![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MAP equation |
MAP = DBP +(1/3PP) |
|
|
Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP) equation |
CPP = MAP - ICP |
|
|
Complex partial seizure |
Localised involuntary purposeless movements Any of: awareness, memory or consciousness impaired |
|
|
Simple partial seizure |
Localised uncontrolled motor activity One part of the body affected Awareness, memory & consciousness all present |
|
|
Tonic-clonic seizure |
Unconscious with episode of - generalised muscle stiffness and - rapid jerking of muscles |
|
|
Absence seizure |
Episode of ACS and unresponsiveness appearing to day dream even with blinking |
|
|
Types of hypoxia |
Hypoxic hypoxia- insufficient PO2 (eg Asthma, head inj, PE) Stagnant hypoxia- failure of blood transportation (eg shock, AAA, crush) Anaemic hypoxia- insufficient functioning Hb (eg haemorrhage, CO poisoning Histotoxic hypoxia- failure of tissues to utilise O2 (eg cyanide poisoning) |
|
|
D Dimer test used for Normal value |
Used to diagnose inappropriate blood clot/thrombus. Used to include/disclude CVA, PE & DVT
Normal level......?
Not always accurate in patients with rheumatism |
|
|
What makes someone frail |
Frailty is a complex syndrome of age, baseline health, strength and endurance |
|
|
Perfusion status assessment Borderline |
Skin: Cool, pale & clammy HR: 50-100 BP: 80-100 CS: Alert & orientated |
|
|
Perfusion status assessment Adequate |
SKIN: Warm, pink & dry HR: 60-100 BP: 100< CS: alert & orientated |
|
|
Perfusion status assessment Extremely poor |
SKIN: CPC HR: <50, >100 BP: <60mmHg CS: altered or unconscious |
|
|
Perfusion status assessment Inadequate |
SKIN: Cool, pale & clammy HR: <50, 100< BP: 60-80 CS: orientated or altered |
|
|
RSA Components |
Appearance Speech Sounds Rate Rhythm Effort (WOB) Skin Pulse Conscious state |
|
|
Perfusion status assessment No perfusion |
SKIN: CPC PULSE: NONE BP: UNRECORDABLE CS: UNCONSCIOUS |
|
|
RSA Appearance |
Normal: calm Mild: calm or mildly anxious Moderate: anxious, distressed Severe:, distressed, catatonic, fighting to breathe, exhausted |
|
|
RSA Speech |
Normal: sentences Mild: sentences Moderate: phrases Severe: words, unablr to speak |
|
|
RSA Sounds |
Normal: quiet, no wheeze, ?scattered fine basal crackles Mild: able to cough, mild expiratory wheeze, some fine basal crackles Moderate: able to cough, exp +/- insp wheeze, mid-zone crackles Severe: unable to cough, insp & exp wheeze or no sounds, full field crackles, UAO- insp stridor |
|
|
RSA Rate |
Normal: 12-16 Mild:16-20 Moderate: 20< Severe: 20<, <8 |
|
|
RSA Rhythm |
Normal: normal Mild: slight increased Moderate: increased +/- access muscle Severe: increased, access muscle, intercostal retraction, +/- tracheal tug |
|
|
RSA HR |
Normal: 60-100 Mild: 60-100 Moderate: 100-120 Severe:120 <, brady |
|
|
RSA Skin |
Normal: normal Mild: normal Moderate: pale & sweaty Severe: pale& sweaty, +/- cyanosis |
|
|
RSA Conscious state |
Normal: alert Mild: alert Moderate: may be altered Severe: altered or unconscious |
|
|
GCS Eyes |
4- spontaneous 3- to voice 2- to pain 1- none |
|
|
GCS Verbal |
5- orientated 4- confused 3- inappropriate 2- incomprehensible 1- none |
|
|
GCS Motor |
6- obeys 5- localises 4- withdraws 3- flexion, abnormal 2- extension 1- none |
|
|
Paediatric Age category/definition |
Newborn: birth to 24 hours Infant: <1 Small child: 1-8 Large child: 9-14 |
|
|
Paediatric Weight calculation |
Newborn: 3.5kg 2 months: 5kg 5 months: 7kg 1 year: 10kg 1-9: (age x2)+8 10-14: age x3.3 |
|
|
Paediatric Adequate perfusion |

|
|
|
Paediatric Inadequate perfusion |

|
|
|
Paediatric Resp rates |
Newborn: 40-60 Infant: 20-50 Small child: 20-35 Large child: 15-25 |
|
|
Paediatric Sisgns of respiratory distress |
- Pale - Cyanosis (late) - Wheeze - Grunt - Tachypnoea - Accessory muscles used - Abdominal protrusion - Chest wall retraction |
|
|
Paediatric Signs of hypoxia- infant |
Lethargy Apnoea Pallor Bradycardia Hypotension |
|
|
Paediatric Signs of hypoxia Children |
Restlessness Tachypnoea Tachycardia (brady late) Cyanosis |
|
|
Paediatric CO2 retention |
Sweating Hypertension Tachycardia Bounding pulse Pupillary dilatation CV & CNS depression
Nb: the thing about paeds- resp failure is common in first 2 years. Small calibre airways are prone to obstruction. Usually indicates failure of another body system |
|
|
Paediatric GCS Eyes <4 |
4- spontaneous 3- reacts to speech 2- reacts to pain 1- none |
|
|
Paediatric GCS Verbal <4 |
5- appropriate words, smiles, fixes 4- Cries but consolable 3- Persistently irritible 2- Restless and agitated 1- none |
|
|
Paediatric GCS Motor <4 |
6- Spontaneous 5- Localises 4- Withdraws 3- Abnormal Flexion 2- Extension response 1- None |
|
|
Paediatric QUESTT principles in obtaining an understanding of pain in paeds |
Q- question the child U- use pain scale E- evaluate behaviour & physiological changes S- secure parent's involvement T- take cause of pain into account T- take action & evaluate results |
|
|
Paediatric FLACC children < 3 |
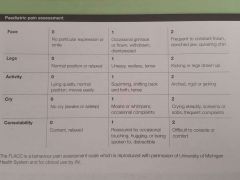
|
|
|
Paediatric Trauma Potential time critical |
Pedestrian impact Prolonged extrication Ejection Explosion Car >60 Motorbike >30 Fall >3m Head strike by object >3m Fatality in same vehicle Rollover |
|
|
Paediatric Trauma Emergent time critical |
Same as adult |
|
|
Paediatric General notes about cardiac arrest |
Most commonly caused by hypoxaemia & hypotension. Conditions include drowning, septicaemia, SIDS, asthma, UAO & congenital abnormalities of the heart & lungs Mx aimed at airway control & adequate ventilation. |
|
|
SV |
SV = EDV-ESV Ie total amount ejected is the total amount before contraction less the amount left after contraction |
|
|
Flow calculation |
F=BP/R Flow = BP ÷ resistance |
|
|
Mental Status Assessment criteria |
Safety Appearance Behaviour Affect Speech Thought process Cognition Thought content Self-harm Perceptions Environment |
|
|
Red flags |
1. Age <1, Frail 2. GCS <15 3. Abnormal VSS 4. Pain >5 5. Possible cardiac symptoms 6. Abdo pain, acute or undiagnosed 7. Obstetrics |

