![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the alveolar-capillary barrier is ___(1) microns thick and a RBC is ___(2) microns thick
|
(1) 0.5 microns
(2) 7-8microns |
|
|
what is interstitial space?
|
space between alveolar epithelium and cells that make up wall of capillary
|
|
|
what makes up wall of alveolar?
|
alveolar epithelium
|
|
|
what is barrier of diffusion?
|
narrow barrier between air and blood
|
|
|
contraction of inspiratory muscles(diaphragm, chest wall) does what to thoracic cavity, Interpleural pressure, lung volume, and alveolar pressure?
|
-Thoracic cavity enlarges
-Interpleural pressure decreses -alveolar pressure decreases -lung volume increases |
|
|
Before breathing: Barometric pressure (<, =,>) Alveolar pressure
|
Before breathing: Barometric pressure = Alveolar pressure (no airflow)
|
|
|
while breathing: Barometric pressure (<, =,>) Alveolar pressure
|
while breathing: Barometric pressure > Alveolar pressure
|
|
|
What would have to be done to alveolar pressure to make air enter lungs?
|
make alveolar pressure lower than barometric pressure.
|
|
|
What is the volume of air that enters the lung during normal inspiration?
|
approximately 0.5L
|
|
|
What is tidal volume?
|
volume of air that enters lung in one breath
|
|
|
At what intrapleural pressure would your lungs collapse?
|
0mmHg
|
|
|
What does exercise do to Tidal Volume?
|
exercise increases tidal volume
|
|
|
What is eupnea?
|
breathing at rest
|
|
|
what would tachypnea do to respiratory rate(f) and Tidal volume?
|
Respiratory Rate(f) would increase and Tidal volume would decrease. (ex. animals do this to lose heat or when their excited)
|
|
|
dypsnea shows what characteristics?
|
labored, difficult breathing
|
|
|
Intrapleural pressure is usually (negative/positive)
|
IP pressure usually negative
|
|
|
in reference to muscles of inspiration, which muscles contain smooth muscle, and which ones contain skeletal muscle?
|
Smooth muscle-respiratory airway
skeletal muscle-muscles in chest wall and diaphragm. |
|
|
what is a pneumothorax?
|
collapsed lung
|
|
|
if there is a pneumothorax or collapsed lung on the left side of the heart, would it do the same to the right?
|
no the intrapleural space in the left lung will stay at negative pressure and continue to respire.
|
|
|
during inspiration, what nerves are stimulated to make diaphragm contract?
|
stimulation of medullar nerves, stimulationg of phrenic nerves, ACh released, making diaphragm contract
|
|
name cell types and give description of their function
|
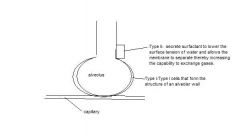
here it is
|
|
label graphs for: Volume, IP pressure, flow, alveolar pressure. (note inspiration for left and expiration for right side of graphs.)
|
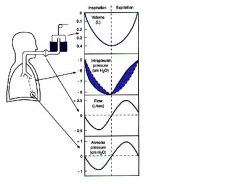
here it is
|
|
|
What stimulates phrenic nerve?
|
Neurons in medulla in brain
|
|
|
At what part of spinal cord are the phrenic nerves originated?
|
C3-C4
|
|
|
what are intercostal muscles?
|
muscles connecting ribs
|
|
|
what would make external intercostal muscles contract?
|
inspiration
|
|
|
what would make internal intercostal muscles contract?
|
expiration
|
|
|
When external intercostal muscles contract, what happens to ribs, chest circumference, and volume of chest.
|
ribs are elevated, circumference of chest is increased, volume of chest in increased
|
|
|
HARD:
Intercostal innervated by _____(1), originating from ____(2) region. |
(1)spinal motors neurons
(2)originating from thoracic region |
|
|
What is the function of scalene, an accessory muscle?
|
elevates 1st two ribs.
|
|
|
What is the function of sternomastoids?
|
pull out on sternum
|
|
|
HARD:
During ____ you would use accessory muscles, such as neck muscles. |
dypsnea
|
|

which line has lower compliance
|
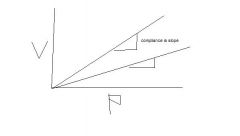
lower line or the one shifted right has lower compliance
|
|
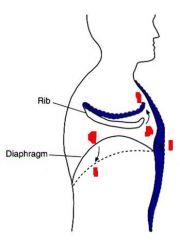
label all red areas with I, or E for inspiration or expiration
|
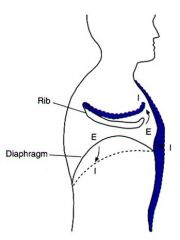
here it is
|
|
|
pulmonary fibrosis is when elastic tissue is replace by fibrous tissue in lungs, making it less distensible. What affect does this have on compliance?
|
lowers compliance
|
|
|
Compliance (increases/decreases) with increasing lung volume.
|
decreases
|
|
|
During inhalation, Volume of each alveolus (increases/decreases) slightly
|
increases or expands
|
|
|
what is surface tension with respect to alveolus?
|
when alveolus expands forces that draw water molecules together creates surface tension. expanding alveoli has to overcome surface tension, influences compliance.
|
|
|
What affect does decreasing surfactant have on compliance?
|
decreases compliance as lung becomes more stiff.(related to respiratory distress syndrome of neonates because Type II cells not significantly mature.)
|
|
|
what affect does surfactant have on surface tension?
|
reduces surface tension by reducing attraction of adjacent water molecules, increasing compliance
|
|
|
HARD:
At end of inspiration, what is the normal change in pressure? |
3cmH2O
|
|
|
What is the equation for Transpulmonary pressure?
|
Pressure of Alveoli - Intrapleural pressure
|
|
|
Prior to inspiration, alveolar pressure is 0 and intrapleural pressure is -5. what is the transpulmonary pressure?
|
0-(-5)=5 cmH2O
|
|
|
At end of inhalation, alveolar pressure is 0 and Intrapleural Pressure is -8. What is the transpulmonary pressure. If pressure is 5cmH2O prior to inspiration, what is the total change is pressure?
|
(-0-(-8)=8cmH2O) transpulmonary pressure
(-5-(-8)=3cmH20) for change of pressure |
|
|
what is transpulmonary pressure?
|
Pressure exerted in system to expand lung
|

