![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ellis Classification
|
Class I- fracture within enamel
Class II - Fracture of enamel-dentin Class III- fracture involving pulp Class IV - Fracture involving root |
|
|
Who classification
|
luxation injuries(to periodontia)
injuries to hard dental tissues injuries to supporting bone injuries to gingiva and oral mucosa |
|
|
Who classifcation-injuries to supporting bone
|
-communion of apical alveolar bone(intrusion)
-fracture of alveolus -fracture of alveolar process(w/ or w/o socket) -Jaw bone fracture(w/ and w/o socket |
|
|
Who classifcation-injuries to gingiva or oral mucosa
|
-contusion
-abrasion -lacerations |
|
|
Who classifcation-luxation
|
-concussion
-subluxation -extrusive luxation -intrusive luxation -avulsion |
|
|
Who classifcation-injuries to hard dental tissue
|
-enamel infraction
-Crown fractures(uncomplicated and complicated) -Root fractures(uncomplicated and complicated) -root fracture |
|
|
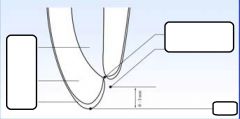
Etiology-
prevalence? age? injuries? |
-25-30%
-0-20, 8-12 prominent -fractures of enamel, enamel/dentin but w/o pulp involvement |
|
|
|
|
|
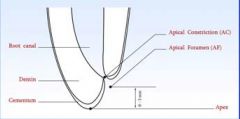
Concept of the Open Apex
Open apex found in? normal in? what happens if pulp undergoes necrosis before root is complete? |
Open Apex
-Found in developing roots of immature teeth -normal in the absence of pulp or perradicular disease -dentin formation stops and root growth is arrested |
|
|
Anomalies which can cause an open apex
|
-developmental anomalies
-dens-in-dente |
|
|
Management of Open Apex-Apex genesis
-also known as -treatment is based on? -pulp is? |
-apexogenesis(vital pulp therapy)
-promotion of root growth to length and amturation of apex -used only when pulp is vital |
|
|
Management of Open Apex-Apex fication
-also known as -treatment is based on? -pulp is? |
-Apexification(root end closure)
-induction of root end formation(apical calcific barrier) -pulp is necrotic |
|
|
Sequelae of traumatic injuries
|
-pulp necrosis
-pulp canal obliteration(calcific metamorphisis) -external inflammatory root resoprtion |
|
|
Examination and Follow up
|
-history
-clinical exmainaiton -radiogrpahic examination -photographs -follow up |
|
|
History:
|
-demographics
-social/family history -medical hsitory -history of present illness> |
|
|
Clinical Examinaiton
|
Soft Tissue
Facial Bones Teeth and teeth fractures Mobility Displacement Injury to periodontal ligament and alveolus Pulpal trauma |
|
|
Radiographic Examination
|
-perapical/occlusal radiographs
-evaluate for disolcations, root & jaw fractures -size of pulp chamber and root cnaal -apical root development -PDL spaces -resorptive and calcific changes |
|
|
Photographs
|
-essential whenever possible
-important in physical abuse cases and litigation cases |
|
|
Follow Up exam?
monitor over? recommended recalls? check for? |
-long period of time
-recalls at: 1,2,3,4,6 weeks -3 months, 6 months, 12 months -yearly after injury |
|
|
Follow up exam-clinical examination
|
-vertical root fractures in peridontal pocket
-development of sinus tract -pulp necrosis |
|
|
Follow up exam-radiographic examination
|
-periradicular rarefaction
-root fractures -internal and external root resoprtion -pulp space changes |
|
|
Diagnostic test:
pulpal status: color changes mobility evaluation percussion palpation periodotnal probing transillumintion radiographic |
pulpal status:CO2, ice, EPT
color changes: gray vs. yellow mobility evaluation: persisitent or lack of mobility percussion: +/- high pitched metallic sound palpation: +/- periodotnal probing: long and narrow pockets transillumintion: fractures radiographic:evidence of dentoalveolar changes |
|
|
Concussion:
|
injury to tooth supporting structures with no loosening or displacement of the tooth but with marked sensivitiy to percussion
-closed apex has large chance of survival, as does open apex |
|
|
Subluxation
|
-injury to the tooth supporting structures with abnormal mobility but with NO DISPLACEMENT of the tooth
-closed apex/open apex good survival chances |
|
|
Exrusive luxation
|
injury to the tooth supporting structures with partial displacement of the tooth out of its socket
-open apex-good chance of survival -closed apex lower chances after 1 year |
|
|
Lateral Luxation
|
injury to tooth supporting structures with DISPLACEMENT in a direction other than axial. Accompanied by communication or fracture of alveolar socket
-open apex good -closed apex: drops after 1/2 year |
|
|
Intrusive luxation
|
-displacement of the tooth INTO the alveolar bone
-accompanied by communication or fracture of alveolar socket -open apex: chances drop to 50% after 1 year -closed apex: chances drop to almost 0 after 1/2 year |
|
|
Avulsion
|
tooth is displaced out of its socket
open apex: drops after 1/2 year to 50% closed apex: drops to 0 after less than 1/2 a year |
|
|
Pulp survival after luxation injury after crown fracture in teeth with open apices
|
concussion+ sublux -good
extrus/lateral lux - 50-70 intrusion-0 |
|
|
pulp survival after fracture in teeth with closed apices
|
-concussion-good
sublux-50% exus/lat lux-12% intrusion-0% |
|
|
PDL Healing after replantation in permananet dention
|
-open: drops to 50 after 1st year
closed- drops to 25 after 1 year |
|
|
PDL healing after dry storage in replanted teeth
|
open: 60-70% for 20 minutes, 45% 20-40 minutes, 15-20% 40-60 minutes, 15% up until 120 minutes, 0% after that
|
|
|
Ellis class 3
|
enamel and dentin with small pulp exposure
|
|
|
ellis class Iv
|
enamel and dentin with large pulp exposure/crown-root fracture
|

