![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
127 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trilafron: Class and mode of action |
Anti-Nauseants. Antidopaminergic blocks dopamine pathways in vomiting centre chemoreceptor trigger zone . |
|
|
Gravol : Class and mode of action |
Anticholinergic, sedative, and H1 blocking contribute to antiemetic effect |
|
|
Odansetron: Class and Mode of action |
antiserotonergic. blocks 5ht receptors on neurons located peripheral or central nervous system. |
|
|
Dexamethasone: Class and mode of action |
Anti-nauseant. MOA unknown |
|
|
Mechanism that causes renal toxicity |
Normal: decrease Hb Volume=decrease renal Hb flow = decrease GFR= Increase vascular resistance+Na retention. PGE1 and PGE2 counters this.
NSAIDS: No Cyclooxygenase = No PGE1 and PGE2=No counter= Uncontrolled increase of renal vascular resistance = renal failure! |
|
|
Typical Dosage for Ibuprofen (Adult and Child): |
Adult: 600mg po q6h Child: 10mg/kg po 6h |
|
|
Typical Dosage for Naproxen (Adult and Child): |
Adult: 500mg po q12h Child: 5mg/kg po 12h |
|
|
Typical Dosage for Acetominophen (Adult and Child): |
Adult: 650-1000mg q4h max 4000mg/24h Child: 10-15mg/kg q4h max65 mg/kg/24h |
|
|
Typical Dosage for Ketoprofen SR (Adult and Child): |
Adult: 200 mg po q24h Child: not indicated under 12 |
|
|
What are the components in Tylenol 1 |
15mg Caffeine 300mg Acetominophen 8mg Codeine |
|
|
What are the components in Tylenol 2 |
15mg Caffeine 300mg acetominophen 15mg Codeine |
|
|
What are the components in Tylenol 3 |
15mg Caffeine 300mg acetominophen 30mg Codeine |
|
|
What are the components in Tylenol with Codeine elixir |
160mg Acetominophen/5ml 8mg Codeine |
|
|
What are the components in 292 |
375mg ASA 15mg Caffeine 30mg Codeine |
|
|
What are the components in Percocet-demi |
325mg Acetominophen 2.5mg Oxycodone |
|
|
Amoxicillin Dosage for Prophylaxis? |
Adults: 2gram 1 hour prior Children: 50mg/kg 1 hour prior |
|
|
Clindamycin dosage for prophylaxis? |
Adults: 600mg 1 hour prior Children: 20mg/kg 1 hour prior (As per AHA guidelines) |
|
|
Contraindications for NSAIDs |
1)PUD 2) Hypersensitivity 3) RIsk of renal failure |
|
|
Contrindications for Acetominophen |
1) Hypersensitivity 2) Alcoholics |
|
|
Contraindications for Opioids |
1) Hypersensitivty 2)Diarrhea caused by poisoning 3) Acute respiratory depression, acute asthma attack, upper airway obstruction 4) MAO Inhibitors 5)Morphine
|
|
|
What is one mechanism in which NSAIDs can cause PUD |
PGE normally inhibits Acid (H+) release in parietal cells. Since NSAIDs prevent production of PGE (normally downstream product of COX but it's knocked out by NSAIDS), you get uncontrolled acid release which causes destruction of GI lining and Ulcers |
|
|
Pathophysiological effects of NSAIDs |
1) GI=ulcer, pain, nausea 2) Allergic reactions 3) CVS: CHF, elevated BP 4) Renal: Acute renal failure 5) Hemostasis: reversible decrease in TXA2, decrease platelet function |
|
|
9 risk factors for NSAID induced Renal failure |
Age >60 Arteriosclerotic Cardiovascular disease Use of Diuretics Acute Gouty Arthritits (caused by over production of uric acid) CHF Renal Disease SLE Severe liver disease and cirrhosis Intravascular volume depletion |
|
|
What percentage of IANB fail? |
15-20% |
|
|
% of infection that are: Aerobe? Anaerobe? both? |
5% Aerobe 35% Anaerobe 65% both |
|
|
List the instruments on a standard oral surgery tray |
Bishops/Austin/Minnesota/Retractor Fraser Suction #15 Blade #3 Bard parker handle #9 Molt Periosteal Elevator #34 straight elevator Reverse Cutting Needle Plain Gut suture Needle |
|
|
If Warfarin is stopped as part of the pre-op preparation, when should the patient stop taking warfarin? |
72 hours pre-op. Day before=useless |
|
|
If a Diabetic patient is about to undergo surgery but does not require NPO, how should they be managed? |
