![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
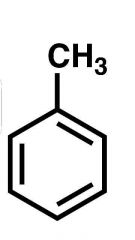
Name |
Toluene |
|
|
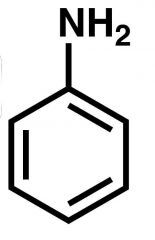
|
Aniline |
|
|
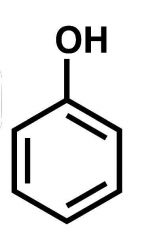
|
Phenol |
|
|
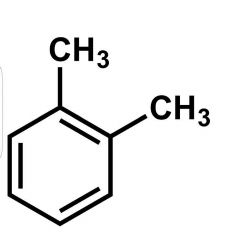
|
Xylene |
|
|

|
Stryene |
|
|
|
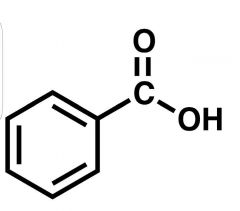
Benzoic Acid |
|
|

|
Benzaldehyde |
|
|
|
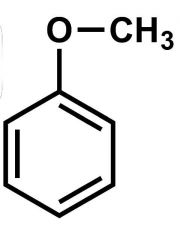
Anisole |
|
|
|
Benzene sulfonation reagents |
SO3/ H2SO4 |
|
|
|
Benzene nitration reagents |
HNO3/ H2SO4 |
|
|
|
Benzene halogenation reagents |
X2/ FeX3 |
|
|
|
Benzene Birch Reduction reagents |
Na, NH3/ MeOH |
|
|
|
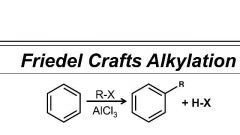
Benzene Friedel-Crafts Alkylation reagents |
R-X/ AlX3 |
|
|
|
Benzene Friedel-Crafts Acylation |
RCOX/ AlX3 |
|
|
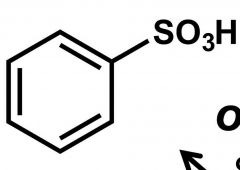
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Sulfonation |
|
|
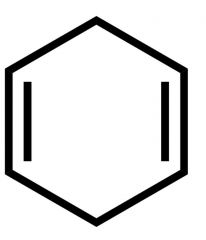
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Birch Reduction |
|
|
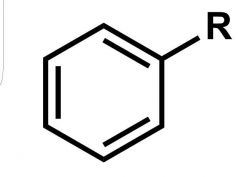
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Friedel Crafts Alkylation |
|
|
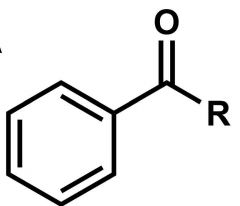
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Friedel Crafts Acylation |
|
|
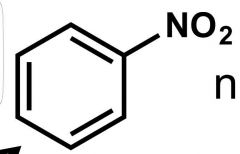
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Nitration |
|
|
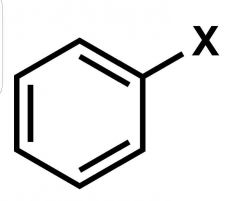
What is this rxn from benzene called? |
Halogenation |
|
|
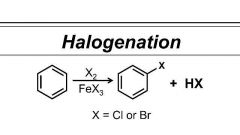
Perform this rxn with both Br and Cl |
Cl uses AlCl3 |
|
|
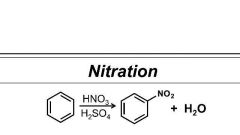
Perform this rxn |
Nitronium ion powerful electrophile |
|
|
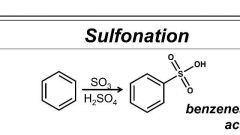
Perform this rxn |
Fuming sulfuric acid made Try the reversible w/ dilute H2SO4 |
|
|
Complete this rxn |
Intermediate carbocation rearrangments |
|
|
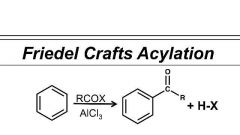
Complete this rxn |
No rearrangments |
|
|
|
What reagents are in the Clemmenson reduction? |
Zn(Hg)/ HCl |
Strong acidic rxn conditions |
|
|
What reagents are in the Wolf Kishner reduction? |
NH2NH2/ NaOH |
Strongly basic |
|
|
What reagents are in nitro group reduction? |
Sn, HCl/ NaOH |
|
|
|
What reagents are in side chain rxns? |
chromic acid ; KMnO4, KOH/ heat |
Alkyl group must have at least one H atom |
|
|
Electron donation in resonance aromatic rings.. |
Activates ring towards reaction |
|
|
|
Electron withdrawing in resonance aromatic rings.. |
Deactivates ring towards reaction |
|
|
|
What do lone pairs directly connected to a resonance ring do? |
Contribute electron density by resonance. |
|
|
|
Pi bonds and highly electronegative atoms are activating or deactivating by resonance? |
Deactivating. Rxn rate decreased. |
|
|
|
Are Halogens activating or deactivating? |
Deactivating. F, Cl, Br, I. Electronegative. Induction. |
|
|
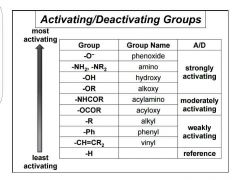
Name some characteristics |
Mostly single bonded (except halogens and CH=CR). Donate e- density. Ortho/para. |
|
|

