![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
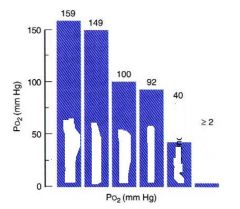
LABEL: Mixed venous blood, arterial blood, mitochondria, alveolar gas, room air, tracheal gas
|
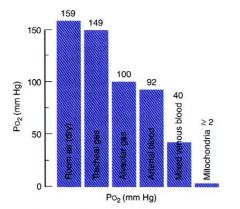
here it is
|
|
|
at the end of maximal inspiration, alveolar pressure is (<,>,=) to atmospheric pressure
|
at the end of MAXIMAL inspiration, alveolar pressure is = to atmospheric pressure
|
|
|
at the end of normal inspiration, alveolar pressure is (<,>,=) to atmospheric pressure.
|
at the end of normal inspiration, alveolar pressure is = to atmospheric pressure.
|
|
|
What is apnea?
|
cessation of breathing
|
|
|
What kind of respiration would cause abdominal walls to contract?
|
during maximal expiration, abdominal walls contract
|
|
|
Compliance of the lung is measured under a (dynamic/static) condition.
|
Static condition. This is when flow equals zero.
|
|
|
What is the equation for resistance in airway?
|
change in pressure/Flow
|
|
|
HARD:
When flow = zero; (P in mouth-P in airway)/Tracheal Air flow. what does this measure and under what conditions? |
measure compliance of lung under static conditions.
|
|
|
What happens to lung volume as airway resistance increases
|
Lung volume decreases
|
|
|
Where do parasympathetic and sympathetic divisions innervate in airway and what kind of muscle is innervated?
|
innervate smooth muscle withing walls of airway
|
|
|
What does vagus do to bronchi, what does that do to airway resistance? What neurotransmitter is released by vagus?
|
vagus causes bronchoconstriction which increases airway resistance. Acetylcholine (ACh)released.
|
|
|
what division of ANS causes bronchodilation? what neuroxmitter is released? and what type of receptors receive this bronchodilating neuroxmitter?
|
Sympathetic division causes bronchodilation by releasing the neuroxmitter Norepinephrine on smooth muscle.
|
|
|
describe neuronal activity if lungs were introduced to an irritant such as smoke, dust, or pollen.
|
sensory nerve in the vagus will be stimulated, which stimulates motor neurons in the medulla, causing bronchoconstriction.
|
|
|
what does histamine do to bronchi?
|
histamine causes bronchoconstriction.
|
|
|
thromboxane is a prostaglandin that causes bronchi to...
|
constrict
|
|
|
what is functional residual capacity (FRC)?
|
volume of air left in lung after normal expiration (2L)
|
|
|
after maximal inhalation, what is the volume of air in lungs?
|
about six liters.
|
|
|
is there any volume in the lungs after maximal expiration? if so, how much.
|
Yes, about 1.2L.
|
|
|
minute volume or breathing volume=_____
|
minute volume or breathing volume=total ventilation
|
|
|
what part of respiratory system contains anatomical dead space?
|
conducting zone.
|
|
|
Respiratory rate(f) refers to...
|
how often we breathe
|
|
|
What is equation for expiratory volume?
|
Expiratory volume=respiratory rate x total ventilation.
|
|
|
If someone breathed 15 times in a minute at tidal volume, what is the total ventilation?
|
15breaths/min x 0.5L/breaths=7.54L/min
|
|
|
What is perfusion?
|
blood flow in the lung
|
|
|
Can physiological dead space be less than anatomical dead space?
|
no, physiological dead space equal to or greater than anatomical dead space, never less.
|
|
|
What is boyle's law?
|
P1V1=P2V2 (or V1/V2=P2/P1)
|
|
|
-If pressure of intrapleural space is is decreased, volume is (increased/decreased).
-Whose law does this follow? |
-pressure decreased, volume increased(Volume is inversely proportional to pressure). -Boyle's Law.
|
|
|
-If temperature is increased, volume is (increased/decreased).
-Whose law does this follow? |
-T increased, V increased
-Charle's Law |
|
|
What is Charle's law?
|
V1/V2=T1/T2
|
|
|
21% of atmosphere ambient air is...
|
oxygen; 21%
|
|
|
79% of atmosphere ambient air is...
|
Nitrogen, N2
|
|
|
What is barometric pressure at sea level? Is there an increase or decrease in pressure as altitiude increases?
|
760mmHg.
Altitude decreases barometric pressure. |
|
|
Does carbon dioxide or oxygen cross capillary-alveolar barrier more quickly? Why?
|
Carbon dioxide crosses about 20 times as fast as oxygen, this is because CO2 is more fluid soluble.
|
|
|
What is perfusion?
|
blood flow in the lung
|
|
|
Can physiological dead space less than anatomical dead space?
|
no, physiological dead space equal to or greater than anatomical dead space, never less.
|
|
|
What is boyle's law?
|
P1V1=P2V2 (or V1/V2=P2/P1)
|
|
|
-If pressure of intrapleural space is is decreased, volume is (increased/decreased).
-Whose law does this follow? |
-pressure decreased, volume increased(Volume is inversely proportional to pressure). -Boyle's Law.
|
|
|
-If temperature is increased, volume is (increased/decreased).
-Whose law does this follow? |
-T increased, V increased
-Charle's Law |
|
|
What is Charle's law?
|
V1/V2=T1/T2
|
|
|
21% of atmosphere ambient air is...
|
oxygen; 21%
|
|
|
79% of atmosphere ambient air is...
|
Nitrogen, N2
|
|
|
What is barometric pressure at sea level? Is there an increase or decrease in pressure as altitiude increases?
|
760mmHg.
Altitude decreases barometric pressure. |
|
|
Does carbon dioxide or oxygen cross capillary-alveolar barrier more quickly? Why?
|
Carbon dioxide crosses about 20 times as fast as oxygen, this is because Co2 is more fluid soluble.
|
|
|
Why is there a decrease in oxygen gas pressure when gas moves into trachea from ambient air?
|
some oxygen gas becomes water vapor.
|
|
|
What is the pressure of Carbon dioxide in:
-Atmosphere -Trachea -Alveola -Arterial -mixed venous blood |
-Atmosphere is 0mmHg
-Trachea is 0mmHg -Alveola is 40mmHg -Arterial is 40mmHg -Mixed venous blood is 46mmHg |
|
|
What is the Alveolar-arterial(A-a) gradient for Carbon dioxide?
|
40-40= 0mmHg
|
|
|
Perfusion is equivalent to ___ in lungs.
|
FLOW
|

