![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anterior uveitis is seen in what conditions |
HLA B27
Sarcoidosis |
|
|
Scleritis is seen in which conditions |
(Autoimmune)
RA, SLE, Sjogrens |
|
|
Keratitis is seen in which conditions |
Vasculitides |
|
|
DDx for gritty eyes ? |
Blepharitis
Conjunctivitis
Dry eyes
Thyroid dx |
|
|
DDx for photophobia related to the eyes |
Acute glaucoma
Keratitis
Anterior uveitis
Scleritis |
|
|
Lisch nodules are seen in... |
NF |
|
|
Band keratopathy is seen in ... |
Hypercalcemia |
|
|
Blue sclera is seen in..
|
Ehler's danlos and osteogenesis imperfect
|
|
|
Lens dislocation is associated w/... |
Hypermetropia
Marfan's |
|
|
Where does the lacrimal duct drain into ? |
Interior meatus (near inferior turbinate/conchi) |
|
|
What is a normal accomodation reflex |
Convergence + miosis |
|
|
What is a CN III palsy caused by ?
S/S |
Vertebrobasilar aneurysms
Eye looks down & out Dilated |
|
|
What is a CN VI (LR6) caused by ?
S/S |
Raised ICP
Fixed convergent squint (i.e ipsilateral lateral gaze palsy ) |
|
|
If a patient has a Hx of trauma, what is your 1st line Ix ? |
Fluorescein stain + wood's lamp
Slit lamp |
|
|
What is Horner's syndrome ?
caused by ? |
Miosis + anhydrosis + pros is
Caused by: Pancoast tumor ,Brain stem lesions , Carotid/aortic aneurysm |
|
|
Characteristics of Holmes-Aldie syndrome ? |
(Opposite of horners)
Fixed dilated pupil + Sweating
hyporeflexia |
|
|
For strabismus, explain
Exo- Eso- -Tropia -Phoria
Manifest Latent |
Exo = out
Eso = in
Tropia = constant
Phoria = squint must be elicited
Manifest (-tropia) Latent (-phoria) |
|
|
Explain how to examine a squint/strabismus ? |
1. Compare light reflexes
2. Cover test ( looking @ uncovered eye) -test for Manifest squint
3. Cover/uncover test ( looking @ Covered eye) - test for Latent squint
4. Alternative cover test |
|
|
Describe the arterial supply to the eye |
Internal carotid --> ophthalmic artery --> central retinal artery + posterior ciliary artery |
|
|
What does the posterior ciliary artery supply ? |
Optic nerve |
|
|
Describe the anatomy of the eye |
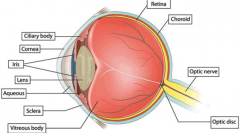
|
|
|
What is the drainage system for the aqueous humor?
Where is the aqueous humor found ? |
Poduced by Ciliary body (posterior chamber) --> drained in Canal of Schlemm ( Anterior chamber)
Found in Anterior & posterior chamber |
|
|
How is the vitreous humor drained ? |
ITS NOT !! |
|
|
What does the macula contain ?
Their function ? |
Rods & cones
Cones- for central vision, color, fine vision
Rods -for peripheral vision, Night vision |
|
|
The fovea contains what ? |
high density of cones |
|
|
describe the pathway for the light reflex |
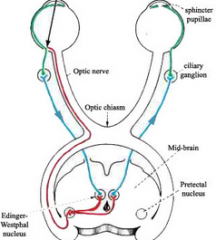
1. Retina 2. Optic nerve 3. Pre-tectal nucleus 4. Edinger westphal (supplies both eyes) 5. Oculomotor nerve -> ciliary ganglion
6. Miosis |
|
|
How do you test for visual acuity ? |
Snellen chart |
|
|
What does 6/36 mean ? |
Top line = distance read
Bottom line = Number on the chart
(6/36 means that @ 6m, this person can read what a normal person could read at 36m) |
|
|
What should you perform on Ophthalmology exam ? |
Inspection
Visual acuity Visual fields Eye movements Reflexes Fundoscopy
Blind spot Ischihara plates Fine reading Slit lamp |
|
|
What is emmetropia ? |
Normal vision |
|
|
What is hypermetropia ?
