![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the hallmarks of osteoarthritis?
|
Loss of articular cartilage
Increased bone formation The end point of these processes is joint pain and dysfunction |
|
|
Where on the bone does the dysfunction take place in osteoarthritis?
|
Subchondral bone plate
|
|
|
What are the cells that synthesize cartilage matrix? What else do they produce?
|
Chondrocytes
Also, generate degradative enzymes |
|
|
What are the molecular components of the the normal extracellular matrix?
|
Collagen II
Hyalouronan Proteoglycans |
|
|
What is the normal blood supply to cartilage?
|
There isn't any!
It's avascular |
|
|
What is the cause of osteoarthritis?
|
Damage to the cartilage caused by biomechanical force/trauma
|
|
|
What occurs to the chondrocytes in reaction to repeated damage/trauma?
|
Altered phenotype
Increased production of degradative enzymes, cytokines results in more net degradation than synthesis-->altered composition |
|
|
What is the role of inflammation in OA?
|
It's usually thought that inflammation doesn't have a big role...
BUT -Some cytokines found -Synovial thickening -Response to NSAIDs |
|
|
What are the risk factors for OA?
|
AGE!!!!! (75% of persons >70)
Genetics Biomechanical factors (Scholiosis, worked in hard labor entire life) Trauma Obesity FEMALES NMJ dysfunction (can't sense trauma) Metabolic disorders |
|
|
Where are the most common places for OA changes on Xray?
|
DIP
Knee Hip More changes in women than in men |
|
|
What are the symptoms of OA?
|
Pain:
-Worse with use -Worse as day progresses -If severe enough, rest/nocturnal pain Minimal morning stiffness Stiffness after inactivity (gelling) |
|
|
What are the signs of OA?
|
Pain with movement
Bony enlargement Restricted movement Crepitation Joint instability Joint deformity |
|
|
Where are the most common places in the body for OA?
|
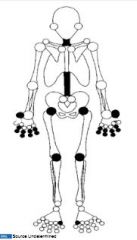
Cervical, lumbar spine
Upper: PIPs, DIP, base of thumb Lower: hips, knees, 1st MT/Phalangeal joint |
|
|
What are the labs that you do for OA?
|
None!
|
|
|
What are the different classes of joint fluids?
|
Class 1: Clear, normal
Class 2: Inflammatory Class 3: Septic/gout; pus, neutrophils Class 4: Sickle cell; hemorrhagic |
|
|
What are the signs of OA on Xray?
|
Joint space narrowign
Marginal osteophytes Subchondral cysts Bony sclerosis Malalignment |
|
|
If there's "OA" in a joint that shouldn't have it, what should you think?
|
Think about a secondary cause!!
-trauma -NMJ disease (diabetic, other neuropathies) -Metabolic disorders |
|
|
How do you differentiate between diabetic neuropathy and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease?
|
Diabetic: lower extremity bias
CPPD: upper extremity bias |
|
|
What parts of the body are affected by diabetic neuropathy?
|
MTPs 2-5, as well as the 1st
Midfoot |
|
|
What are the signs of diabetic neuropathy on plainfilms?
|
Super destructive changes!
|
|
|
What are some of the nonpharmacologic therapies for OA?
|
Weight loss
Hot/cold application Joint protection: strengthen the muscles around the joint PT: splints, exercises, water therapy Orthotics!!! (correct the valgus deformity of the knees) |
|
|
When giving meds to old people, what are some concerns that you need to have?
|
GI: slowed motility, altered pH, past surgery
Increased fat: lean body weight Hepatic: decreased oxidation, liver disorders Decreased GFR Neurologic disorders--> increased cholinergic SEs |
|
|
What are some of the medical therapies for OA?
|
1. Acetaminophen
2. NSAIDs Higher/more extreme -Tramadol -Opioids -Topical agents -Central pain agents |
|
|
What is the maximum dose of acetaminophen?
|
4 g/day in healthy person; elderly, 3g/day or less
|
|
|
What are some of the side effects of acetaminophen?
|
Liver toxicity
|
|
|
What is a special concern that you need to have when giving out acetaminophen?
|
Lots of different kinds of meds have it inside of it...need to be careful about dosing/educating the patient
|
|
|
What substance shouldn't you use with acetaminophen?
|
Alcohol
|
|
|
What are some of the toxicities associated with NSAIDs?
|
GI
Renal CV |
|
|
What is the mechanims of the NSAIDs?
|
COX-2 inhibitors
|
|
|
What pathways does tramadol affect?
|
Opoid
Serotonin |
|
|
What is the effect of tramadol on mucosal membranes?
|
NOTHING!
It doesn't cause ulcers |
|
|
What are some of the side effects of tramadol?
|
Nausea
Vomiting Lowered seizure threshold Constipation Drowsiness Diziness |
|
|
What are some of the topical agents used in OA?
|
Capasacin
NSAIDs |
|
|
What is the effect of using capsaicin in OA?
|
Desensitizes the body there to pain by having pain fibers fire all of the time.
|
|
|
What are indications for using intra-articular steroids?
|
Knee pain
Gives good pain relief |
|
|
What is a transient effect of intra-articular steroids?
|
Poor glucose control for up to 10 days.
|
|
|
What are the effects of injecting hyalouronate into joints? How long does it take to work?
|
Symptomatic relief; improved function
Benefits don't take place until after a month of injecting Also, it requires a series of injections |
|
|
What are some of the CAM therapies for OA?
|
Ingested: ginger, willow bark, stinging nettle, MSM, fish oil
Glucosamine sulfate + chondroitin Acupuncture Tai Chi |
|
|
What are some of the surgical interventions for OA?
|
Osteotomy: resection of some of the joint to shift load to a different portion
Arthroplasty: joint eplacement Arthrodesis of 1st TMT joint |
|
|
What is the initial treatment for OA?
|
-Muscle strengthening exercies
-Weight loss -Adunctive therapies -Acetaminophen -Local heat/cold |
|
|
What is the second-line treatment for OA?
|
-NSAIDs
-Intra-articular agents -Others -Opioids -Central pain agents |
|
|
What are the third-line treatments for OA?
|
-Osteotomy
-Joint replacement |

