![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List 4 Primary Malignant Neoplasms that occur in children.
|
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Osteosarcoma Chrondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma |
|
|
Are tumours of EPITHELIAL origin in the orbit extremely rare?
|
YES! The large majority are SARCOMAS!
|
|
|
Which is the most common primary pediatric orbital malignancy?
|
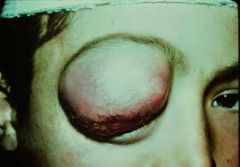
Rhabdomyosarcoma
|
|
|
What is a rhabdomyosarcoma?
|
an EMBRYONAL SARCOMA.
|
|
|
What is the source of a rhabdomyosarcoma?
|
Undifferentiated MESENCHYMAL CELL nests. They have the potential to differentiate into striated muscle.
|
|
|
What is the ave age of onset?
|

5 - 7 years
|
|
|
What % manifest before before the age of 1 year
|
5%
|
|
|
What % occurs before the age of 16 years?
|
90%
|
|
|
Where in the orbit is the tumour most commonly situated?
|
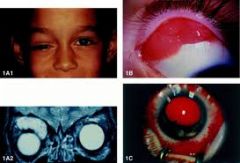
Superonasal or retrobulbar
|
|
|
Where else would you expect to find it in the orbit?
|
Superiorly & Inferiorly
|
|
|
What is the usual presenting sign of a pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma?
|
Acute onset unilateral proptosis
Results in downward and lateral displacement of the globe |
|
|
What other symptoms may the patient present with?
|
Eyelid swelling, ecchymosis, injection
Palpable mass Ptosis and strabismus Regional lymphadenopathy (mets) |
|
|
What symptoms are uncommon?
|
Pain and vision loss
|
|
|
How many histological types are there?
|
4
|
|
|
What are they?
|
Embryonal
Alveolar Botryoid embryonal Pleomorphic (Rabi - pregnant w embryo - bursts out bird - then turns into a robot and smashes to the ground - into a ballet class doing plies) |
|
|
Which is the most common type?
|
Embryonal
|
|
|
Describe features of embryonal
|
Most common type
Histo: loose fascicles of undifferentiated spindle cells . Few cells contain striations Site: superonasal quadrant |
|
|
Which is the second most common type?
|

Alveolar
|
|
|
Describe its features
|

Second most common
Most malignant form. Poor prognosis Histo: poorly differentiated tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) compartmentalized (alveolar like) by orderly connective tissue septae Site: inferior (down in the grave) |
|
|
Which type is rarely found in the orbit?
|
Botryoid embryonal (grapelike)
|
|
|
Features of botryoid embryonal
|
Rarely found in the orbit
variant of embryonal that occurs in grape-like clusters May originate from the conjunctiva or paranasal sinuses |
|
|
Which is the rarest form?
|

Pleomorphic
|
|
|
Features?
|
Rarest form
Occurs in adults Well differentiated |
|
|
What is the disease course?
|
Rapid progression
Bony invasion Metastasis to LN, marrow, brain & lung |
|
|
What are the features on CT?
|
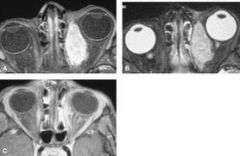
Irregular, but well circumscribed mass of uniform density. Often with adjacent bony destruction
|
|
|
What must be done immediately when this malignancy is suspected?
|

Biopsy
Metastatic work up: CXR, LP, Marrow biopsy |
|
|
What is the treatment?
|

Small encapsulated or well-localised: excised in entirety
Large, extensive: Chemo (vin, actinomy, cyclophos) & ray Excenteration rarely indicated |
|
|
What is the prognosis?
|
Based on the staging and histo
Best to worst: adult pleomorphic > embryonal (incl botryoid) > alveolar Primary ORBITAL rhabdo has the best prognosis of any site Long-term survival: nearly 90% |
|
|
What is the DDx?
|
Orbital cellulitis
Idiopathic orbital inflammation Neuroblastoma Lymphangioma with heamorrhage Capillary heamangioma Ruptured dermoid cyst |