Rx ? Associated w/? |
Long-sighted (i.e Taller eye)
Rx: Convex lens
Associated w/: Lens dislocation , acute glaucoma |
|
|
What is Myopia?
Rx? Associated w/ ? |
Short-sighted ( Short eye)
Rx: Concave lens
Associated w/: Retinal detachment, Chronic glaucoma |
|
|
What is astigmatism ? |
irregular cornea |
|
|
What is presbyopia ?
What is it similar to ? Rx? |
hardening of lens - normal ageing process
Similar to Hypermetropia
Rx: Convex lens |
|
|
What is benzalkonium ? |
Preservative for eye drops |
|
|
Steroids are indicated for what eye condition ? |
Scleritis
Anterior uveitis
post-op (e.g grafts, cataracts) |
|
|
give examples of mydriatics
how do they act? |
Antimuscarinic --> Dilation
E.g - Tropicamide , Cyclopentolate |
|
|
Punctal occlusion is useful for .. |
preventing systemic absorption of eye drops |
|
|
What are these types of drug administrations?
-intracameral -Intravitreal -Subtenons |
Intracameral - into anterior chamber
intravitreal - into vitreous humor
Subtenons - to penetrate into optic nerve |
|
|
How is Anti-VEGF administered? |
Intra-vitreal |
|
|
Complications of mydriatics ? |
Acute glaucoma |
|
|
Complications of vigabatrin (AED) |
Visual field defect |
|
|
Complications of Steroids |
Cataracts
Glaucoma
worsens dendritic ulcers |
|
|
Complications of Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine
|
Retinopathy and corneal deposits
|
|
|
Complications of Rifampicin |
Orange tears |
|
|
Complications of Ethambutol |
optic neuritis |
|
|
Complications of amiodarone |
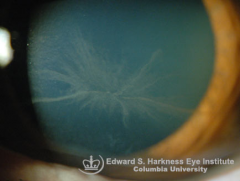
Corneal verticillata |
|
|
Complications of digoxin |
Xanthopsia ( change in color vision) |
|
|
Complications of chloramphenicol |
Gray baby
Aplastic anemia |
|
|
If there is a hypema, what do you do ? |
Emergency referral
|
|
|
If there is a chemical burn to the eye , what do you do ?
|
WASH OUT |
|
|
If there is a ?FB in the eye, what do you look out for ? |
Sympathetic ophthalmia ( blindness in unaffected eye) |
|
|
What are the S/S of a blow out fracture |
Inability to look up/down |
|
|
What is Seidel's sign ? |
Fluorescein stain showing anterior chamber leakage due to a penetrating injury |
|
|
How would you manage a penetrating trauma ? |
Cyclopentolate ( mydriatic) |
|
|
Which one is worse, an alkali or acidic burn |
Alkali! |
|
|
What is a physical burn to the eye caused by ?
Risk factor Rx |
UV radiation
Risk factor: Welding, sports (i.e snow blindness)
Rx: Cyclopentoate + analgesia/lubrication/protection |
|
|
What does CN III do ? |
Elevates eye lid
Constricts the pupil
Eye movements |
|
|
What does SO4 (trochlear) do ? |
Down & out |
|
|
Which CN palsy is a false localizing sign for raised ICP ?
What does it result in ? |
LR 6 ( Abducens nerve)
Ipsilateral Lateral gaze palsy |
|
|
A head tilt is seen in which type of CN palsy ? |
CN IV (SO4- trochlear) |
|
|
If a patient complains of difficulty walking down stairs due to double vision... what is the diagnosis ? |
CN IV (SO4) palsy |
|
|
What causes optic disc swelling ?
(3) |
Papilloedema (Bilateral + painless + normal vision)
Optic neuritis ( Unilateral + gradual central scotoma + Painful movements + Desaturation)
Ischemic optic neuropathy ( Unilateral + Altitudinal defect + painless + Pale disc ) |
|
|
DDx of RAPD ? |
optic neuritis
Ischemic optic neuropathy
Vitreal hemorrhage/CRAO/CRVO |
|
|
DDx of increased cupping |
Ischemic optic neuropathy
Glaucoma |
|
|
Ischemic optic neuropathy is caused by what ? |
-Atherosclerotic dx or -Giant cell arteritis |
|
|
DDx of bitemporal hemianopia |
Pituitary adenoma OR Craniopharyngioma (kids) |
|
|
What are the eye S/S of myasthenia gravis ?
