![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbohydrates |
-Made of C, H, O (1:2:1 ratio) -Monossacharides, Disaccharides, Polyssacharides
|
|
|
Why are Carbohydrates Important? |
-Main source of energy for most organisms -Provide structure to plants and animals |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
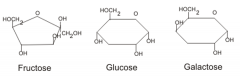
-Simple or single sugars (monomers) -Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
|
|
|
Glucose |
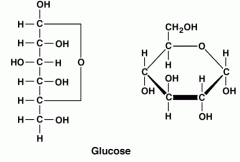
-C6H12O6 -The most common monosaccharide |
|
|
Fructose |
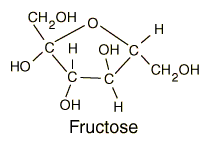
-C6H12O6 -Found in corn syrups and fruits
|
|
|
Galactose |
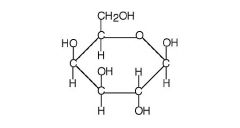
-Found in lactose |
|
|
Isomers |
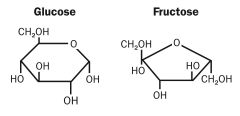
Molecules with the same molecular formula but have different molecular structures |
|
|
Disaccharides |
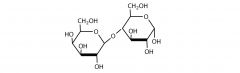
-Two linked monosaccharides -Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose |
|
|
Sucrose |
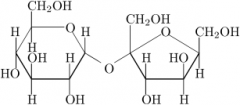
-Table sugar -Glucose + Fructose
|
|
|
Lactose |
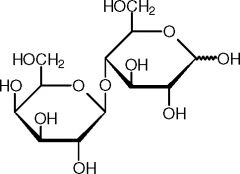
-Milk sugar -Glucose + Galactose |
|
|
Maltose |
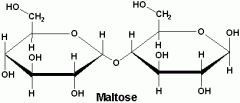
-Malt sugar -Glucose + Glucose |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
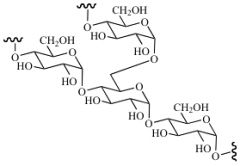
-Long chain of monosaccharides -Energy store and structural polysaccharides |
|
|
Energy Store Polysaccharides |
-Starch -Glycogen
|
|
|
Structural Polysacharides |
-Cellulose -Chitin |
|
|
Starch |
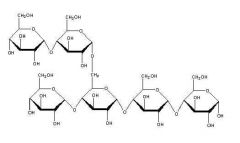
-Glucose storage in plants |
|
|
Glycogen |
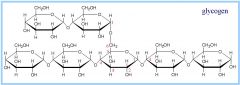
-Glucose storage in animals (found in liver and muscles)
|
|
|
Cellulose (insoluble fiber) |
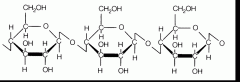
-Found in cell walls of plants -Indigestible for most animals |
|
|
Chitin |
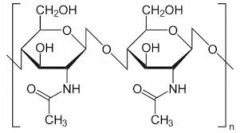
-Found in the outer coverings of insects, crabs and spiders |
|
|
Lipids |
-Made of C, H, O (not a 1:21 ratio) -All lipids are non polar, hydrophobic and water insoluble. -Oils and Fats -Steroids |
|
|
Why are lipids important? |
-Serve as structural components of biological membranes -Provide energy reserves, predominantly in the form of triglycerides -Both lipids and lipid derivatives serve as vitamins and hormones |
|
|
Oils and Fats |
-Triglycerides -Phospholipids |
|
|
Triglycerides |
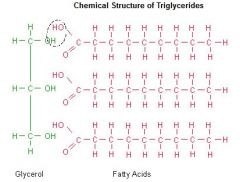
-Three fatty acids joined by one molecule of glycerol (carboxyl group attached to a hydrocarbon chain) -Used for long term energy storage, thermal insulation, and protection -Can be saturated or unsaturated |
|
|
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fats |
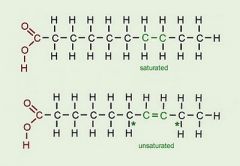
-Saturated fat = all single bonds between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail (straight). Animal fats; solid at room temp -Unsaturated fat = presence of a double bond between the carbons in the hydrocarbon tail (kink). Plant fats; liquid at room temp |
|
|
Phospholipids |
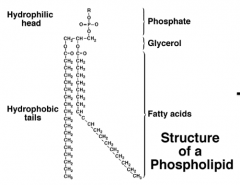
-Two fatty acids joined to one molecule of glycerol and a phosphate group -Form plasma membranes around all cells
|
|
|
Steroids |
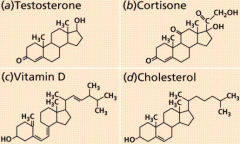
-Four fused carbon rings -Different structure and function from other lipids -Cholesterol, sex hormones (Estrogen, Testosterone) |
|
|
Proteins |
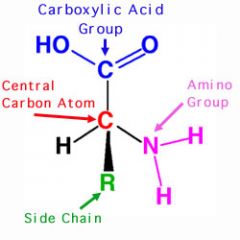
-Made of C, H, O, N -Monomers are amino acids (20 different amino acids)
|
|
|
Why are proteins important? |
-Catalyzing reactions (enzymes) -Structure [keratin (hair, horns), collagen] -Movement (muscles) -Cell-to-cell communication (cell signaling) -Defense (antibodies) |
|
|
Amino Acid Structure |
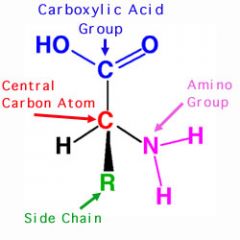
-All amino acids have similar structure -Amino group NH2 -Hydrogen H -Carboxyl group COOH -Side/Functional group R |
|
|
Polypeptides |
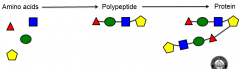
-Chain of amino acids bonded together -Dehydration synthesis is responsible for this -Many polypeptides bond and fold to make a protein -A protein's function is determined by its 3-D folded structure |
|
|
Enzymes |
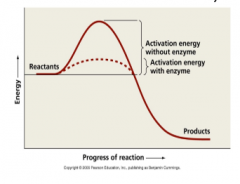
-Proteins that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy (increase rates of reaction) |
|
|
How do enzymes work? |
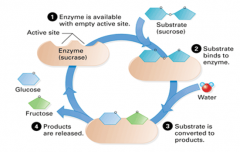
|
|
|
Denaturing |
1. Environmental conditions- temp, pH, etc.
2. Jello = Protein/Gelatin 3. Alls a rxn to occur which breaks down gelatin |
|
|
Organic |
-molecules containing a carbon skeleton that is covalently bonded to hydrogen |
|
|
Inorganic |
-Molecules that don't contain carbon |
|
|
Shapes of organic molecules |
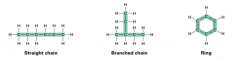
-Straight chain -Branched chain -Ring
|
|
|
Types of Macromolecules |
-Carbohydrates -Lipids -Proteins -Nucleic acids |
|
|
Monomers |
-The repeating subunits that compose a macromolecule |
|
|
Polymers |
-A large molecule consisting of many monomers bonded together. This is another term for macromolecules |
|
|
Dehydration Synthesis |
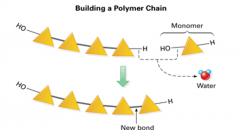
-How monomers bond to make a polymer |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
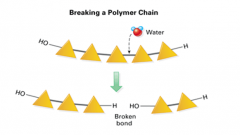
-How polymers break down into monomers |

