![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
152 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Human movement system
|
The combination and interrelation of the nervous, muscular and skeletal system
|
|
|
What are the three primary functions of the nervous system?
|
1. Sensory function - the ability to sense changes in internal and external environment
2. Integrative function – ability to analyze sensory information and make proper decisions 3. Motor function – the neuromuscular response to the sensory info |
|
|
Nueron
|
The functional unit of the nervous system; a specialized cell that provides and transmits information through both electrical and chemical signals
|
|
|
Sensory function
|
The ability of the nervous system to sense changes in either the internal external environment
|
|
|
Integrative function
|
The ability of the nervous system to analyze and interpret sensory information to allow for proper decision making
|
|
|
Integrative function
|
The ability of the nervous system to analyze and interpret sensory information to allow for proper decision making
|
|
|
Motor function
|
The neuromuscular response to the sensory information
|
|
|
Proprioception
|
The cumulative sensory input to the central nervous system for all mechanical receptors that sends body position and limb movement
|
|
|
Sensory neurons
|
Transmit nerve impulses from effector sites via receptors to the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
Sensory neurons
|
Transmit nerve impulses from effector sites via receptors to the brain and spinal cord
|
|
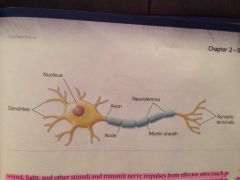
What is this?
|
A neuron
|
|
|
Interneurons
|
Transmit nerve impulses from one neuron to another
|
|
|
Motor neurons
|
Transmit nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to effector sights
|
|
|
What are the three functional classifications of neurons?
|
1. Sensory neurons
2. Interneurons 3. Motor neurons |
|
|
What is the central nervous system?
|
The portion of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What is the central nervous system?
|
The portion of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What is the peripheral nervous system?
|
Cranial and spinal nerves that spread throughout the body
|
|
|
How do the Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system work together?
|
The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body and the external environment
|
|
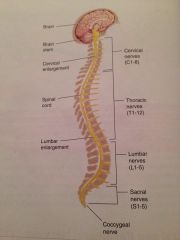
What system is this?
|
The central nervous system
|
|
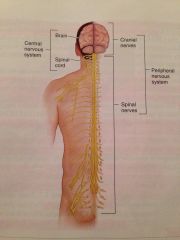
Which system is this?
|
The peripheral nervous system.
|
|
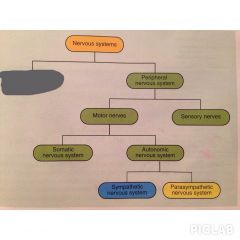
What is missing?
|
Central nervous system
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are Golgi tendon organs ?
|
Receptor sensitive to the change tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are Golgi tendon organs ?
|
Receptor sensitive to the change tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are joint receptors?
|
Receptor surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration, and deceleration of the joint
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are Golgi tendon organs ?
|
Receptor sensitive to the change tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are joint receptors?
|
Receptor surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration, and deceleration of the joint
|
|
|
What is the skeletal system?
|
The bodies framework composed of bones and joints
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are Golgi tendon organs ?
|
Receptor sensitive to the change tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are joint receptors?
|
Receptor surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration, and deceleration of the joint
|
|
|
What is the skeletal system?
|
The bodies framework composed of bones and joints
|
|
|
What forms junctions that are connected by muscles and connective tissue ?
|
Bones
|
|
|
What are muscle spindles?
|
Receptors sensitive to the change in length of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are Golgi tendon organs ?
|
Receptor sensitive to the change tension of the muscle and the rate of that change
|
|
|
What are joint receptors?
|
Receptor surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration, and deceleration of the joint
|
|
|
What is the skeletal system?
|
The bodies framework composed of bones and joints
|
|
|
What forms junctions that are connected by muscles and connective tissue ?
|
Bones
|
|
|
Junctions that are formed by bones, muscles and connective tissue are called what?
|
Joints
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the skeletal system?
|
The axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the skeletal system?
|
The axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
|
|
|
What is the axial skeleton?
|
The portion of the skeleton system that consist of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
|
|
|
What are the divisions of the skeletal system?
|
The axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
|
|
|
What is the axial skeleton?
|
The portion of the skeleton system that consist of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
