![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
isomer
|
Isomers are different compounds with the same molecular formula
|
|
|
Stereoisomer
|
isomers that differ only in the way the atoms are oriented in space. They have the same functional group and the same IUPAC name except for prefi xes such as cis, trans, R, and S.
• Enantiomers—stereoisomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other (5.4). • Diastereomers—stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other (5.7). |
|
|
chiral
|
not superimposable
upon its mirror image. |
|
|
enantiomers
|
Enantiomers are mirror images that are not superimposable
|
|
|
R and S configuration of stereogenic centers
|
R=clockwise
S=Counter... |
|
|
Diastereomers
|
stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other
|
|
|
Constitutional isomers
|
isomers that differ in the way the atoms are connected to each other. aka structural isomer
• different IUPAC names • the same or different functional groups • different physical and chemical properties |
|
|
Max stereoisomers
|
For n stereogenic centers, the maximum number of stereoisomers is 2n
|
|
|
Structural Isomer
|
Two compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the way the atoms are connected to each other. Structural isomers are also called constitutional isomers.
|
|
|
Alkene + HBr/ROOR, hv --> ________
|

Halogenates less substituted C
|
|
|
Alkene + NBS/(hv or ROOR) --> _____
|

The allyl radical is more stable than other radicals because two resonance structures can be
drawn for it |
|
|
Radical vs Ionic Bromination
|
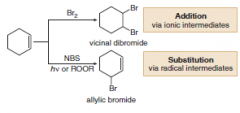
• Treatment of cyclohexene with Br2 (in an organic solvent like CCl4) leads to addition via
ionic intermediates (Section 10.13). • Treatment of cyclohexene with NBS (+ hν or ROOR) leads to allylic substitution, via radical intermediates. |
|
|
Halide + KOC(CH3)3, DBU, and DBN
(Bulky, nonnucleophilic bases) |
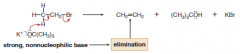
favor elimination over substitution
|
|
|
Alkyll Halide + t-butoxide --> _____
|
E2 Elimination rxn.
|
|
|
Secondary R-X + CH3O-/DMSO -->
|
SN2 Substitution
Inverts config. |
|
|
H2O and ROH
|
Polar protic solvents
(O – H or N – H) favored for E1 and SN1 |
|
|
DMSO, Acetone, DMF, THF, HMPA
|
Polar aprotic solvents
(no O – H or N – H) favored for E2 and SN2 |
|
|
Primary R-X + CH3O- -->
|
SN2 prod
|
|
|
Secondary R-X + CH3O-/CH3OH -->
|
E2 Prod
|
|
|
Tertiary R-X + CH30- -->
|
E2 Prod
|
|
|
Tertiary R-X + CH3OH/hv -->
|
SN1 Prod
|
|
|
Tertiary R-X + acetone/hv -->
|
E1 Prod
|
|
|
Nucleophiles for Sub
|
-CN, N3-, HS-
CH3O- (Strong base) CH3OH |
|
|
Most reactive halide?
|
Primary>secondary>tertiary
more room for Nu to attack. |
|
|
Strong Nucleophiles
|
neg charge, have weak conj acid, stronger going left and down the periodic table
Ex. OH-, I- in polar protic solvent |
|
|
The Zaitsev rule:
|
The major product in a elimination has the more substituted double
bond. |

