![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why use IR instead of NMR?
|
If you want to know which functional groups are present in a molecule, use IR. If you want to know how many H's are present and where they are in a molecule, use NMR.
|
|
|
1) The vibration must result in a _________ to show up in the IR spec
|
1) change in bond dipole moment
|
|
|
1) What is measured in IR spec?
2) Eqn for wavelength & frequency 3) What is transmittance look like on a IR spec? |
1) How much a bond stretches/compresses - Vibration
2) Speed = Frequency * Wavelength 3) Transmittance is on the y axis - it shows how much light was absorbed at each frequency |
|
|
IR spec - Where are they located:
1) Ketones 2) Amines 3) Alcohols 4) Aldehydes |
1) 1700-1750
2) 3100-3500 (sharp) 3) 3100-3500 (broad) 4) 2700-2900 (O)C-H |
|
|
IR spec - Where are they located:
1) Alkanes 2) Alkenes 3) Alkynes 4) Carbonyl |
1) 1200 (C-C)
2) 1645 (C=C) 3) 2200 (C≡C) 4) 1700 |
|
|
1) Anything around 3000cm-1 involves a ________
2) Anything around 2000 cm-1 and below does not involve ____________ 3) What is bond order? 4) The higher the bond order, the faster it __(a)__, and so the ((b) lower or higher) the wavenumber. |
1) hydrogen atom, be it O-H, N-H, or C-H
2) hydrogen, be it C=O, C=C, C-C, or C-O 3) Number of bonds b/t a pair of atoms 4) (a) vibrates (b) higher |
|
|
1) Broad IR peaks are due to _____.
2) Below 1300 in IR is called the _________. 3) Primary and Complementary colors? |
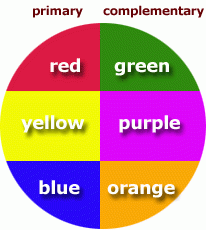
1) H bonding
2) Fingerprint Region |
|
|
1) Describe an indicator
H-indicator <--> H+ + Indicator- 2) At low pH, ________ and it's color will predominate 3) At high pH, ________ and it's color will predominate |
1) Molecules that can change structure and varying pH's causing more/less absorption
2) H-indicator 3) Indicator- |
|
|
1) What are the colors of the universal indicator? Mention the acidity level of each
2) |
1) (ROY-G-BIV) R:very acidic, O:acidic, Y:weakly acidic, G:neutral, B:basic, V:very basic
|