|
|
|
What is the appendicular skeleton?
|
The portion of the skeletal system that includes the upper and lower extremities
|
|
|
How many bones are in the axial skeleton?
|
Approximately 80 bones
|
|
|
How many bones are in the axial skeleton?
|
Approximately 80 bones
|
|
|
How many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
|
Approximately 126 bones
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
What is an example of a long bone?
|
The humerus or the femur
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
What is an example of a long bone?
|
The humerus or the femur
|
|
|
What is an example of a short bone?
|
Carpals of the hand or tarsals of the feet
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
What is an example of a long bone?
|
The humerus or the femur
|
|
|
What is an example of a short bone?
|
Carpals of the hand or tarsals of the feet
|
|
|
What is an example of a flat bone?
|
Scapulae or patella
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
What is an example of a long bone?
|
The humerus or the femur
|
|
|
What is an example of a short bone?
|
Carpals of the hand or tarsals of the feet
|
|
|
What is an example of a flat bone?
|
Scapulae or patella
|
|
|
What is an example of an irregular bone?
|
Vertebrae
|
|
|
Explain bone growth using the words remodeling osteoclast an osteoblast.
|
Phone is renewed through a pot process called remodeling. Old bone tissue is broken down and removed by cells called osteoclast. New bone tissue is laid down to replace the old, this is performed by cells called osteoblast.
|
|
|
What are the five major types of bones?
|
Long bones, short bones, flat bones, a regular bones, and the sesamoid bones.
|
|
|
What is an example of a long bone?
|
The humerus or the femur
|
|
|
What is an example of a short bone?
|
Carpals of the hand or tarsals of the feet
|
|
|
What is an example of a flat bone?
|
Scapulae or patella
|
|
|
What is an example of an irregular bone?
|
Vertebrae
|
|
|
What is an example of a sesamoid bone?
|
Patella
|
|
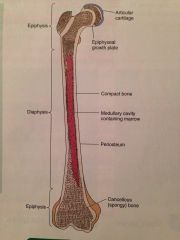
What type of phone is this?
|
A long bone
|
|
|
What are the three parts of a long bone?
|
Epiphysis (the end)
Diaphysis (shaft portion) Epiphyseal plate (The region of a long bone connecting the diaphysis and the epiphysis) |
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What are the two types of surface markings that can be found on bones?
|
Depressions and processes
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What are the two types of surface markings that can be found on bones?
|
Depressions and processes
|
|
|
What is the difference between depressions and processes?
|
Depressions are flattened or indented portions of bones where muscles attach. processes our projections protruding from bone where muscles tendons and ligaments can attach.
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What are the two types of surface markings that can be found on bones?
|
Depressions and processes
|
|
|
What is the difference between depressions and processes?
|
Depressions are flattened or indented portions of bones where muscles attach. processes our projections protruding from bone where muscles tendons and ligaments can attach.
|
|
|
What is the vertebral column?
|
A series of a regular shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What are the two types of surface markings that can be found on bones?
|
Depressions and processes
|
|
|
What is the difference between depressions and processes?
|
Depressions are flattened or indented portions of bones where muscles attach. processes our projections protruding from bone where muscles tendons and ligaments can attach.
|
|
|
What is the vertebral column?
|
A series of a regular shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What are the five different categories that make up the vertebral column?
|
The cervical vertebrae - first 7 vertebrae
The thoracic vertebrae - next 12 vertebrae The lumbar vertebrae- the last five vertebrae The sacrum - triangular bone below lumbar Coccyx - also known as the tailbone |
|
|
What is periosteum?
|
A dense membrane composed of fibrous connective tissue you that closely wraps all bone except articulating surfaces in joints.
|
|
|
What is a medullar cavity?
|
The central cavity of bone shaft where marrow is stored
|
|
|
What is articular cartilage?
|
Cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of bones
|
|
|
What are the two types of surface markings that can be found on bones?
|
Depressions and processes
|
|
|
What is the difference between depressions and processes?
|
Depressions are flattened or indented portions of bones where muscles attach. processes our projections protruding from bone where muscles tendons and ligaments can attach.
|
|
|
What is the vertebral column?
|
A series of a regular shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord.
|
|
|
What are the five different categories that make up the vertebral column?
|
The cervical vertebrae - first 7 vertebrae
The thoracic vertebrae - next 12 vertebrae The lumbar vertebrae- the last five vertebrae The sacrum - triangular bone below lumbar Coccyx - also known as the tailbone |
