![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the commonest benign lung tumor? |
Pulmonary Hamartoma |
|
|
Typical features of pulmonary hamartoma? 2 |
Macroscopic fat Popcorn Calcifications |
|
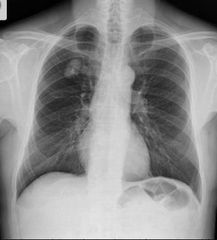
Finding Diagnosis Next step |
A solitary well marginated homogeneous radiodensity is seen in the right upper zone with focal central area of increased density within. The ribs in relation to the lesion show normal contour and density. Otherwise, the chest radiograph is unremarkable. Hamartoma CT chest |
|
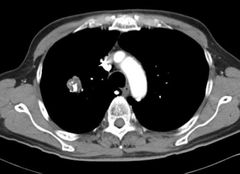
Finding Diagnosis |
Contrast CT revealed a lobulated >2 cm size lesion with central and eccentric popcorn calcification within suggestive of a benign aetiology like pulmonary hamartoma. |
|
|
Three ways of metastasis in the lungs might happened? |
Direct invasion Hematogenous spread Lymphatic spread |
|
|
Hematogenous spread of malignancy will present with ? Which lobe? Examples? 5 |
Randomly distributed nodules Lower lobes ( rich in blood supply) Breast, kidney, thyroid, colon and head and neck SCC |
|
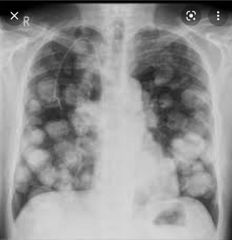
Finding Examples 3 |
Cannonball mets RCC Choriocarcinoma Less ( prostate, endometrial and adrenal) |
|
|
Lymphangetic carcinomatosis Main primaries ? 4 |
Breast Gastric Pancreas Prostate |
|
|
Example of Unilateral lymphangetic carcinomatosis? |
Bronchogenic carcinoma |
|
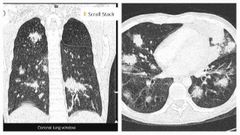
Finding Diagnosis ( buzzword) |
Multifocal consolidation both lungs with a 'flame shaped' appearance, best observed in the upper lobes. These lie at the distal end of the bronchovascular bundles. This is both perihilar and distal in distribution.
Kaposi sarcoma |
|
|
Most common pulmonary CA in AIDs patients is Second most common is |
Kaposi sarcoma Lymphoma |
|
|
Kaposi sarcoma radiotracer ? |
Thallium positive Gallium negative |
|
|
What are the 4 flavours of pulmonary lymphoma ? |
Primary Secondary AIDS related Post transplant |
|
|
What are the 3 radiographic pattern of pulmonary lymphoma? |
Lymphadenopathy Lymphangetic carcinomatosis Parahilar airspace opacities |
|
|
What primary pulmonary lymphoma is commonest? How you define it? |
Non hodgekin lymphoma (80% MALTomas) No extrathoracic involvement in 3 months |
|
|
Differences BTW secondary hodgekin and non hodgekin lymphomas? 1 |
HL intrathoracic is more common and it shows both intrathrocaic and lymph node involvement NHL only parenchymal involvement Common is NHL but if you have HL it is more likely to involve the lungs |
|
|
Post transplant lymphoma? Type Risk factor Time of onset |
B cell lymphoma EBV 1 year if more than 1 year it is more aggressive |
|
|
AIDS related lymphoma commonest type? Associated virus? CD4 count ? Radiology features?3 |
High grade non hodgekin lymphoma EBV <100 Lung nodules, pleural effusion and lymphadenopathy it is lymphoma |
|
|
Kaposi vs lymphoma Nuclear radiotracer? |
Kaposi thallium positive Lymphoma thallium and gallium positive |

