![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
For ______ muscle, phase 4 is flat before rapid depolarization caused by stimulation from another section of the heart.
|
Ventricular
|
|
|
Phase 4 in the ____ node has a positive slope.
|
SA
|
|
|
Does ventricular muscle depolarize spontaneously?
|
No
|
|
|
all the events that include one heart beat is known as
|
The Cardiac cycle
|
|
|
What is the vagus?
|
Parasympathetic nerve that innervates the Heart.
|
|
|
What does the vagus do to heart rate?
|
Lowers HR, part of parasympathetic system.
|
|
|
Give two examples of natural CATECHOLAMINES and explain their effect on the heart.
|
Epinephrine and norepinephrine, increases stage 4, thus increase HR.
|
|
|
A drug w/ positive chronotropic activity (increases/decreases) Heart rate. Give two examples
|
Increases. Norepinephrine, epinephrine.
|
|
|
A drug w/ negative chronotropic activity (increases/decreases) Heart rate. Give two examples
|
decreases. ACh and vagus.
|
|
|
What is the function of an Electrocardiogram (EKG)?
|
used for recording electrical activity of the heart, measured w/ recording electrodes @ surface of the body
|
|
|
An EKG can give a lot of electrical activity information about the heart. seven things an EKG can measure was mentioned in class...
|
1. origin & conduction of the cardiac impulse.
2. Site of pacemaker. 3. Rate of pacemaker. 4. COnduction pathway. 5. Abnormal arrythmias. 6. Anatomical orientation of the heart. 7. relative size of RV in relation to LV. |
|
|
Which wall is thicker? LV or RV wall.
|
Left ventricle
|
|
|
Can RV hypertrophy alter appearance of EKG?
|
yes
|
|
|
Does EKG provide mechanical activity of heart? (i.e. amount of blood being pumped from heart)
|
NO
|
|
|
What is the difference between interval and segment on EKG?
|
Intervals are time and segments are voltage.
|
|
|
Location of electrodes for a Lead I EKG?
|
right shoulder & left shoulder.
|
|
|
Location of electrodes for a Lead II EKG?
|
right shoulder & left foot.
|
|
|
Location of electrodes for a Lead III EKG?
|
Left shoulder & left foot
|
|
|
______ is a type of arrythmia that elevates HR.
|
tachycardia
|
|
|
What is Tachycardia?
|
Arrythmia that elevates HR.
|
|
|
_____ is a type of arrythmia that has a lower than normal Heart Rate.
|
Bradycardia
|
|
|
What is bradycardia?
|
Arrythmia with lower than normal HR.
|
|
|
What causes a premature contraction in atria?
|
If contraction occurs outside SA node and depolarizes the atria early.
|
|
|
What causes premature contraction in ventricles?
|
if contraction occurs outside the SA node and depolarizes ventricles Early. plus no P wave would precede QRS.
|
|
|
When coronary blood flow is inadequate to meet requirements of heart, this is called..
|
myocardial ISCHEMIA
|
|
|
Why is there a delay at the AV node before contraction?
|
SO atria is allowed to contract prior to ventricular contraction
|
|
|
What is the cause of a lengthened delay between SA and AV node?
|
Conduction block @ AV node. 1st degree heart block.
|
|
|
What is first-degree Heart block?
|
Increased PR interval, and if every P wave is followed by a QRS complex, abnormally slow conduction thru AV node is suspected.
|
|
|
What is second-degree Heart block?
|
not all P waves are followed by QRS complexes. conduction thru AV node intermittently fail.
|
|
|
What is third-degree heart block?
|
no relationship between P wave and QRS complex, occur independently.
|
|
|
how would someone deal with uncoordinated or bizarre electrical activities of ventricles?
|
Electrical shock of entire heart coordinates refractory period to reverse fibrillation, inducing normal HR.
|
|
|
is it possible to live if filling of ventricle occurs independently of atricular activity?
|
Yes
|
|
|
How would someone born with complete heart block compensate for low heart rate?
|
increase stroke volume.
|
|
|
When would the tricuspid valve be open in respect to gradient pressure?
