![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Acous/o |
Hearing |
|
|
|
AD |
Right Ear |
|
|
|
Adenoids |
Lymphatic tissue in the throat behind the uvula. |
|
|
|
An- |
Without; not |
|
|
|
Apnea |
Absence of breathing |
|
|
|
AS |
Left Ear |
|
|
|
Attic |
Small space in the middle ear. Contains the body of the incus and the head of the malleus. |
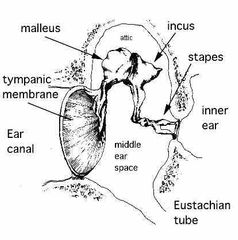
|
|
|
AU |
Both Ears |
|
|
|
Audi/o |
Hearing |
|
|
|
Auricle |
The outer portion of the ear. |
|
|
|
Bilateral |
Pertaining to two sides. |
|
|
|
Carina |
The ridge at the end of the trachea separating the openings of the bronchi. |
|
|
|
Cerumen |
Waxy secretion of the glands of the external acoustic meatus. |
|
|
|
Cholesteatoma |
A cystic mass of cells in the middle ear as well as cholesterol. These cells are keratinizing squamous epithelium cells. |
|
|
|
Chondroradionecrosis |
Serious complications of radiation therapy in the larynx. This can worsen and become fatal. |
|
|
|
Cochlea |
A spiral shaped cavity in the inner ear containing nerves essential for hearing. |
|
|
|
Epistaxis |
Hemorrhage from the nose, usually due to rupture of small vessels overlying the anterior part of the nasal septum. |
|
|
|
Conchacongenital |
A shell shaped structure. |
|
|
|
Congenital |
Referring to conditions that are present at birth. |
|
|
|
Contralateral |
Pertaining to the opposite side. |
|
|
|
-cusis |
Hearing |
|
|
|
Deglutition |
The process of swallowing. |
|
|
|
Dynamic Equilibrium |
The state of being evenly balanced. |
|
|
|
Epi- |
Above; upon |
|
|
|
Epi-Epiglottis |
Above; upon |
|
|
|
Epiglottis |
A thin elastic cartilaginous structure located at the root of the tongue that folds over the to prevent food and liquid from entering the trachea during swallowing. |
|
|
|
Eustachian Tube |
The narrow tube that connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx. |
|
|
|
-itis |
Inflammation |
|
|
|
Labyrinth |
The bony cavity of the inner ear composed of the semicircular ducts, vestibule, and cochlea. |
|
|
|
Laryng/o |
Larynx (voice box) |
|
|
|
Laryngopharynx |
The portion of the pharynx below the upper edge of the epiglottis, opening into the larynx and esophagus. |
|
|
|
Larynx |
The muscular and cartilaginous structure, lined with mucous membrane, located at the top of the trachea and below the root of the tongue and the hyoid bone; it contains the vocal cords. |
|
|
|
Lingual Tonsils |
Collection of lymphoid follicles on posterior or pharyngeal portion of dorsum of the tongue. |
|
|
|
Malleus |
The outermost and largest of the three ossicles of the ear. |
|
|
|
Mastoid Sinus |
Located behind the auricle within the mastoid process of the temporal bone. |
|
|
|
Mastoid/o |
Mastoid process (behind the ear) |
|
|
|
Meniere Disease |
Characterized by vertigo, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and progressive deafness due to swelling of the endolymphatic duct. |
|
|
|
External Auditory CanalFaci |
The passage leading inward through the tympanic portion of the temporal bone, from the external ear to the eardrum. |
|
|
|
Facial Nerve |
Seventh pair of cranial nerves that control facial muscles and relay sensation from the taste buds of the front part of the tongue. |
|
|
|
Fauces |
The passage from the back of the mouth to the pharynx, bounded by the soft palate, the base of the tongue, and the palatine arches. |
|
|
|
Gelfoam |
Absorbable gelatin sponge, used as a hemostatic. |
|
|
|
Glottis |
The opening between the vocal cords at the upper part of the larynx. |
|
|
|
Hypertrophy |
Enlargement of an organ or tissue from the increase of size of the cells. |
|
|
|
Incus |
The middle of the three ossicles of the ear. |
|
|
|
Inner Ear |
The portion of the ear located within the temporal bone that is involved in both hearing and balance and includes the semicircular canals, vestibule, and cochlea |
|
|
|
Ipsilateral |
Located on or affecting the same side of the body. |
|
|
|
Middle Ear |
Consisting of an air-filled cavity bound externally by the tympanic membrane and containing three ossicles that send sound waves and amplified sound to the inner ear. |
|
|
|
Ostium |
An opening that forms the drainage channel in the maxillary sinus. |
|
|
|
Ot/o |
Ear |
|
|
|
Otitis Externa |
an infection of the ear canal, the tube leading from the outside opening of the ear in towards the ear drum. |
|
|
|
Otitis Media |
an infection of the middle ear space, behind the eardrum. It is characterized by pain, dizziness, and partial loss of hearing. |
|
|
|
Soft Palate |
Seals off the cavity of the nose from the mouth during swallowing. Located between the mouth and the oropharynx and between the oropharynx and the nasopharynx. |
|
|
|
Hard Palate |
Bony anterior portion of the palate. Provides structure in the mouth and allows the tongue to move freely. |
|
|
|
Oval WindowP |
