![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Cell wall |
*outer layer *rigid, strong, stiff *made of cellulose *support (grow tall) *protection *allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell |
|

Cell Membrane |
*plant - inside cell wall *animal - outer layer; cholesterol *selectively permeable *support *protection *controls movement of materials in/out of cell*barrier between cell and its environment*maintains homeostasis |
|
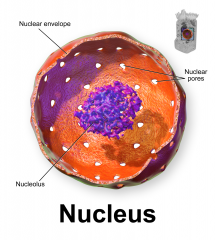
Nucleus |
The nucleus is where the DNA is kept and RNA is transcribed. RNA is moved out of the nucleus through the nuclear pores. Proteins needed inside the nucleus are transported in through the nuclear pores. The nucleolus is usually visible as a dark spot in the nucleus, and is the location of ribosome formation. |
|
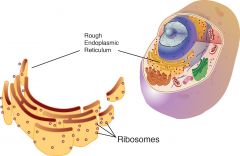
Ribosome |
Ribosomes are where RNA is translated into protein. This process is called protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is very important to cells, therefore large numbers of ribosomes are found in cells. Ribosomes float freely in the cytoplasm, and are also bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). ER bound to ribosomes is called rough ER because the ribosomes on the ER give it a rough sandpaper like look.. These organelles are very small, made up of 50 proteins and several long RNAs bound together. Ribosomes do not have a membrane. Ribosomes fall into two seperate units while not synthesizing protein. |
|
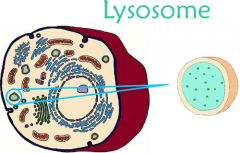
Lysosome |
The lysosome is the digestive system in the cell. It breaks down molecules into their base components digestive enzymes. This demonstrates one of the reasons for having all parts of a cell compartmentalized, the cell couldnt use the destructive enzymes if they werent sealed off from the rest of the cell. |
|
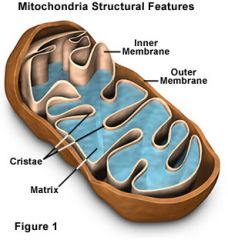
Mitochondria |
organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur. It has a double membrane, the inner layer being folded inward to form layers (cristae). |
|
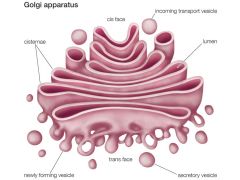
Golgi Apparatus |
If the proteins from the rough ER require further modification, they are transported to the Golgi apparatus (or Golgi complex). Like the ER, the Golgi apparatus is composed of folded membranes. It searches the protein’s amino acid sequences for specialized “codes” and modifies them accordingly. These processed proteins are then stored in the Golgi or packed in vesicles to be shipped elsewhere in the cell. |
|
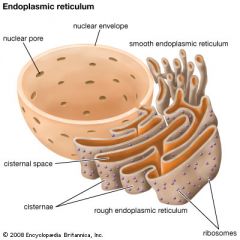
Endoplasmic Reticulum |
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membranous organelle that shares part of its membrane with that of the nucleus. Some portions of the ER, known as the rough ER, are studded with ribosomes and are involved with protein manufacture. The rest of the organelle is referred to as the smooth ER and serves to produce vital lipids (fats). |
|
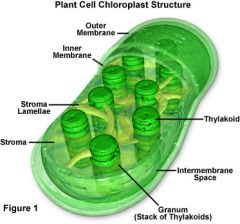
Chloroplast |
In plants and some algae, organelles known as chloroplasts serve as the site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain a pigment known as chlorophyll, which captures the sun’s energy to transform water and carbon dioxide into glucose for food. Chloroplasts allow autotrophic organisms to meet their energy needs without consuming other organisms. |
|
Vacuole |
A vacuole is a membrane-enclosed fluid filled sac found in the cells of plants including fungi.Vacuoles can be large organelles occupying between 30% and 90% of a cell by volume.Vacuoles appear to have three main functions, they:contribute to the rigidity of the plant using water to develop hydrostatic pressurestore nutrient and non-nutrient chemicalsbreak down complex molecules. |
|
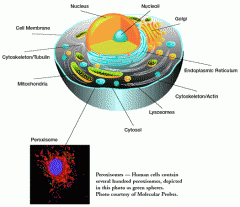
Peroxisome |
Small organelle that is present in the cytoplasm of many cells and that contains the reducing enzyme catalase and usually some oxidases. |
|
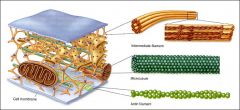
Cytoskeleton |
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers that provide the framework for cellular movement, shape, organelle movement and cell division. These protein fibers make up the microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules. |