normal diet & oral hypoglycemics; if anticipate difficulty with eating post-op, hold am hypoglycemic til able to eat post-op |
|
|
If a Diabetic patient is about to undergo surgery and requires NPO, how should they be managed? |
Oral hypoglycemics should be withheld 24 hrs pre-op if the patient is made NPO |
|
|
How long does Plain Gut last and when should it be used? |
4-7 days, quick healing mucosa |
|
|
How long does Chromic Gut last and when should it be used? |
9-14 days, quick healing mucosa |
|
|
How long does Vicryl (Polyglactic acid) last and when should it be used? |
20-30 days, subcutaneous sutures, mucosa, muscle |
|
|
How long does Dexon last and when should it be used? |
14-21 days, subcutaneous sutures, mucosa |
|
|
What are major risks of tooth extraction? |
a) Altered sensation: 1% permanent b) Vital organ infection c) Fracture of the mandible (>0.01%) and maxillary tuberosity d) injury and litigation |
|
|
Risks of not extracting 3rd molar? |
a) Infection (20-40%) b) Trismus c) Caries which may lead to loss of second molars d) Development of pathological condition such as cyst (3%) or tumor (0.2%) e) Vital Organ infection f) Resorption of adjacent tooth g)Increase risk of permanent nerve injury if have to remove when root fully developed |
|
|
Components of Alvogyl |
Iodoform, Butyl paraminobenzoate, Eugenol, Penghawar, Excipient |
|
|
MOA of Alvogyl |
Antiseptic, Analgesic |
|
|
Contraindications to Alvogyl |
Allergy to Procaine type anesthetics, hypersensitivity to iodone |
|
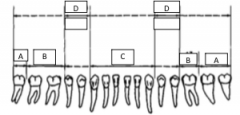
What forceps are used to take out A? |
222 |
|
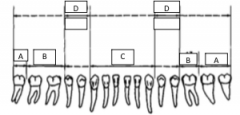
What forceps are used to take out B? |
17, 23 |
|
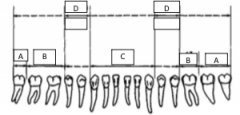
What forceps are used to take out C? |
203, 74 |
|
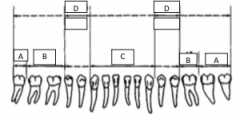
What forceps are used to take out D? |
151,151A |
|
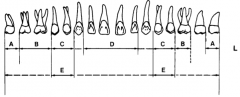
What forceps are used to take out A? |
121S |
|
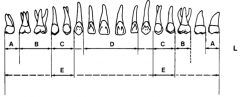
What forceps are used to take out B? |
53R/L 88 R/L 89/90 |
|
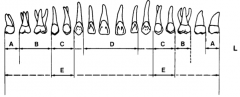
C and E? |
150 and 150A |
|
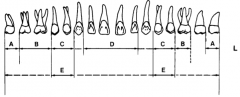
D? |
1, 99C |
|
|
Minor transient risks of intervention (surgery)? |
1. Sensory Nerve alteration 2. Alveolitits 3. Trismus 4. Infection 5. Hemorrhage 6. Dentoalveolar fracture 7. Displacement of Tooth 8. Oral-Antral fistula |
|
|
What some minor PERMANENT risks of injury? |
Periodontal Injury Adjacent tooth injury TMJ injury |
|
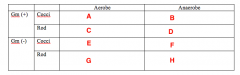
Likely pathogens. What Bacterias belongs in Box A |
Strep (Viridans) |
|
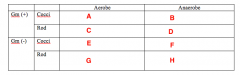
Likely pathogens. What bacteria goes in Box B |
Peptostreptococcus |
|
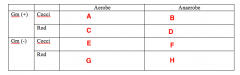
Likely pathogens. What bacteria goes in Box C |
Lactobacillus |
|
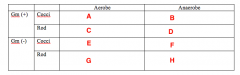
Likely pathogens. What bacteria goes in Box D |
Nothing. |
|
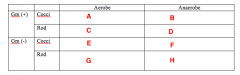
Likely pathogens. What bacteria goes in Box E, F and G? |
Nothing! |
|
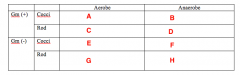
Likely pathogens. What bacteria goes in Box H? |
Bacteroides Porphyromonas Prevotella Fusobacterium |
|
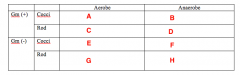
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box A? |
Staph |
|
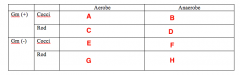
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box B? |
Nothing |
|
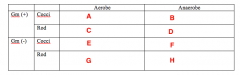
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box C? |
Cornybacterium |
|
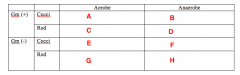
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box D? |
Actinomycetes |
|
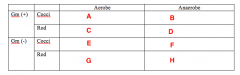
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box E? |
Moraxella |
|
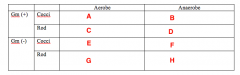
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box F? |
Veillonella |
|
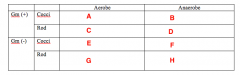