The oval opening in the middle ear to which the base of the stapes is connected and through which the ossicles of the ear transmit sound vibrations to the cochlea. |
|
|
|
Palatine Tonsils |
A large oval mass of lymphoid tissue embedded in the lateral wall of the oral pharynx on either side between the pillars of the fauces. |
|
|
|
Rhin/o |
Nose |
|
|
|
-sclerosis |
Hardening |
|
|
|
Myring/o |
Tympanic membrane (eardrum) |
|
|
|
Sapling/o |
Eustachian Tube |
|
|
|
Staped/o |
Stapes (middle ear bone) |
|
|
|
Tympan/o |
Tympanic membrane (eardrum); middle ear |
|
|
|
Perforation |
A hole through the full thickness of the wall of an organ or tissue made by disease. |
|
|
|
Oval Window |
The oval opening in the middle ear to which the base of the stapes is connected and through which the ossicles of the ear transmit sound vibrations to the cochlea. |
|
|
|
Perilymph |
The fluid in the space between the membranous and bony labyrinths of the inner ear. |
|
|
|
Pharyngeal Tonsils |
A collection of more or less closely aggregated lymphoid nodules on the posterior wall and roof of the nasopharyn |
|
|
|
Pharynx |
Part of the throat that lies between the mouth and the larynx or voice box. |
|
|
|
Polyp |
polyps in the nasal cavity or sinuses, usually produced by local irritation (allergies). |
|
|
|
Nares |
The external opening of the nasal cavity. |
|
|
|
Nasopharynx |
The part of the pharynx above the soft palate that is continuous with the nasal passages. |
|
|
|
Nas/o |
Nose |
|
|
|
Olfaction |
The sense of smell. |
|
|
|
Olfactory Nerve |
The first pair of cranial nerves that conduct impulses from the mucous membranes of the nose to the olfactory bulb. |
|
|
|
ORL/ENT |
ORL: Otorhinolaryngology ENT: Ear, Nose and Throat |
|
|
|
Oropharynx |
The part of the pharynx between the soft palate and the upper edge of the epiglottis. |
|
|
|
Ossicles |
The three small bones of the middle ear: the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. These bones help carry sound from the eardrum to the inner ear. |
|
|
|
Polysomnography |
An overnight test to evaluate sleep disorders |
|
|
|
Prebyacusis |
Loss of hearing in both ears. |
|
|
|
Pressure Equalizing Tubes |
A grommet placed through the tympanic membrane to provide continuous middle ear ventilation. |
|
|
|
Propriception |
The unconscious perception of movement and spatial orientation arising from stimuli within the body itself. |
|
|
|
Round Window |
The outer wall of the inner ear that allows free movement of the fluid within the cochlear of the inner ear when sound vibrations are conveyed to it. |
|
|
|
Semicircular Canal |
Three tubular and looped structures of the inner ear, together functioning in maintaining of the sense of balance in the body. |
|
|
|
Septum |
A thin wall dividing two cavities or masses of softer tissue. |
|
|
|
Sinus |
A cavity or hollow space in bone or other tissue. |
|
|
|
Stapes |
The innermost of the three ossicles of the ear. |
|
|
|
Static Equilibrium |
The ability to maintain a steady position of the head and body in relation to gravity |
|
|
|
SMR |
Submucous Resection |
|
|
|
Submucous Resection (SMR) |
Removal of the tissue below the mucosal tissue of the nose. |
|
|
|
T&A |
Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy |
|
|
|
Temporal Bone |
Bones forming the part of the lateral and inferior surfaces of the skull and contain the organs of hearing. |
|
|
|
Tinnitus |
Hearing ringing, buzzing, or other sounds without an external cause in one or both ears. |
|
|
|
Tonsillar Pillars |
The anterior and posterior borders of the tonsillar fossa. |
Tonsillar fossa is a space delineated by the triangular fold of the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches within the lateral wall of the oral cavity. |
|
|
Turbinate |
A small curved bone that extends horizontally along the lateral wall of the nasal passage. |
|
|
|
Tympanic membrane |
Tissue that stretches across the ear canal and separates the middle ear from the outer ear. It is also known as the eardrum. |
|
|
|
Tympanostomy |
An incision that is crest to relieve pressure and allow drainage of fluid from the middle ear. |
|
|
|
UPPP |
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
An procedure that removes excess tissue from back of the throat to prevent it from closing off the airway during sleep. |
|
|
|
Uvula |
The small, fleshy mass of tissue, that hangs from the soft palate above the base of the tongue. |
|
|
|
Vertigo |
A distortion of perception characterized by a sensation of dizziness or loss of equilibrium. |
|
|
|
Vestiy |
A small cavity or a space at the entrance of another structure. |
|
|
|
Vestibulocochlear Nerve |
The eighth cranial nerve, which emerges from the brain between the pons and medulla oblongata, behind the facial nerve. Connecting the inner ear to the brain stem. |
|
|
|
Zenker’s Diverticulum |
Herniation of the mucous membrane of the esophagus through a defect in the wall of the esophagus. |
|

