![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the features of synovial joints? Include the structures that MAY be associated with synovial joints. |
1. Synovial joint cavity 2. Articular cartilage: hyaline, avascular, aneural 3. Joint capsule: blends with periosteum 4. Synovial membrane: produces s. fluid 5. Synovial fluid
-Fat pads: movable space fillers, pain if trapped -Labrum: fibrocartilage, increases socket depth -Discs and menisci: firbocartilage, increases shock absorption, congruence, proprioception -Bursae: flattened sacs of synovial membrane, reduce friction |
|
|
What colour is synovial fluid? What does it contain? (4) What function does it serve? (3) |
Clear, pale yellow, viscous.
Hyaluronic acid (creates viscosity - reduced in OA) Lubricin (PRG4) A few cells (monocytes, lymphocytes, macrophages): immune privileged site Nutrients
Lubricates joint surface Reduces friction Nourishes joint cartilage |
|
|
Knee Joint What kind of joint is the knee joint? |
Synovial, modified hinge joint Biaxial condylar joint between condyles of femur and tibia. Saddle joint between femur and patella. |
|
|
Knee Joint What movements are possible at the knee joint? When is it most stable? |
Flexion/extension Some medial/lateral rotation and gliding in flexion. It is most stable in extension Tibia rotates medially on extension to lock knee and draw ligaments taut. Line of CoG is anterior to knee joint and maintains extension. |
|
|
Knee Joint What ligaments are associated with the knee joint? |
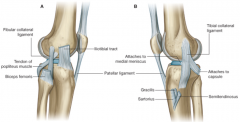
Tibial collateral ligament Broad, flat, limits extension and abduction of the leg Attached to the medial meniscus and blends with joint capsule More commonly damaged Fibular collateral ligament Round, cord-like, limits adduction Separate from joint capsule
Anterior cruciate ligament From anterior intercondylar area of tibia to medial wall of intercondylar fossa of femur Limits anterior movement of tibia and hyperextension Posterior cruciate ligament From posterior aspect of inercondylar tibia to anterior medial wall of intercondylar fossa of femur Limits posterior movement of tibia and hyperflexion (landing after jump) Shorter and stronger than ACL so not torn as easily
The ligaments constrain movement and aid proprioception. |
|
|
Knee Joint Describe the vascular supply and innervation of the knee joint. |
Genicular branches of the popliteal artery Descending branches of the femoral and lateral femoral circumflex Anastomosis formed. The knee joint is innervated by branches from the obturator, femoral, tibial, and common fibular nerves. |
|
|
Knee Joint Describe the menisci of the knee joint. |
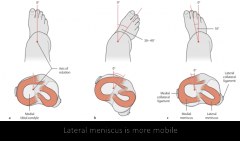
Fibrocartilage. Increases the congruence between curved femoral condyles and relatively flat tibial plateau Attaches to tibia and to joint capsule peripherally Wedge-shaped in cross-section - Periphery - thick, blends with capsule, good blood supply --> repairs mor ereadily - Inner aspect - thin, free edge, avascular
Lateral meniscus is more mobile, medial meniscus is more commonly injured |
|
|
Knee Joint How many bursae are associated with the knee joint? Do any of them communicate directly with the knee joint? |
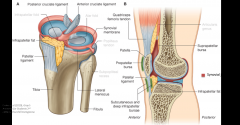
11 bursae The suprapatellar bursa communicates with the synovial joint cavity. |
|
|
Knee Joint Which muscles are responsible for the different movements of the knee? |
Flexion: -Hamstrings: BF, SM, ST -Sartorius -Gracilis
Extension: -Quadriceps femoris: RF, VL, VI, VM
Medial rotation: -extended: popliteus -flexed: SM, ST, Sart, Grac
Lateral rotation: -flexed: Biceps femoris |
|
|
Hip Joint What type of joint is the hip joint? |
Synovial ball and socket joint |
|
|
Hip Joint What movements occur at the hip joint? |
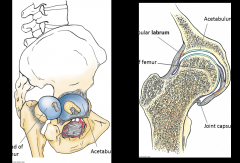
Flexion/extension Abduction/adduction Medial/Lateral rotation |
|
|
Hip Joint What are the ligaments of the hip joint? In what position are they drawn taut? |
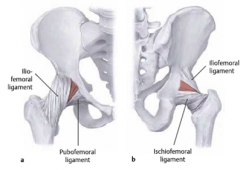
Iliofemoral (inverted Y-shape, thickest) Pubofemoral Ischiofemoral Thickenings of the capsule Taut on extension - most stable position |
|
|
Hip Joint Which muscles are responsible for the different movements of the hip joint? |
Flexion: - Iliopsoas, RF, Sart, TFL, Pectineus
Extension: - Hamstrings (SM, ST, BF), Glut Max, Add Mag
Abduction: - Glut Med, Glut Min, TFL, (Piri)
Adduction: - Add Long, Brev, Max, Grac, Pect
Medial Rotation: - TFL, Glut Min, Glut Med
Lateral Rotation: - Glut Max, P,Q,2Obt,2Gem |
|
|
Hand Joints Describe the type and movements of the 1st carpometacarpal joint. |
Synovial saddle joint
Flexion/extension Abduction/adduction Opposition/reposition |
|
|
Hand Joints Describe the type and movements of the metacarpophalangeal joints. |
Synovial ellipsoid (or condyloid) joints
Flexion/extension Abduction/adduciton |
|
|
Hand Joints Describe the type and movements of the interphalangeal joints. |
Synovial hinge joints
Flexion/extension |

