![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Organic chemistry |
The branch of chemistry which deals with carbon compounds, including those with no relationship to life |
|
|
Covalent bond |
Inter - atomic relationship created by the sharing of at least one pair of electrons |
|
|
Saturated hydrocarbons |
Contains only only carbon-to-carbon single bonds. The most chemically inert of all organic chemistry |
|
|
Unsaturated hydrocarbons |
Contains carbon-to-carbon double or triple bonds |
|
|
Atomic structure of Carbon |
Atomic number =6, Protons =6, Electrons= 6, atomic weight =12.0. Electrons in first energy level=2; second energy level = 4 |
|
|
Carbon |
An element that has the capacity to share four electrons in order to achieve a more stable configuration |
|
|
Bonding: Carbon to Hydrogen or halogens |
Shares one electron |
|
|
Bonding: carbons to oxygen or sulfur |
Shares up to two electrons |
|
|
Bonding: carbon to Nitrogen |
Shares up to three electrons |
|
|
Halogens |
Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), and Iodine (I) |
|
|
Hydrocarbon molecules |
Contains only carbon and hydrogen. Can be divided into aliphatic and aromatic classes |
|
|
Substituted hydrocarbon |
One of more hydrogen atoms are replaced by another atom or group of atoms called a Functional Group |
|
|
Aliphatic Hydrocarbon |
A saturated hydrocarbon that contains only hydrogen (the max number) and carbon. Does not contain benzene ring |
|
|
Aromatic hydrocarbon |
Contains at least one benzene ring or similar structural features |
|
|
Benzene |
Consists of a ring of 6 carbon atoms with altering single and double carbon-carbon bonds |
|
|
Alkanes |
(CnH2n+2) |
|
|
Cycloalkanes |
(CnH2n) |
|
|
Classification: primary |
(1degree) Carbons that are covalently bonded to one other carbon. They are at the end of a carbon chain and referred to as terminal carbons |
|
|
Classification: secondary |
(2 degree) Carbons that are covalently bonded to two other carbons |
|
|
Classification: tertiary |
(3 degree) carbons that are covalently bonded to three other carbons |
|
|
Condensed formula |
Shows all the atoms in a molecule and places them in a sequential order |
|
|
Molecular formula |
States the actual number of each kind of atom found in a molecule |
|
|
Structural isomerism |
Compounds that have identical molecular formulas but different structures |
|
|
Cis-trans isomerism |
The formation of cis-trans isomers is a consequence of the absence of free rotation. Geometric isomers that only differ from each other in the 3- dimensional arrangement of the substituents in space. They have identical bonding and substituents |
|
|
Cis-trans isomerism |
The formation of cis-trans isomers is a consequence of the absence of free rotation. Geometric isomers that only differ from each other in the 3- dimensional arrangement of the substituents in space. They have identical bonding and substituents |
|
|
Alkane |
Saturated hydrocarbons (containing only carbon to carbon single bonds ); derivative of methane. Noted by the suffix “-ane” and sometimes by the prefix “-cyclo” |
|
|
Alkene |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon to carbon double bond. Noted by the suffix ene |
|
|
Alkyne |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one carbon to carbon triple bond. Noted by the suffix -yne |
|
|
The organization that formulated nomenclature rules to name hydrocarbons |
International union of pure and applied chemistry |
|
|
Hydrocarbon combustion |
The reaction of alkanes, alkenes, or alcohols with excess oxygen yields carbon dioxide, water and heat |
|
|
Hydration |
A reaction involving the addition of water H2O |
|
|
Dehydration |
Removal of water H2O |
|
|
Halogenation |
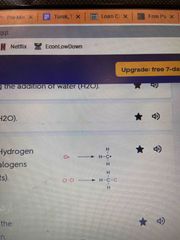
The substitution of Hydrogen with one or more Halogens (group VIIA elements) |
|
|
Hydrogenation |
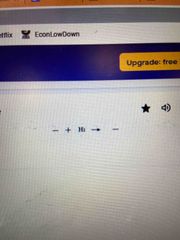
A reaction involving the addition of Hydrogen |