Less Common Pathogens What bacteria goes in Box G? |
Enterobacteriaceae Eikenella |
|
|
What percent of cleft patients have other anomalies? |
7-13% CL 20-50% CP 2-11% CL/CP |
|
|
What percent of cleft palates have other anomalies associated with a syndrome? |
2-4% |
|
|
What is involved in an assessment to determine whether an alveolar bone graft is required for a cleft patient? |
1. Oronasal fistula (do you get ice cream going through your nose?, clinical exam) 2. Lack of alveolar bone stock (by xray, clinical exam) |
|
|
What are the goals of alveolar bone grafting in the cleft patient? |
1) Closure of vestibular and palatal oral nasal fistulae 2) Provision of bone of sufficient quality and quantity to allow eruption of permanent LI and Canine 3) Provisional of support of lateral ala of nose and skeletal nasal base 4) Provision of suitable bone architecture of premaxilla and anterior face of maxilla on cleft side to support accurate nasolabial muscle reconstruction. 5) Establishment of functional nasal airway on cleft side |
|
|
Reasons for removing root tips |
1) Superficial 2) Tooth was infected 3) Tooth is far from Vital structures 4) future implant |
|
|
Reasons for not removing the root tip |
1) Small (less than 5mm) 2) Deep 3) Near vital structures |
|
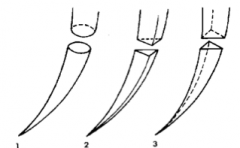
What type of needle is 1? |
Tapered |
|
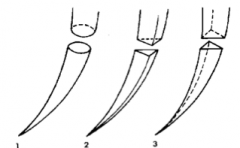
What type of needle is 2? |
Cutting |
|
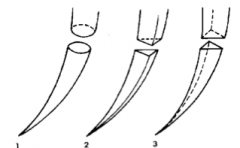
What type of needle is 3? |
Reverse Cutting |
|
|
What is the most likely emergency associated with asthma? |
Bronchospasm |
|
|
What medication should be administered to the patient in the event of a bronchospasm? |
Salbutamol |
|
|
What is mechanism of action of a Beta 2 agonist? |
Stimulates Beta 2 receptors in bronchial smooth muscles leading to increased cAMP and bronchodilation |
|
|
What are contraindications to the drug of choice (Ventolin)? |
Hypersensitivty, tachyarrhythmia, hypokalemia |
|
|
What are the side effects of Salbutamol? |
Nervousness, tremor, headache, tachycardia, palpitations, nausea, weakness, hypokalemia |
|
|
In the event of a bronchospasm, how much salbutamol should you administer to the patient? |
1-2 puffs (100-200ug) PRN |
|
|
What are 3 indications for biopsy a lesion? |
1) Persists for more than two weeks with no apparent cause 2) Persistant tumor-like structure either visible/palpable 3) Interferes with local function |
|
|
Does 81mg have a antiplatelet effect? |
Yes |
|
|
List 6 risk factors for NSAID associated GI toxicity in the general population |
Age >60 years Concommitant use of corticosteroids Previous upper GI bleed Use of excessively high NSAID doses History of peptic ulcer disease History of CVD |
|
|
What spectrum of activity does Penicillin V target? |
Strep, peptostrep, +/- actinomyces |
|
|
What spectrum of activity does Amoxicillin target? |
Strep, peptostrep, actinomyces, prevotella, +/- H.influenza |
|
|
What spectrum of activity does Amoxicillin w/Clavulanic acid target? |
Strep, S. Aureus, H. Influenza, M. Catarrhalis, actinomyces, prevotella, peptrostrep |
|
|
What spectrum of activity does metronidazole target? |
Anaerobes (Bacteroides, prevotella, peptostrep) |
|
|
What spectrum of activity does Clindamycin target? |
Strep, S. Aureus, Actinomyces, bacteroides, prevotella |
|
|
Patient is having a MI. List 4 first line agents including dose and administration you will use |
1. Nitroglycerin sublingually 0.3-0.6mg every 5 minute up to 3 times (if systolic >90) 2. ASA 325mg chewed. 1 more taken orally 3. Morphine 5-10mg IM/SC 4. Oxygen 4L/min nasal canula |
|
|
6 year 44lb (20kg). 2% lidocaine 1:100,000 epi. You injected 3 carpules. How much lido in mg did you inject? |
36mg lidocaine/carpule x 3 carp=108mg |
|
|
6 year 44lb (20kg). 2% lidocaine 1:100,000 epi. You injected 3 carpules. How much epi did you inject? |
0.018mg epi/carp x 3carp=0.054mg |
|
|
