![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osmosis |
As the net movement ofwater molecules from a region of higher waterpotential (dilute solution) to a region of lowerwater potential (concentrated solution), througha partially permeable membrane. Water moves in and out of cells byosmosis through the cell membrane |
|
|
Uptake of water by Plants |
Water potential is the correct term for saying ”water concentration” a high water potential is equivalent to a low solute concentration and vice versa;For plants to take in water through their roots they must have a high solute concentration or low water potential in the roots and low solute concentration or high water potential outside the roots.In osmosis, water molecules diffuse down a water potential gradient.Usually, the water in the soil is more dilute than that in root hair cells So water enters root hair cells by osmosis which is a passive process that requires no energy. |
|
|
Vocabulary |
Hypertonic - higher solute concentration outside the cell than inside it so water will leave the cell. Hypotonic - lower solution concentration outside the cell than inside it so water moves into the cell. Isotonic - same osmotic pressure outside and inside the cell so no net movement of water. Flaccid - a plant cell that is limp Turgid - a plant cell fully inflated with water Plasmolysed - a plant cell that has lost water, causing the cell membrane to pull away from the inside of the cell wall Crenation - shrinking an animal cell by osmosis Lysis - bursting an animal cell by osmosis |
|
|
Effect on cells of immersing them in solutions of different concentrations |
When placed in pure water, plant and animal cells will take in the water by osmosis. This is because there is a higher concentration of water molecules outside the cell than inside it. Plants become turgid, but do not burst because of their tough cell wall. Animal cells will burst, because they have no cell wall. The reverse happens when plant and animal cells are placed in a concentrated sugar or salt solutions. This is because there is a higher concentration of water molecules inside the cell than outside it. Plant cells become flaccid and the cytoplasm is no longer pressed against the cell wall. Animal cells also become flaccid and their shape changes- they can become crenated. |
|
|
Turgid Plant Cells |
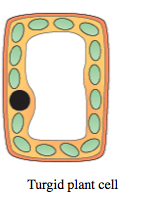
|
|
|
Flaccid Plant Cells |
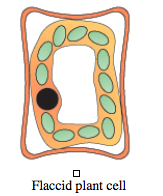
|

