![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Put these events in order:
-SL valves close(2nd heart sound "dub") -T wave of EKG -ventricular systole begins -Ventricular diastole begins -P wave of EKG -QRS complex -AV valves close (1st heart sound "lub") -SL valves open -AV valves open -Atrial systole |
P wave of EKG -> atrial systole -> QRS complex (ventricular depolarization) -> ventricular systole begins -> AV valves close ("lub") ->SL valves open -> T wave of EKG -> ventricular diastole begins -> SL valves close("dub") -> AV valves open
|
|
HARD
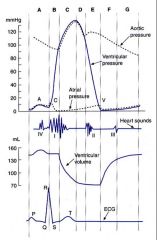
Label these events of left side of heart using letters above each section: -Ventricular systole -Isovolumetric contraction in left ventricle. -Rapid ejection phase (into aorta) -Reduced ejection phase -Isovolumetric relaxation phase -Rapid filling phase (AV valves open, SL valves closed) -Reduced ventricular filling phase -Atrial systole -Ventricular diastole -End of diastole -Ventricular systole -SL valves open -AV valves open |
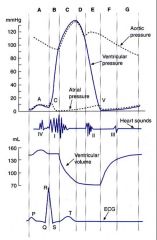
-Ventricular systole is B,C,D.
-Isovolumetric contraction in left ventricle is B. -Rapid ejection phase is C. -Reduced ejection phase is D -Isovolumetric relaxation phase is E. -Rapid filling phase is F -Reduced ventricular filling phase is G. -Atrial systole is A -Ventricular diastole is E,F,G,A -End of diastole is between A + B. -Ventricular systole is B,C,D SL valves open during C,D AV valves open in F,G,A |
|
|
What is the highest pressure during diastole of left ventricle?
|
80mmHg
|
|
|
What is pressure of the heart at the end of diastole?
|
0mmHg
|
|
|
What are the units for cardiac output?
|
L/Min
|
|
|
What is the equation for cardiac output? (two equations)
|
Heart Rate(beats/min) x Stroke Volume(L/beat)
or CO=(MABP-Rt atrial BP)/TPR |
|
|
what are units for heart rate?
|
beats/min
|
|
|
What are the units for stroke volume?
|
L/Beat
|
|
|
If heart rate is 70beats/min and Stroke volume is 75mL, what is cardiac output?
|
5.25L
|
|
|
If cardiac output is increased, Metabolic rate is _____(increased/decreased)
|
increased
|
|
|
During ventricular systole, the Pressure in the Right Atrium is _____(increased/decreased)
|
increased
|
|
|
While AV valves are closed, the _____ continues to fill
|
Atria
|
|
|
the amount of blood heart pumps/Unit time is ______
|
Cardiac output
|
|
|
The vagus is what division of ANS? what affect does the vagus have on HR?
|
parasympathetic. lowers heart rate
|
|
|
If cardiac output is decreased, _____(stroke volume/heart rate) is decreased.
|
Heart rate
|
|
|
If cardiac output increases, heart rate increases, what about the stroke volume?
|
stays the same
|
|
|
What is atropine and what effect does it have on heart rate.
|
Antagonist for muscarinic receptors(parasymp/vagus). Increases heart rate
|
|
|
Heart pumps all the blood it receives, blood that returns is called....
|
venous return
|
|
|
If venous return is increased, ______ is increased also.
|
Cardiac output
|
|
|
If Heart rate is unchanged but Stroke volume is increased, what happens to cardiac output?
|
increased
|
|
|
increase in venous return -> (increase/decrease) end diastolic volume -> (increase/decrease) stretch of ventricular muscle. ->(increase/decrease) myocardial contractility-> (increase/decrease) in stroke volume and Heart rate
|
increased venous return -> increased end diastolic volume -> increased stretch of ventricular muscle ->increased myocardial contractility -> increased stroke volume and heart rate
|
|

label: atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block, atrial premature contraction, atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular premature contractions, nodal premature contractions, normal,ventricular fibrillation
|

labeled
|
|

-what does the line with increased contractility mean(mention ANS and SV)?
-Which line in middle picture represents greater parasympathetic stimulation? |

-increased contractility means more activity from sympathetic NS, and increased stroke volume.
-the lowest line, decreased contractility. |
|

-at what letters are SL valves open and blood ejected from ventricle?
-When are AV valves opened? -When does rapid injection phase start? -When does rapid ejection slow down? -Where is isololumentric contraction and relaxation? -where is there a slight increase in ventricular volume becuase atrial contracts? |

-SL valves open and blood ejected from ventricle during C+D. (aortic)
-AV valves open during F,G,A.(mitral). -rapid injection starts at beginning of C. -rapid ejection slows during D. -Isovolumetric contraction is at B while relaxation is at E. -slight volume increase at A |

