![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Light |
The form of energy you can see |
|
|
Luminous |
Something that produces light |
|
|
Non-luminous |
Something that reflects light |
|
|
Light ray |
The way light travels, straight and fast |
|
|
Penumbra |
The outer shaded region of a shadow |
|
|
Umbra |
The fully shaded inner region of a shadow |
|
|
Reflection |
The process in which light strikes a surface and bounces back off that surface |
|
|
Incident ray |
Light coming from a light source |
|
|
Reflecting ray |
Light that bounces off a surface |
|
|
Normal line |
The line perpendicular to the plane mirror |
|
|
Angle of incidence |
Angle between the incidence ray and the normal line |
|
|
Angle of reflection |
Angle between the reflected ray and normal line |
|
|
Refraction |
A process in which light is bent, when is travels between mediums |
|
|
Concave mirrors |
Reflective surfaces that cave inwards |
|
|
Convex mirrors |
Reflective surfaces that bulge out |
|
|
The law of reflection |
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection |
|
|
3 Types of light energy |
Chemical, thermal, and electrical |
|
|
Natural lights |
Sun, stars |
|
|
Artificial lights |
Incandescent light bulbs, LEDs |
|
|
3 properties of light |
Translucent, opaque, transparent |
|
|
2 types of reflections |
Specular- smooth reflective surface Diffuse- rough reflective surface |
|
|
*ray diagrams* |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
*A person looking at himself in a mirror* |

|
|
|
*A target is hit by a laser pointer after reflecting off 2 mirrors* |
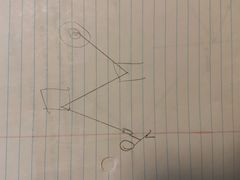
|
|
|
*You are sitting out under the stars at night* |
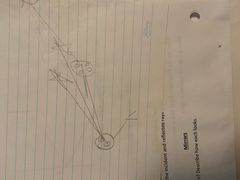
Moon is not needed |
|
|
Why do concave mirrors make images appear upside down? |
Because you are beyond the focal point, if you are in front of the focal point your reflection is right-side up |
|
|
Why does a convex mirror show a VIRTUAL reflection? |
Because the focal point is behind the mirror |
|
|
How will the light refract as it goes through these mediums? A)air to water B)oil to water C)air to oil D)water to air |
A) when going from air to water, light moves TOWARDS the NL B) when going from oil to water, light moves AWAY from the NL C) when going from air to oil, light moves TOWARDS the NL D) when going from water to air, light moves AWAY from the NL moves to a denser medium= towards moves to a less dense medium= away |
|
|
Two types of vision problems |
Myopia and Hyperopia |
|
|
Myopia |
Nearsightedness, eyes focus light rays in front of the retina |
|
|
Hyperopia |
farsightedness, eye is too short. Images form behind the retina |
|
|
Squinting helps vision? How? |
limits the amount of light rays allowed into the eye. unfocused light rays don't reach the retina |
|
|
Glasses help vision? How? |
The lens bend(refract) the light rays to make them meet at the retina |
|
|
How is white light broken into diffirent colours? |
White light gets refracts into seven colours with a prism. The colours bend at different angles |
|
|
Light sources on the electromagnetic spectrum |
ultraviolet and infrared light. Infrared light has longer wavelengths |

