![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nucleic acid |
They're polymers made of nucleic acids, which include DNA and RNA, which are made of monomers known as nucleotides. A nucleotide has 3 basic components: a sugar, phosphate, and a base. Main purpose though to remember is to build protein. |

|
|
|
DNA & RNA structures |
Sugar DNA- deoxyribose RNA- Ribose--> a type of pentose. sugar
BASES Dna. RNA--> thymine-uracil Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine
Structure
DNA -2 strands are twisted forming a double helix -the bases do occur in a definite order A-T C-G. Held together by hydrogen bond (......)-> found pg.41 RNA Single stranded |

|
|
|
What is a strand? |

A singlen strand has a back bone made of phosphate and then a sugar, with the base projecting to one side of the backbone. |
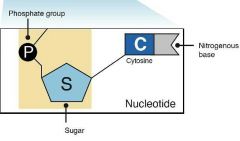
Nucleotide, use words such as backbone |
|
|
What are important functions of proteins? |
Helps to form structures (muscle, membrane, hair) and function as enzymes |
|
|
|
What are the protein monomer called? And why so what those function play to the role of the name? |
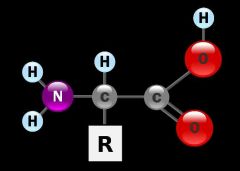
Amino acid. Made of a carboxyl group (acidic) which loses and H+ which makes it an ion molecule and acidic which is where acid comes from, and then there is the the amino group NH which is where amino derives from |
|
|
|
Purine |
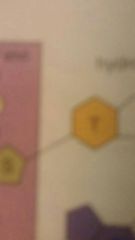
|
|
|
|
Pyrimidines |

|
|
|
|
Carbohydrate ? |
Made up of one carbon 2 hydrogen and an oxygen which is why its called carbo hydrate --> water |
|
|
|
What are monosaccharide and which 3 are hexose |
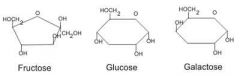
A simple sugar (carbohydrate) they have up to 3-7 carbon atoms, they are known as monosaccharide. The three hexoses are (glucose, fructose, and galactose) |
|
|
|
Dissacahrides |
2 monosaccahrides linked together by condensation synthesis, make sure to draw the branch of water properly so you can show the molecules losing water.
2 glucose= maltose Glucose+fructose= sucrose |
|
|
|
Starch and Glycogen. |
Starch = chain of glycose in a polysaccharides form which the chains straightly branch.
Glycogen= the storage form that stores glucose in the liver. Which has more side chains. |
|
|
|
What will enzymes always be? |
Proteins |
|
|
|
What are proteins? |
Polymers of amino acid (monomers) |
|
|
|
What are polymers of protein known as ? |
Peptide bond throgh condensation synthesis have a bunch of amino acids together. A polypeptide has many peptides bonded together. |
|
|
|
Difference between glyceride and glycogen |
Gly=sugar Glycogen is the actual storage form of glucose
Glycerol- alcohol \> sugar C h2 O. CH3 O Center is carbon and then a hydroxl group which is an alcohol |
|
|
|
What is the difference between hormones and enzymes? |
Enzymes= catalyst which speeds up biochemical reaction without undergoing any change
Hormone= a peptide(amino acid) not protein which refers to quantenary structure hormones are substances that act as messengers of information which regulates timing and speed that take place in the body. But not like catalyst taking part in the chemical process. It triggers a specifical chemical reaction |
|
|
|
What is an important fact of cholesterol? |
Made up of four fused carbon rings and a functional group attach to them which differentiates one from another. However, cholesterol is a precursor which is a biological process where other mature substances are formed such as sex hormones |
|
|
|
What is the difference between hydrogen bond and water molecule |
H20 is about polarity great solvent, Hydrogen bond is the connection between different water molecules due to electronegative forces and it is hard bond to break up thats why heat can form up good buffer system |
|
|
|
What is an isomer |

Same chemical formula but different 3d shape |
|
|
|
Starch glycogen and cellulose chain |

|
|
|
|
Why is it hard for the digestive system to break down fibers such as cellulose |
Due to the type of linkage its hard for fibers to pass through |
Also helps to prevent colon cancer cleans out impurities |
|
|
What are fats |

|
|
|
|
What are neutral fats? |

|
|
|
|
Why are lipids not polar |
They do not dissolve in water due to they lack polar groups remember properties of water so they dont break up cant dissolve so when they have low solubility in water like oil they go and sit on top of the surface of water |
|
|
|
How does condenstaion synthesis happen with lipids |
Due to functional groups at the end hydroxl group of glycerol will react with carboxyl group at end of fatty acid chain |
|
|
|
Why isn't a phospholipid a neutral fat? |
Due to the phosphate group which takes over the third fatty acid chain, this chains make the molecules electrically not neutral becuase the nitrogen group makes it ionize(ionic metal to non netal makes electric charge) making it hydrophillic |
|
|
|
Carbon hydrogen bond stearic and oleic acid and linoleic |

Stearic acid- saturated fat Oleic acid- unsaturated Linoleic acid- polyunsaturated fatty acid |
|
|
|
CIS Bond |
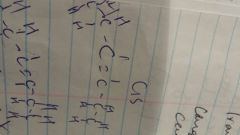
CIS bonds are present in naturally occuring unsaturated vegetable oil |
|
|
|
Trans fat |

|
|
|
|
What are globular proteins involved in |

|
|
|
|
Denaturation |
When proteins undergo a irreversible change happens due to the R groups are disturbed, which if it loses shape it's no able to perform it usual functions
Ex. Egg frying to white albumni, milm curdling |
|
|
|
What maintains a the tertirary structure? |
Is the various bondings between the R group which can be covalent, ionic and hydrogen bond One common bond is called cysteine |
|
|
|
Which bases are the double ringed groups? |
Purine |
|
|
|
Which nitrogenous base is single ring |
Pyrimidine thymine cystonine |
|
|
|
What is ATP like |
Energy currency, when one phosphate group is removed an amount of high energy is released |
|
|
|
What is facilitated transport associated with? |
Carrier protein allow polar or charged molecules through since the inside is hydrophobic to be hydrophillic since it combines with the molecule such as amino acid and glucose |
|
|
|
Active transport examples |
Active transport is a way to transport ions or molecules against their concentration gradient from low to high which requires energy. Which is why its called a pump or acts like one, which is when protein (carrier protein) is pushed against concentration gradient like pushing water against gravity. Ex. Withdrawing urine from kidney tubules Or such as the sodium potassium pump When sodium moves to the outside and potassium moves to the inside. ATP will influence a change in shape which drives the molecule across the membrane |
|
|
|
Which type of molecules are involved with vesicle formations? ( endocytosis, excocytosis) |
Macromolecules like polynucleotides, polysaccharides and such. |
|
|
|
Is endocytosis or exocytosis passive transport or active? |
It is active transport, vesicle formation requires energy |
|
|
|
Which are some examples where exocytosis is used? |
Some cells are specialized to produce and release particular molecules such as digestive enzymes, hormones such as growth produced by pancreatic cells. The vesicles only release when they are stimulated by a certain type of signal. Ex. Rise in blood sugar signals pancreatic cells to release hormones--> only fuses when its appropiate to the body needs |
|
|
|
What is the buffer system? |
It takes up excess acidic and basic ions to keep pH within normal limits. Because it contains weak acids |
|
|
|
What is the buffer formula for excess hydrogen |

Hydrogen + bicarbonate --> carbonic acid |
|
|
|
When there's excess hydroxide ions what is the formula for the buffer system? |

Hydroxide + carbonic acid -> neutralization reaction Bicarbonate and water |
|

