![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
HX addition
|
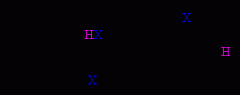
electrophilic addition
carbocation intermediates Markovnikov's rule apply carbocation rearrangements possible both anti and syn addition |
|
|
Radical addition of hydrogen bromide (HBr) to alkenes.
|
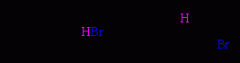
chain reaction
radical intermediates anti-Markovnikov's products both syn and anti addition |
|
|
Electrophilic addition of halogens (X2) to alkenes.
|
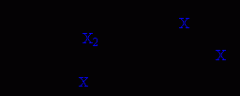
electrophilic addition
bromonium or chloronium ion intermediates anti addition |
|
|
Electrophilic addition of HX to conjugated dienes.
|
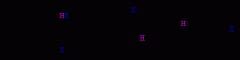
electrophilic addition leading to allyl (resonance stabilized) carbocations
the allyl cation can be attacked by the bromide anion at two positions the 1,2-adduct in this example (A) is kinetically favored (predominates at low temperatures) the 1,4-adduct in this example (B) is thermodynamically more stable and it predominates at higher temperatures |
|
|
Electrophilic addition of halogens to conjugated dienes.
|
electrophilic addition leading to allyl (resonance stabilized) carbocations
the allyl cation can be attacked by the bromide anion at two positions the 1,2-adduct is kinetically favored in this molecule (predominates at low temperatures) the 1,4-adduct is thermodynamically more stable and predominates at higher temperatures for this molecule |

