![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what does PoM mean in the BNF? |
Prescription only medicine |
|

|
Preparations considered less suitable for prescribing but may be justifiable in certain circumstances |
|
|
what does CD mean in the BNF? |
Controlled drug - subject to requirements of the misuse of drugs act |
|
|
Detail the Medicines Act 1968 |
1. General sales list meds (GSL) - no need for presence of pharmacist 2. Pharmacy meds (P) - Pharmacist must see pt before drug sold 3. Prescription only meds (PoM) |
|
|
Detail the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 |
Deals with manufacture, supply and posession of 'controlled drugs' 3 classes: A - cocaine, diamorphine, MDMA B - codeine, cannabis C - buprenorphine, benzos |
|
|
Detail the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001 |
Defines classes of person who are allowed to supply and posses controlled drugs while acting in their professional roles Lay down conditions under which these activities may be carried out Divides drugs into 5 schedules - CD1, CD2, CD3, CD4-1, CD4-2 |
|
|
What advice would you give to a patient when prescribing a drug? |
1. take drugs at correct time and finish course 2. STOP in event of unexpected reactions and contact prescriber 3. Discuss known side effects and interactions 4. keep medicines safe, esp with children |
|
|
What type of virus is HIV? |
RNA retrovirus |
|
|
How does HIV infection affect the immune system? |
Infects T-lymphocytes and binds to CD4 receptors, T-cells unable to function in surveillance for infections and cancer |
|
|
How is HIV diagnosed? |
ELISA test - antibody test |
|
|
How is the viral load of HIV monitored? And what is the significance of this? |
HIV RNA test Gives indication of prognosis |
|
|
When might diagnostic tests produce 'false negative' results? |
6-12 wks post infection |
|
|
When might oral fungal infections be seen in HIV infected patients? |
Relatively early in CD4 dip, 500/mm^3 |
|
|
Which oral lesions are strongly associated with HIV? |
1. Candidosis 2. Hairy leukoplakia - EBV 3. Kaposi's sarcoma 4. Non-hodgkin's lymphoma 5. Perio diseases eg ANUG 6. candida-associated lesions eg angular cheilitis |
|
|
When should you be suspicious of HIV infection with regards to candidal infections? |
1. Pseudomembranous candidosis more anteriorly - steroid inhalers hit further back 2. Erythematous candidosis with no denture 3. Treatment not making it better |
|
|
What are the histological features of hairy leukoplakia? |
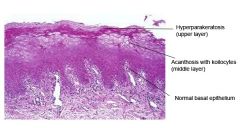
Keratin overgrowth in columns Koilocyte = virally active cell |
|
|
What are the causes of an upper motor neurone lesion? |
1. CVA (stroke) 2. Cerebral tumour 3. trauma |
|
|
What are the causes of a lower motor neurone lesion? |
1. Middle ear infection 2. MS 3. HIV 4. Lyme's disease 5. Sarcoidosis 6. Misplaced LA 7. Bell's palsy 8. Ramsay-Hunt syndrome |
|
|
What is the clinical difference between an upper motor neurone lesion and a lower motor neurone lesion? |
UMN spares the upper half of the face - ability to wrinkle forehead maintained |
|
|
How can HSV cause a bells palsy? |
HSV reactivated, causes nerve to swell, nerve constricted by stylomastoid foramen |
|
|
How can a bells palsy be treated? |
Oral predisnolone 50-80g/day in one dose for 10 days Anti-inflammatory - allows nerve to return to normal |
|
|
How may gonorrhoea present in the mouth? |
Dry, burning sensation with diffuse mucosal erythema + lymph node enlargement |
|
|
Describe primary syphilis |
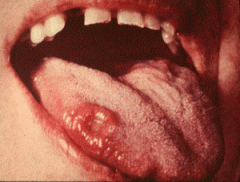
chancre - painless round ulcer at point of infection Resolves 2-3 months Regional lymphadenopathy |
|
|
Describe secondary syphilis |
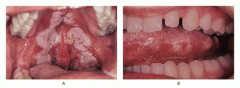
1-4 months after primary infection Macular skin rash Snail-track ulcers Generalised rash and lymphadenopathy Oral papules Resolves 2-6 weeks |
|
|
Describe tertiary syphilis |
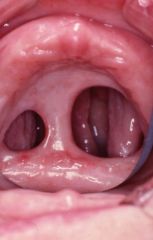
Gumma of palate - bone and ST lesions - perforation Many years after first infected |
|
|
What is the treatment for syphilis? |
high dose penicillin / tetracycline |
|
|
which human herpes virus is associated with kaposi's sarcoma? |
HHV-8 |
|
|
what are the clinical features of herpes simplex virus infection? |
1. gingivostomatitis 2. herpes labialis 3. keratoconjunctivitis 4. herpetic whitlow 5. bells palsy 6. Genital herpes |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of HSV? |
1. Replication in epithelium 2. Uptake by sensory nerves 3. Retrograde transport to sensory ganglia 4. a) productive replication in neurones b) establishment of latent infection 5. Anterograde transport to mucosal and cutaneous sites 6. Release from nerve ending 7. Viral replication 8. Lesion formation 9. Viral shedding |
|
|
How would you sample vesicle fluid from a viral infection? |
dacron tip swab |
|
|
What is varicella? |
'Chicken pox' Primary infection with varicella-zoster virus |
|
|
What is zoster? |
'Shingles' Reactivation of latent VZ virus from sensory ganglion |
|
|
When do you produce IgM? |
The first time you produce an immune response |
|
|
When do you produce IgG? |
The second time you produce an immune response |
|
|
What are the clinical features of EBV? |
1. infectious mononucleosis 2. oropharyngeal lymphadenopathy and sore throat 3. Duration 2-3 wks 4. oral hairy leukoplakia in HIV pts |
|
|
What is the pathogenesis of EBV |
stimulation of T-cells in cytotoxic response to EBV infected B cells |
|
|
What are the clinical features of kaposi's sarcoma? |
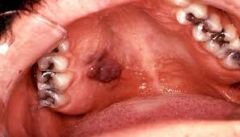
Vascular tumour with different clinical manifestations Dusky coloured areas on oral mucosa and skin AIDS associated |
|
|
Which virus is a risk factor for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma? |
Human papilloma virus HPV-16 |

