![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Is output for right and left ventricles the same or different?
|
the same
|
|
|
If cardiac output is 5, and the change in pressure is 100, what is the TPR? (hint: relate to flow)
|
20
|
|
|
What is the BP in pulmonary artery?
|
25/10
|
|
|
BP in pulmonary vein/left atrium is...
|
2-3mmHg
|
|
|
Flow in pulmonary circulation is (<,>, =) flow of systemic circulation
|
=
|
|
|
If pressure in pulmonary circulation is decreased, pressure in systemic circulation is (increased/decreased)
|
decreased
|
|
|
Pulmonary system has (more/less) resistance than systemic
|
less
|
|
|
systemic system has (more/less) resistance than pulmonary
|
more
|
|
|
____ = pulmonary arterial pressure - Left atrial pressure/pulmonary vascular resistance(PVR)
|
Cardiac output
|
|
|
force exerted on walls of vessel is....
|
Blood pressure
|
|
|
What is normal systemic arterial Blood pressure?
|
120/80
|
|
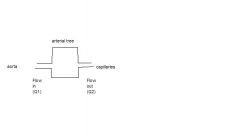
describe flow at Q1 and Q2.
explain why the flow is able to work this way... |
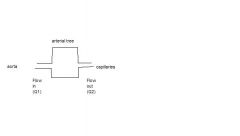
At Q1: flow is intermittent or pulsative
At Q2: there is continuous flow. Due to elasticity of arterial walls, stretch on heartbeat, recoil on relaxation, creating constant bloodflow at Q2. |
|
|
if distensibility is reduced, systolic BP is (increased/decreased)
|
increased
|
|
|
If stroke volume is increased, systolic BP is (increased/decreased)
|
increased
|
|
|
if volume is increased at a certain capacity, Pressure is (increased/decreased)
|
increased
|
|
|
Volume of fluid/capacity of system is ....
|
pressure
|
|
|
what two things might influence systolic BP
|
Stroke volume and distensibility
|
|
|
if distensibility is decreased, Arterial blood pressure (increases/decreases)
|
increases
|
|
|
What changes diastolic BP?(3 things mentioned in class)
|
-arterial outflow (blood leaving arteries)
-Heart rate - systolic BP |
|
|
increasing outflow (increases/decreases) pressure
|
decreases
|
|
|
what controls blood leaving arterial tree?
|
TPR
|
|
|
Most of resistance to blood flow leaving arterial tree is through
|
arterioles
|
|
|
Increasing TPR (increases/decreases) outflow leaving arterial tree which (increases/decreases) DBP
|
decreases outflow and increases DBP
|
|
|
decreasing TPR (increases/decreases) outflow leaving arterial tree which (increases/decreases) DBP
|
increases outflow and decreases DBP
|
|
|
Increasing HR, (Increases/decreases) DBP = (increases/decreased) outflow.
|
increased DBP, decreased outflow
|
|
|
Increasing SV = (increasing/decreasing) SBP = (increasing/decreasing) DBP
|
increasing SBP + DBP
|
|
|
dilation (increases/decreases) TPR
|
decreases(reduced by r^4)
|
|
|
constriction (increases/decreases) TPR
|
increases
|
|
|
Why does increasing Heart rate increase Diastolic pressure?
|
less time for outflow before next beat making blood pump faster
|
|
|
What are ejection rates?
|
blood pumped into aorta
|
|
|
Partial state of contraction (kidney, skin, abdominals) is _______(1), is cause by ____(2) stimulation..
|
(1)vasomotor tone
(2)sympathetic |
|
|
If there was no sympathetic stimulation, how would that effect Vasomotor tone, TPR, and MABP?
|
decrease them all
|
|
|
medullar neurons stimulate _____(1) nerves, this causes _______(2)
|
(1)sympathetic
(2)vasomotor tone |
|
|
A vasomotor center is...
|
a collection of medullar neurons
|
|
|
Cardiac _____ center in medullary nerve can increase HR
|
acceleratory
|
|
|
Cardiac _____ center in medullary nerve can decrease HR
|
inhibitory
|
|
|
connective tissue around lung is called....
|
visceral pleura
|
|
|
_____ BP is affected by ejection rate
|
systolic
|
|
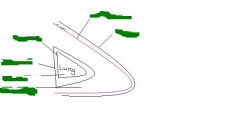
label all green parts
|
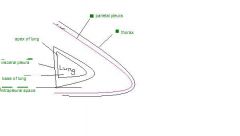
labeled
|
|
|
give pathway from nasal to trachea
|
nasal -> nasal sinuses -> pharynx ->trachea
|
|
|
what are three ways upper airways condition Oxygen
|
warming, filtering, humidifying
|
|
|
cartilage containing part of lungs are...
|
bronchi
|
|
|
these are smaller than bronchi, no cartilage, and higher density of Smooth muscle relative to bronchi and trachea
|
bronchioles
|
|
|
They're 300 million of these and they are 1/3mm in diameter
|
alveolus make up airsac.
|
|
|
when the entire airway is made up of alveoli, this would be called the...
|
alveolar sac
|
|
|
conducting zone is...
|
region of lungs w/out alveoli
|
|
|
respiratory zone is...
|
region of lungs with alveoli
|
|
|
_____ have alveolus in wall
|
respiratory bronchioles
|
|
|
_____ have more alveolus than bronchioles but less that sac.
|
alveolar duct
|
|
|
T/F. air is 100% saturated w/ H20 vapor before it reaches trachea
|
True
|
|
|
The right lung has _#__(1) lobes, while the left lung has __#_(2) lobes.
|
(1) 3 lobes
(2) 2 lobes |

