![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
monosaccharide |
the monomer of a carbohydrate |
|
|
C H O |
elements of a carbohydrate |
|
|
C6H12O6 |
basic formula of a carbohydrate |
|
|
Rings or Chains |
Structure of a carbohydrate |
|
|
Triglyceride |
Monomer of a lipid |
|
|
C H O |
Elements of a lipid |
|
|
Chains |
Structure of a lipid |
|
|
Maximum # of Hydrogen; Carbon atoms joined by single bonds |
Saturated Fats |
|
|
Does not have maximum # Hydrogen atoms: Carbon atoms joined by double bonds. |
Unsaturated Fats |
|
|
Amino Acid |
monomer of proteins |
|
|
C H O N (Nitrogen only found in proteins) |
Elements of a protein |
|
|
peptide bonds |
Bonds between the amino acids |
|
|
specialized proteins that act as catalysts (speed up chemical reactions) |
Enzymes: |
|
|
Amino Acid--> dipeptide--> polypeptide--> protein |
examples |
|
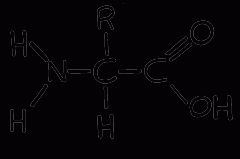
|
Basic formula for proteins |
|
|
messenger, transfer, and ribosomal |
three types of RNA |
|
|
single strand helix |
RNA |
|
|
two strands twisted into a double helix |
DNA |
|
|
adenine (base) + ribose + 3 phosphate |
Adenosine Triphosphate |
|
|
nucleotide |
monomer of a nucleic acid |
|
|
sugar, base, phosphate group |
nucleotides |
|
|
adenine, and guanine |
purine bases |
|
|
cytosine, thymine, and uracil |
Pyrimidine bases |
|
|
phosphoric acid + deoxyribose + base base= adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine |
formula for DNA |
|
|
phosphoric acid + ribose + base base= adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil |
formula for RNA |
|
|
single sub unit |
monomer |
|
|
large; repetition of monomers |
polymer |
|
|
same formula, nut different shape |
isomer |
|
|
2 Hydrogen to 1 oxygen |
Must be ____ _________ to _____ ________ in order to be a carbohydrate |
|
|
sugar, starch, cellulose, and glycogen |
examples of a carbohydrate |
|
|
short term energy |
function of a carbohydrate |
|
|
butter, animal fat, oil, wax, and soap |
examples of fats & lipids |
|
|
long term energy |
function of fats and lipids |
|
|
meat, nuts, peanut butter, beans, muscle, connected tissue, enzymes, hormones, and bones |
example of proteins (polypeptide) |
|
|
chemical reactions |
function of a protein |
|
|
chains |
structure of nucleic acids |
|
|
RNA DNA ATP |
examples of nucleic acids |
|
|
information |
function of nucleic acids |
|
|
not associated with life, small, and simple |
inorganic |
|
|
associated with life, large, carbon back bon, and chains or rings |
organic |
|
|
to cut with water, force water in to break a polymer |
hydrolysis |
|
|
dehydration synthesis |
polymerization |
|
|
insoluble in water |
lipids |
|
|
energy needed to start a chem. reaction |
activation energy |
|
|
lowers the activation energy |
how does a catalyst work |
|
|
active sites |
substrates must fit in what |
|
|
inhibiters |
ruin enzymes forever |