Name some characteristics |
Pi bond and highly electronegative atoms deactivate by resonance. Halogens. Inductive effect dominates. |
|
|
|
Why are alkyl groups ortho/ para? |
They are electron donating by induction. Cause 2nd substituent to add onto ortho/ para due to resonance. |
|
|
|
Is ortho or para better with steric hindrance? |
Para, it's farther away from substituents. |
|
|
|
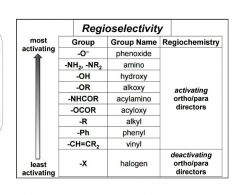
Regioselectivity of groups |
|
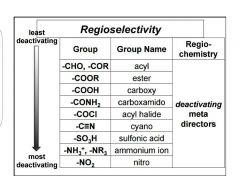
|
|
|
Lewis theory vs Bronsted-Lowry theory |
Lewis- Acid: electron donor Base: electron acceptor Bronsted- Acid: proton donor Base: proton acceptor |
|
|
|
What is the acidity of: Fuming sulfuric acid, hydronium, cyanide, benzoic acid, water, ammonium |
-9, -1.7, 9.1, 10.2, 15.7, 36 |
|
|
|
Conjugate acid/base of a strong acid/base is a ___ acid/base. |
Weak. And vice versa. |
|
|
|
Aromatic systems on acidity: Induction |
Available H to lose as H+. Electron withdrawing groups. |
|
|
|
Aromatic systems on acidity: Resonance. |
Bond strength and length. Resonance delocalization. |
|
|

Frost Circle |
Where n# a whole number and its set equal to 2x number of bonds. |
|
|
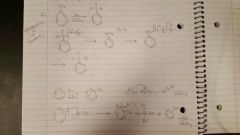
Halogenation of Benzene |
Br2/ FeBr3 or Cl2/ AlCl3 |
|
|
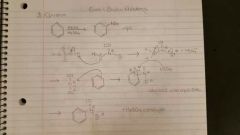
Nitration |
HNO3/ H2SO4. Involves protonation by HSO4-. |
|
|
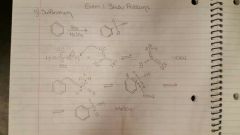
Sulfonation. |
SO3/ H2SO4. Involves protonation by HSO4- |
|
|
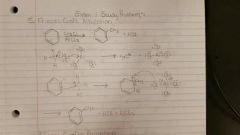
Friedel Craft Alkylation |
CH3CL / AlCl3 or RX / AlX3 1) bond reagents 2) bond electrophile to starting molecule 3) protonate with left over nucleophile
Prone to carbonation arrangement. 3° most stable. |
|
|
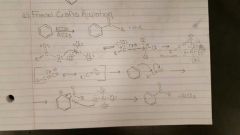
Friedel Craft Acylation |
RCOX / AlCl3. 1) bond reagents 2) resonance? 3) break nucleophile and electrophile 4) bond electrophile to starting molecule 5) protonate with nucleophile |
|
|
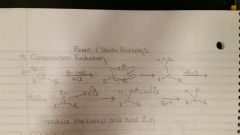
Clemmensen Reduction |
Zn (Hg)/ HCl. More acidic. Reduces R- C=O into R-CH2. |
|
|