|
When Pressure in RA is greater than Pressure In RV.
|
|
|
When would the tricuspid valve be closed in respect to gradient pressure?
|
When Pressure in RV is greater than Pressure In RA.
|
|
|
Name atrioventricular valves and give location.
|
-Tricuspid is between RA and RV. -Bicuspid or mitral valve is between LA and LV.
|
|
|
Where is mitral valve located?
|
Between LA and LV, bicuspid.
|
|
|
what is systole?
|
contraction of heart.
|
|
|
what is diastole?
|
relaxation of heart.
|
|
|
When would blood volume be fixed?
|
When both valves are closed.
|
|
|
what is isovolumetric contraction and when would it occur?
|
beginning of systole, volume fixed but heart contracting.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of an antagonist of Vitamin K like Coumadin?
|
Vitamin K is necessary for clotting factors so coumadin is an anticoagulant.
|
|
|
Name the two semilunar valves and give location.
|
-aortic valve-between Aorta and LV.
-pulmonary valve-between RV and pulmonary artery. |
|
|
Ventricular _____ is isovolumetric contraction. Where is this on EKG? which Heart sound is it?
|
Ventricular systole, QRS complex, Sound 1 or "lub". Both aortic and mitral valve closed.
|
|
|
Ventricular _____ is isovolumetric relaxation. which Heart sound is it?
|
diastole, sound 2 or "dub"
|
|
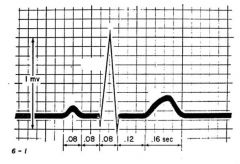
Label P, QRS, and T wave. Also Give information on the events occuring at each interval and segment:
-QRS complex -P wave -T wave -PR interval(location and duration) -ST interval(location on graph and duration) -ST segment(location on graph and voltage) - |
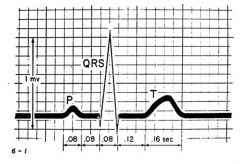
-QRS complex=ventricular depolarization.
-P wave=atrial depolarization -T wave=Ventricular repolarization -PR interval=start of P wave to beginning of QRS complex;0.16seconds on normal EKG. -ST interval=end of QRS to beginning of T wave;0.12 secongs. ST segment=end of QRS to beginning of T wave; baseline. |
|
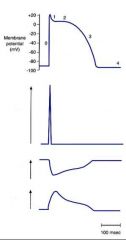
label Permeabilities of Na, Ca, and K
|
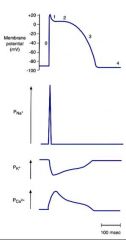
Permeabilities
|
|

label colored lines as intervals
|
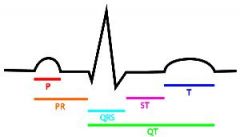
labeled
|
|
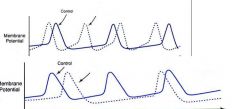
This is a graph of rate of pacemaker.
label the dotted lines, one is effected by ACh while the other is influenced by catecholamines, also which autonomic division is responsible for catecholamines and ACh. |
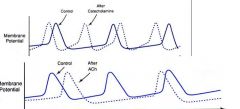
-Top is catecholamines. Sympathetic
-Bottom is ACh. parasympathetic |
|
|
Which area has shorter action potentials, subepicardium or subendocardium?
|
Subepicardium.
|
|
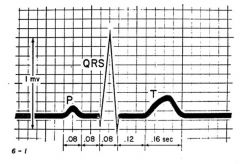
at what point is there.
A. Atrial beating? B. When all ventricles are depolarized? C. The first deflection? |
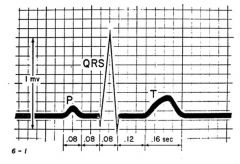
A. P wave
B. ST interval C. R wave |
|
|
Where are purkinje fibers located?
|
in the endocardium
|
|
|
Depolarization begins at the _____(1) and spreads to the _______(2).
|
1. endocardium.
2. epicardium. |
|
|
Repolarization starts at the _____(1), back towards the _____(2).
|
1. epicardium
2. endocardium |