|
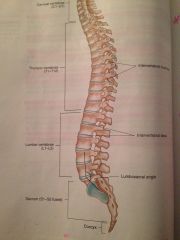
What is this?
|
Vertebral column
|
|
|
What is joint motion called?
|
Arthrokinematics
|
|
|
What is joint motion called?
|
Arthrokinematics
|
|
|
What is the difference between synovial and non synovial joints?
|
Synovial joints are held together by a joint capsule and ligaments and are most associated with movement. Non synovial joints do not have a joint cavity, connective tissue or cartilage.
|
|
|
What is joint motion called?
|
Arthrokinematics
|
|
|
What is the difference between synovial and non synovial joints?
|
Synovial joints are held together by a joint capsule and ligaments and are most associated with movement. Non synovial joints do not have a joint cavity, connective tissue or cartilage.
|
|
|
What is the function of joints?
|
Joins provide stability allowing for movement to take place without unwanted movement
|
|
|
What is the function of joints?
|
Joins provide stability allowing for movement to take place without unwanted movement
|
|
|
What are ligaments?
|
Primary connected tissue that connects bone to bone and provide stability as well as input to the nervous system
|
|
|
What are ligaments made up of?
|
Ligaments are made up of a protein called collagen.
|
|
|
What is the muscular system?
|
A series of muscles that moves the skeleton.
|
|
|
What is the muscular system?
|
A series of muscles that moves the skeleton.
|
|
|
Multiple bundles of muscle fibers held together by connective tissue is what?
|
Muscle
|
|
|
What are tendons ?
|
Structures that attach muscle to bone and provide anchors from which the muscle can exert force and control the bone and joint
|
|
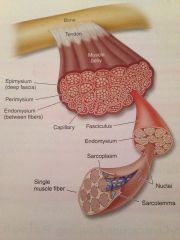
What does this diagram show?
|
Structure of skeletal muscle
|
|
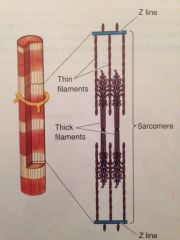
What is the function of a sarcomere ?
|
Produces muscular contraction and consists of repeating sections of actin and myosin
|
|
|
What is Neural activation
|
The contraction of a muscle generated by neural stimulation
|
|
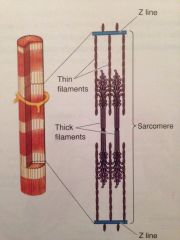
What is the function of a sarcomere ?
|
Produces muscular contraction and consists of repeating sections of actin and myosin
|
|
|
What is Neural activation
|
The contraction of a muscle generated by neural stimulation
|
|
|
What is a motor unit?
|
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it connects
|
|
|
What are neurotransmitters?
|
Chemical messages that cross the synapse between the neuron and muscle fiber transporting the electrical impulse from the nerve to the muscle
|
|
|
What are neurotransmitters?
|
Chemical messages that cross the synapse between the neuron and muscle fiber transporting the electrical impulse from the nerve to the muscle
|
|
|
Explain motor units "all or nothing" law
|
A single motor unit consist of one motor neuron and the muscle fibers it connects. Motor units cannot very in the amount of force they generate they either contract maximally or not at all.
|
|
|
What are neurotransmitters?
|
Chemical messages that cross the synapse between the neuron and muscle fiber transporting the electrical impulse from the nerve to the muscle
|
|
|
Explain motor units "all or nothing" law
|
A single motor unit consist of one motor neuron and the muscle fibers it connects. Motor units cannot very in the amount of force they generate they either contract maximally or not at all.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the two types of muscle fibers?
|
Type I - slow twitch; smaller and more resistant to fatigue. contain a large number of capillaries mitochondria and myoglobin.
Type II - fast twitch; larger in size produced maximal tension but Teague more quickly |
|
|
What are neurotransmitters?
|
Chemical messages that cross the synapse between the neuron and muscle fiber transporting the electrical impulse from the nerve to the muscle
|
|
|
Explain motor units "all or nothing" law
|
A single motor unit consist of one motor neuron and the muscle fibers it connects. Motor units cannot very in the amount of force they generate they either contract maximally or not at all.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the two types of muscle fibers?
|

|
|

What are examples of exercises and muscles used for this muscle category?
|

|
|

What are examples of exercises and muscles used for this muscle group?
|
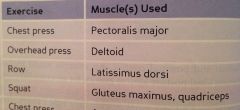
|
|

What are examples of exercises and muscles used for this muscle category ?
|

|
|

What are examples of exercises and muscles used in this muscle category?
|
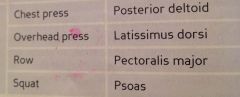
|
|
|
What is the endocrine system?
|
A system of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream to regulate ever righty of bodily functions.
|
|
|
What are the primary endocrine glands?
|
Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal
|
|
|
What are the effects of exercise in relation between insulin and glucagon?
|
As activity levels increased glucose uptake by the body cells also increases; insulin levels will drop during physical activities. Glucagon secretion from pancreas increases helping maintain a steady supply of glucose.
|

