
|
|
Where is the sulcus terminalis located?
|
behind the circumvallate papillae
|
|
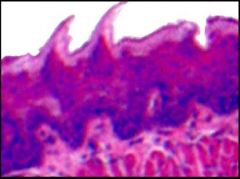
name the type of papilla?
|
filiform
|
|
|
Which is the most common type of lingual papilla?
|
filiform
|
|
|
T or F: filiform papillae are keratinized?
|
True
|
|
|
T or F: filiform papillae have many taste buds?
|
False, no taste buds
|
|
|
T or F: filiform papillae have a mechanical function and have sensory nerve ending to feel food.
|
True
|
|
|
__ __________ do not extend into the filiform papillae.
|
CT papillae
|
|
|
Fungiform papillae are what shape?
|
mushroom
|
|
|
Fungiform papillae are more numerous in (younger/older) individual?
|
younger
|
|
|
T or F: Fungiform papillae have a thick layer of keratinized tissue?
|
Fase, thin
|
|
|
Keratinization of fungiform papillae (thin/thicken) with age?
|
thicken
|
|
|
Name three things fungiform papillae can detect?
|
1. sweet
2. salty 3. sour |
|
|
Which papillae are the largest?
|
circumvallate
|
|
|
Circumvalate papilla are associated with what gland?
|
von Ebner
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the von Ebner glands?
|
to flush bitter stimuli from the trough which holds the taste buds
|
|
|
Taste buds are composed of three types of cells, what are they?
|
1. taste cells
2. supporting cells 3. basal cells |
|
|
Which cells in the taste bud regenerate the other cells?
|
basal cells
|
|
|
Which cells line the taste pore?
|
taste cells
|
|
|
What is a taste pore?
|
portion of taste bud which contacts the oral cavity
|
|
|
cells in taste pore are protected by a _______________?
|
taste pore substance
|
|
|
What is stimulated on the receptor cell in a taste pore?
|
microvilli
|
|
|
Nerves contact taste cells at the (basal/apical) surface?
|
basal
|
|
|
5 yr survival rate for oral/pharynx cancer?
|
59%
|
|
|
Tobacco causes __% of head and neck cancers?
|
85
|
|
|
what two substances are the greatest contributors to head and neck cancers?
|
tobacco and alcohol
|
|
|
_________ American men and women developed cancer in 2005?
|
39,000
|
|
|
What is the #1 site for oral cancer?
|
ventral side of tongue
|