Wolf Kishner Reduction |
NH2NH2/ KOH. More basic. 1) bond reagents 2) kick off all O (making H2Os) 3) kick off nucleophile 4) bond nucleophile with H2O to make product + -OH
|
|
|
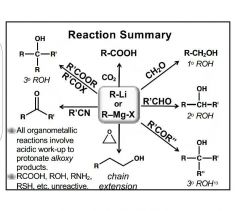
Grignard Reagents |
R-Mg-X : weak, more Nu:, pKa: 22- 32 R-Li : strong, less Nu:, pKa: 30- 50 |
|
|
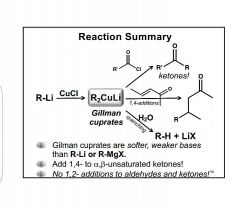
Gillman cuprates |
Also includes R2Cu(CN)Li2 |
|
|
|
Tautomerization |
Enol/enolate form? Add pic of example. |
|
|
|
Acidity of Carbonyl groups |
Elctron withdrawing & resonance stabilization: decrease pKa Electron donating: increase pKa |
|
|
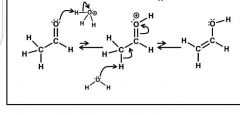
Enolate formation: Acid |
1) protonate oxygen 2) remove alpha H - equilibrium favors keto form |
|
|
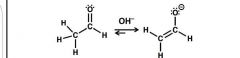
Enolate formation: base |
1) remove alpha H - enolate stabilized by resonance |
|
|
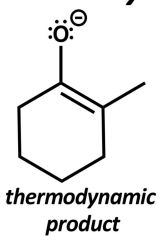
|
Equilibration allowed, more stable product predominates. Bases: NaOH/ H2O NaOEt/ EtOH Higher temp. |
|
|
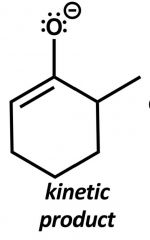
|
More acidic H removed first. Bases: LDA, LCHIA Avoid equilibrium. Low temp. |
|
|
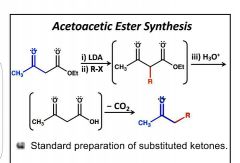
Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis |
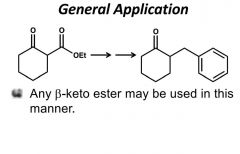
OH replaces OEt -CO2 takes away carboxy and OH |
|
|
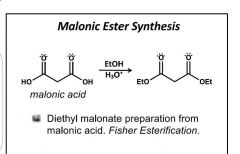
|
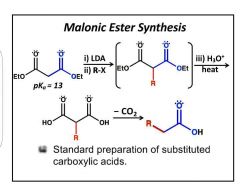
Starts from 2x -OH instead of -CH3 and OEt (acetoacetic). |
|
|
|
Write complete Aldo rxn |
OH-, H3O+ |
|
|
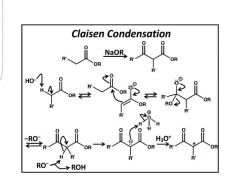
|
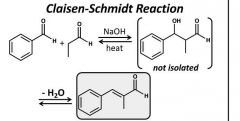
Loss of H2O drives rxn Aromatic aldehydes dehydrate to form alpha and beta unsaturated aldehydes. |
|
|
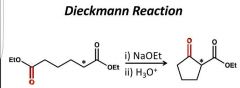
|
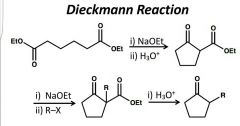
5-6 membered rings High yield alkylation rxns Alpha substituted cycloalkanones |
|
|
|
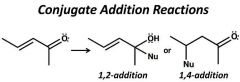
1,2- kinetic, C=O electrophilic 1-4- thermodynamic, C=O more stable R2CuLi removes double bond |
|
|
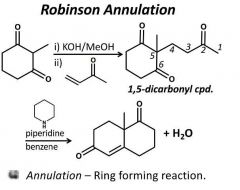
|
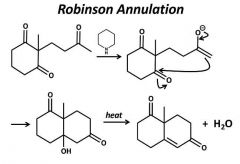
Make sure to count the carbons. |
|
|
|
Imine synthesis |
Write entire rxn 1° amine, 1 R group added with N. pH: 4.5 H2SO4 |
|
|
|
Enamine synthesis |
Write entire rxn 2° amine, 2 R groups added to N. pH: 4.5 H2SO4 |
|
|
|
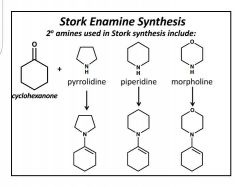
Stork Enamine Synthesis |
Write complete rxn 2° amines. LG- H2O, which deprotonates and creates a double bond (enamine). + Michael donor= iminium ion connected to enolate ion. Stabilized with H3O+ |
Enamine effective Michael Donors |
|
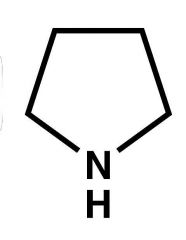
Name? |
Pyrrolidine |
|
|
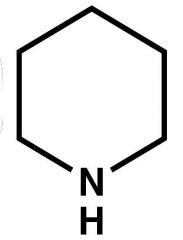
Name? |
Piperidine |
|
|
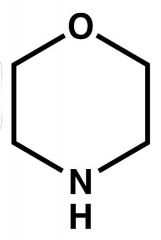
Name? |
Morpholine. |
|
|

|
??? |
|
|
|
What are the classifications of means? Explain. |
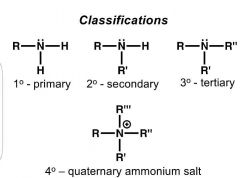
|
|
|
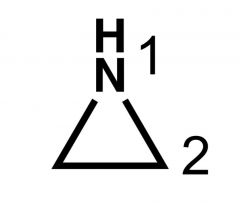
Name? |
Aziridine |
|
|
|
Amines as bases: NH3 + -OH ---> ? NH4 + NaOH ----> ? |
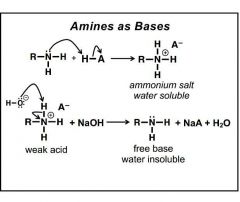
|
|

