![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Reduction of Enones to secondary alcohols |
NaBH4, CuI, MeOH
|
|
|
Reduction of ketones and aldehydes
|
NaBH4
|
|
|
Reduction of esters, acyl chlorides, ketones, aldehydes, tosylates, nitriles and amides
|
LiAlH4
|
|
|
Reduction of enones (only C=O)
|
Luche reduction - NaBH4, CeCl3
|
|
|
Reduction to aldehyde oxidation level
|
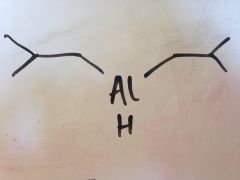
DIBALH - diisobutyl aluminium hydride
|
|
|
Oxidation of alcohols to ketones and carboxylic acids
|
CrO3, H2SO4, H2O - Jones reagent
|
|
|
Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde
|
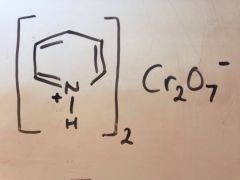
Pyridinium dichromate - NO water (PDC)
|
|
|
Carbonyl --> Immine
|
R-NH2
|
|
|
Immine --> Amine
|
NaCNBH3
|
|
|
Azide --> Amine
|
H2, Pd/CaCO3
|
|
|
Carbonyl --> Acetal
|
Diol and acid
|
|
|
Carbonyl --> Oxime
|
NH2OH
|
|
|
Carbonyl --> Dithiane
|
Thiol / Acid
|
|
|
Nitrile --> Amide
|
NaOH / H2O
|
|
|
Nitrile --> Carboxylic acid
|
H+ / H2O
|
|
|
Carboxylic acid --> Acyl chloride
|
SOCl2
|
|
|
Removal of acetal/dithiane protecting group
|
H2O / H+ (acetal) Hg 2+ / H2O (thiane)
|
|
|
Protection of alcohols
|
TBDMSCl - tertbutyldimethylsilyl + Imidazole
|
|
|
Deprotection of alcohols
|
Bu4NF (strong Si-F bond encourages removal of TBDMS)
|
|
|
Hard nucleophiles - 1,2-carbonyl addition
|
R-Li, R-MgBr, LiAlH4, NaBH4 / CeCl3
|
|
|
Soft nucleophiles - conjugate (1,4-addition)
|
R2-CuLi, RMgBr/CuI, RNH2, RONa, NaCH(CO2Et)
|
|
|
Why is conjugate attack useful?
|
Enolate intermediate can be captured by an electrophile
|
|
|
Baeyer Villiger Oxidation
|
Insertion of oxygen between carbonyl and most substituted carbon. MCPBA - metachlorobenzoic acid
|
|
|
Hydration of double bond - least substituted alcohol
|
i) BH3, THF ii) H2O2, NaOH
|
|
|
Hydration of double bond - most substituted alcohol
|
i) Hg(OAc)2 ii) NaBH4
|
|
|
Addition of HBr - least substituted bromoalkane
|
HBr, H2O2 - radical mechanism
|
|
|
Addition of HBr - most substituted bromoalkane
|
HBr - ionic mechanism
|
|
|
Opening of an epoxide
|
Acidic conditions - Least sub. alcohol
Basic conditions - Most sub. alcohol |
|
|
Kinetic vs. Thermodynamic enolates
|
Kinetic - Least sub. H removed
Thermo - Most sub H removed |
|
|
Diels - Alder
|
Diene and alkene
Heat |
|
|
Wittig Reaction
|
Ph3P=CH-R, Ketone or aldehyde
|
|
|
Preparation of a phosphonium ylide
|
Phosphonium salt and base e.g.
Ph3P+CH3 Br- and NaH |
|
|
Reactive ylides
|
R=alkyl, strong base needed, Z-alkenes
|
|
|
Moderate ylids
|
R= Ph or vinyl, moderate base, E/Z
|
|
|
Stabilised ylids
|
R= electron withdrawing, weak base, E alkenes, (WON'T REACT WITH KETONES).
|
|
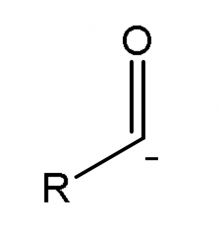
|
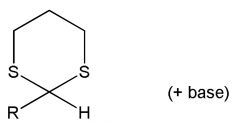
|
|
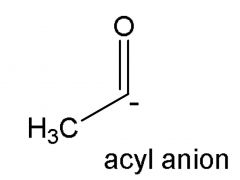
|
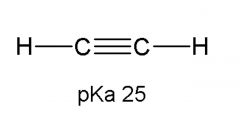
|
|
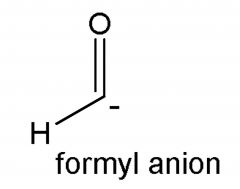
|
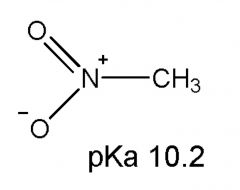
|
|
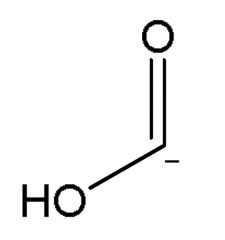
|
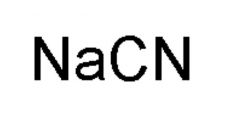
|
|
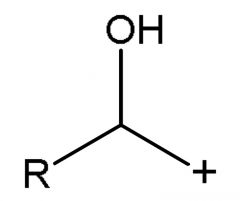
|
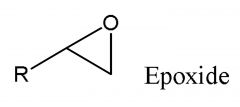
|
|
|
Reduction of alkyne (Z)
|
H2, Lindlar's catalyst (Pd/CaCO3)
|
|
|
Reduction of alkyne (E)
|
i) Na/NH3, ii) H2O
|
|
|
Baeyer-Villiger oxidation mechanism
|
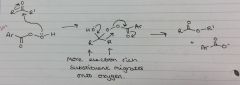
|

