![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Tissue |
A group of similar cells that work together to carry out a particular function |
|
|
|
Organ |
A group of different tissues that work together to carry out a particular function |
|
|
|
Catalyst |
A substance which increases the speed of a reaction without being changed or used up in the reaction |
|
|
|
Enzymes |
Biological catalyst made from large proteins |
|
|
|
Lock and key |
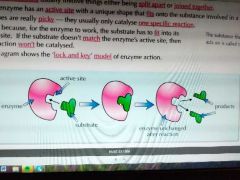
|
|
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Amylase breaks down starch, and it is found in the salivary glands, the pancreas and the small intestine |
|
|
|
Proteins |
Protease enzymes break down proteins to animo acids. They are found in the stomach (pepsin), the pancreas and the small intestine |
|
|
|
Lipids |
Lipase enzymes convert lipids to glycerol and fatty acids. They are found in the pancreas and the small intestine |
|
|
|
Bile |
It is produced in the liver. It's stored in the gall bladder before it is released into the small intestine. The HCl in the stomach makes the pH too acidic for enzymes in the small intestine to work properly. Bile is alkaline, it neutralises the acid and makes the conditions alkaline, which is best for enzymes in the small intestine. |
|
|
|
Enzymes used in the digestive system are produced by... |
Specialised cells in glands and in the gut lining |
|
|
|
The digestive system |
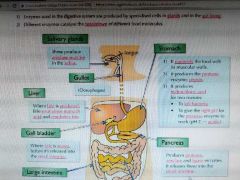
|
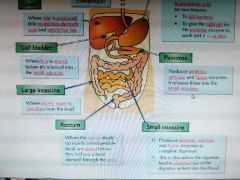
|
|
|
Lungs |
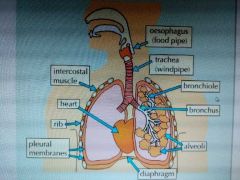
|
|
|
|
Alveoli |
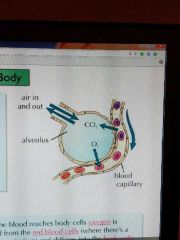
They are tiny air sacs that carry out gas exchange in the body. They are surrounded by a network of blood capillaries. The blood passing next to the alveoli has just returned to the lungs from the rest of the body, so it contains lots of CO2 and very little oxygen. Oxygen diffuses out of the alveolus into the blood. CO2 diffuses out of the blood into the alveolus to be breathed out. |
|
|

|
When the blood reaches body cells, oxygen is released from the red blood cells and diffuses into body cells. At the same time, CO2 diffuses out of the body cells into the blood. It is then carried back to the lungs. |
|
|
|
Circulatory system |
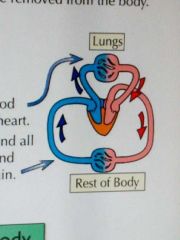
It carries food and waste products around the body. It is made up of the heart, blood vessels and blood. Humans have a double circulatory system. |
|
|
|
The heart |
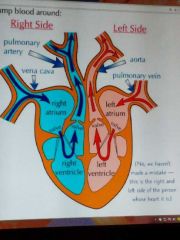
It keeps blood flowing around the body. The walls of the heart are made of muscle tissue. The heart needs it's own supply of oxygenated blood so coronary arteries branch of the aorta and the surround the heart. |
|
|
|
Arteries |
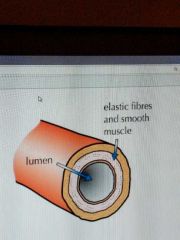
Carries blood under pressure. The heart pumps blood at high pressure so the artery walls are strong and elastic. They have thick layers of muscle to make them strong, and elastic fibres to allow them to stretch and spring back. |
|
|
|
Capillaries |

Arteries branch into capillaries. They are tiny. They carry the blood really close to every cell to exchange substances with them. They have permeable walls, so substances can diffuse in and out. They supply food and oxygen, and take away CO2. |
|
|
|
Veins |
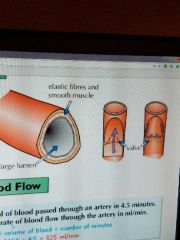
Capillaries eventually join up to form veins. The blood is at lower pressure so there are not thick. They have valves. |
|
|
|
Blood |
It is a tissue. RBC carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. They have a biconcave shape for a larger surface area for absorbing oxygen. They have no nucleus. They have a red pigment called haemoglobin. In the lungs, haemoglobin binds to oxygen to become oxyhaemoglobin. In body tissues, the reverse happens. It splits up into oxygen and haemoglobin, to release oxygen to the cells. |
|