6 year 44lb (20kg). 2% lidocaine 1:100,000 epi. You injected 3 carpules. How much epi did you inject? What is the max dose of lido you can give her? What is the Max epi you can give her? |
Max =7mg/kg x 20=140mg lido 0.2mg Epi MAX |
|
|
Write a prescription for pain medication |
Name, Date Age Address Rx: Tylenol 3 (three) Dispense 24 (twenty four) tabs Directions: take 2 tabs PO q4h PRN pain Do NOT Refill Signature and name |
|
|
Please write prescription for amoxicillin |
Name, Date Age Address Rx: Amoxicillin 500mg Dispense 22 (twenty two) tabs Directions: take 2 tabs (1g) STAT, and then T 1 tab (500mg) po q8h until finished Signature and name |
|
|
Indications for antibiotic prophylaxis |
1)Artificial Heart valves 2) History of infective endocarditits 3) Certain specific, serious congenital heart conditions such as: -Unrepaired or incompletely repaired cyanotic congenic congenital heart disease including those with palliative shunts and conduits -Completely repaired congenital heart defect with prosthetic material or device by surgery or catheter intervention during the first 6 months after the procedure -repaired congenital heart defect with a residual defect at the site or adjacent to the site of a prosthetic patch or a prosthetic device 4) Cardiac transplant recipients who develop cardiac valulopathy |
|
|
Technical goals of overcoming complex extractions? |
Improve Mechanical advantage Reduce resistance Correct an inadequate path |
|
|
What are some methods of achieving the technical goals in complex extractions? |
Improved Access: Flap, bone removal Improved MA: bone removal Reduced resistance: bone removal, section teeth Correct path of removal: Remove bone, section teeth |
|
|
4 general contraindications for vertical releasing incisions |
1. Canine prominence 2. Palate 3. Over mental foramen 4. Lingual of the mandible 5. Bony Defects 6. Over incisive papilla |
|
|
List signs and symptoms of Acute MI |
Visceral or precordial chest pain, crushing, heavy, squeezing, burning, or dull ache, +/- radiation to neck jaws, back, shoulders or arms, dyspnea, diaphoresis, restlessness, presyncope, n/v, diarrhea |
|

Draw surgical flap incision for tooth 46 below. |
|
|
Draw surgical flap incision for tooth 37 |
|
|
Draw where you would make the biospy |
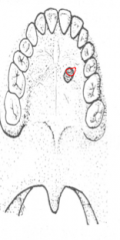
|
|
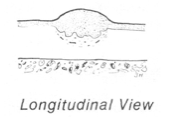
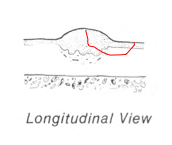
Draw where the knife would cut for a biopsy in the longitudinal view |
|
|
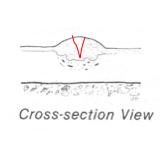
Draw where the knife would cut for a biopsy in the cross-section view |
|
|
|
Definition of Local infiltration |
Anesthesia that targets terminal branches of the nerves to block transmission |
|
|
Definition of Conscious sedation |
A depressed level of consciousness via the use of oral, inhaled or IV drugs |
|
|
Regional block definition |
Blocks transmission in a entire dermatome |
|
|
GA definition |
State of reversible loss of sensation and consciousness causing reversible drug induced coma |
|
|
What are the three ways to use a elevator? |
Displacement: putting it into PDL space Lever Action: Engaging tooth through purchase point and using bone as fulcrum to life tooth up Wheel and axle: When elevator engages purchase point and handle is roated and tooth is displaced laterally to line of shaft. |
|
|
Definition of Osteogenesis |
new bone formation by surviving pre-osteoblasts and obsteoblasts within the graft |
|
|
Definition of Osteoconduction |
Vascular tissue invades the graft, bringing with it the osteoblasts that deposit new bone = creeping substitution |
|
|
Definition of Osteoinduction |
Components in bone graft (e.g. BMP) stimulate recipient cells to form new bone |
|
|
Name the function of axon: |
Long projection of neuron that conducst electrical impulses away from cell body |
|
|
Name the function of Cell body |
contains nucleus and other organelles |
|
|
Name the function of Dendrites |
branched projections of neuron that receives signals from body |
|
|
Three components of LA and their functions |
Lipophilic- allows it to cross cell membrane Intermediate- determines if it’s amide/ester (ester metabolized in tissue by plasma esterase and amide in the liver by CYPs) Hydrophilic- allows it to dissolve in interstitial fluid |
|
|
Biochemically why is it difficult to anaesthetize an infected area? |
Infectious environment is an acidic one thus it is difficult to achieve anesthesia as there will not be enough free base from RN RNH+ <-- --> RN + H+
|
|
|
Vasovagal syncope – what is it, cause, and tx for it? |
Loss of consciousness resulting from inadequate blood flow to brain. 1. Stop Supine position ABC and CPR 4. Oxygen |
|
|
What do you do when anesthetic fails? |
Find out if it’s psychological/ physiological. |
|
|
What is akinosi? |
Closed mouth IANB. |
|
|
Where to take bone from for a graft? How to prevent p/o complications |
Ramus, zygoma, chin, iliac crest (ant/post), rib, tibia, calvarium |
|
|
Radiograph with 2 fractures – describe fractures, list 10 clinical features of trauma and where to place plates |
localized pain localized swelling intraoral hematoma intraoral laceration/bleeding trismus malocclusion crepitations mobility of teeth loss of teeth fetid oral malodor - If anterior to mental foramen, need to place 2 plates because you need to resist movement in two plates. |
|
|
Sequence of treatment for cysts/tumors: |
1) Ablative procedures =take tumor/cyst out 2) Soft tissue reconstruction -Mycocutaneous flaps -Immediate nerve repair(remove nerve from tumor then reanastamose to NV bundle) 3) osseous reconstruction 4) Denture ready surgery |
|
|
Steps and age at which they are performed for Cleft and palate surgery
|
1) Lip repair and Soft palate repair at 5-6 months
2) Primary hard palate repair with primary gingivoperiosteoplasty at 12 months 3) Alveolar bone graft at 5-6 years 4) Orthognathic surgery at 13-17 years |
|
|
What is the definition of Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome? |
-Characterized by repetitive episodes of apnea and/or hypopnea -Due to obstruction of upper airway during sleep -Assoc w excessive daytime sleepiness -Relatively common, known to be assoc w significant health + social consequences Obstructive apnea = no airflow for 10 sec while there is still effort for respiration |
|
|
What is the Apnea hyponea index? What is the threshold of the AHI before a patient is dxed as Obstructive sleep apnea? |
# of apneas + hypopneas per hour of sleep . AHI of at least 5 is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness |
|
|
List symptoms of Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
Prominent snoring -Excessive daytime sleepiness -Early morning headaches -Impaired memory -Dry throat on awakening -Enuresis (uncontrolled urination) -Nocturnal choking/gasping -Depression -Recurrent awakenings from sleep |
|
|
Medical complications with OSAS |
Hypertension CV and Cerebrovascular disease Neurocognitive functions |
|
|
Range of success rate for maxillomandibular advancement for tx of OSAS? |
Overall 70% With uvulopalatopharyngealoplasty-85% With Genioplastiy-100% |
|
|
What are the advantages of performing a bone graft in a cleft patient just after eruption of the central incisor rather than canines erupt? |
+: 1)If bone graft is done at beginning of maxillary permanent central incisor, then the 2 centrals will be the same length on both the normal and cleft side. If wait till permanent canines, then the teeth on the cleft side will be 25% shorter than normal side. Therefore, good aesthetics 2) Second reason: much better perio support of the permanent teeth on the cleft side if graft done earlier |
|
|
Analgesic ladder(dosages) |
Ketoprofen SR (200mg q24h) T3: 2 tab q4h prn pain Percocet: 1 tab q4h prn pain OxyContin: 10-20mg q12h pain Dilaudid(hydromorphone): 2-4mg q4h pain
|