Rx? |
Fatiguability
-Ptosis -Diplopia
Rx: pyridostigmine, steroids/IV Ig |
|
|
What are the eye S/S of Multiple sclerosis ? |
Intranuclear ophtalmoplegia
Optic neuritis |
|
|
What is intranuclear ophtalmoplegia ? |
Inability to aDDuct affected eye + nystagmus in other eye |
|
|
DDx of acute visual loss
|
(VARICOSE)
Vitreal hemorrhage/Vascular (CRVO/CRAO) ARMD - wet Retinal detachment Ischemic optic neuropathy Closed glaucoma Optic neuritis Stroke |
|
|
DDx of chronic visual loss |
(CARDIGAN)
Cataracts ARMD- dry Refractive error DM retinopathy Inherited Glaucoma - open
A Neuro |
|
|
What are the characteristics of CRAO ? |
Pale retina
Cherry red spot |
|
|
What are the characteristics of CRVO |
Retinal/Flame hemorrhages
Maculopathy |
|
|
Which is more acute , CRAO or CRVO? |
CRAO |
|
|
What are the risk factors for CRVO |
Glaucoma
Virchow's triad ( DM,HTN ect..) |
|
|
What are the risk factors for CRAO |
Emboli (Atherosclerotic-carotid, cardiac emboli)
GCA |
|
|
Rx for CRAO ? |
Ocular massage (If < 24 hrs) |
|
|
Rx for CRVO ? |
Rx underlying cause
Photocoagulation - if neovascularization |
|
|
For vitreous hemorrhage, describe
Etiology S/S Rx |
etiology: Retinal detachment, Wet ARMD
S/S: Absent red reflex, Sudden painless visual loss, RAPD
Rx: Vitrectomy (If retinal detachment --> surgery) (If Wet ARMD -> anti VEGF/photocoagulation) |
|
|
What conditions are associated with retinal detachment ? |
DM
Myopia |
|
|
Characteristics of retinal detachment |
"Curtain coming down" visual loss
Flashers/Floaters |
|
|
What is Wet ARMD caused by ?
Characteristics |
Dry ARMD + neovascularization --> hemorrhage
Metamorphopsia + sudden scotoma
|
|
|
What is characteristic of cataracts ?
What condition is associated with cataracts ? |
Glare around lights + Worse at night
Associated w/ DM, Steroid use, elderly |
|
|
What is commonest method for removing cataracts? |
Phacoemulsification |
|
|
What are the characteristics of Dry ARMD?
S/S |
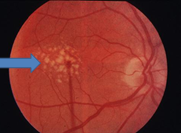
Drusen's sign
Gradual bilateral scotoma
|
|
|
what is glaucoma ?
risk factor ? |
optic nerve damage + visual field loss
risk factor: Raised IOP, Afrocaribean, FHx, Steroid use, age |
|
|
myopia is associated with which type of glaucoma ? |
Open angle glaucoma |
|
|
Hypermetropia is associated with which type of glaucoma ? |
Closed angle glaucoma |
|
|
What is normal IOP ? |
10-22 mmHg |
|
|
What is characteristics of acute closed angle glaucoma ? |
Acute painful red firm eye
Decreased vision
Haloe's around lights
Fixed mid-dilated pupil
Hazy cornea |
|
|
What is the Rx for Acute glaucoma ? |
paracentesis (1st)
Pilocarpine (constricts the eye) , acetazolamide
Surgery - Iridotomy |
|
|
What is characteristics of chronic open angle glaucoma ?
|
Arcuate defect
Increased cupping |
|
|
Rx for closed angle glaucoma |
1st - Latanolost (PG) ( ↑ outflow) 2nd -Timolol ( ↓ production)
3rd- acetazolamide or pilocarpine |
|
|
What are the side effects of latanolost ? |
Brown pigmentation of iris |
|
|
When is timolol contraindicated ? |
Asthmatic
Heart block |
|
|
What does latonolost do ? |
↑ outflow |
|
|
What does timolol do |
↓ aqueous production |
|
|
What does pilocarpine do ?
Side effects |
Mitotic (i.e parasympathomimetic)
Side effects: Headache, blurred vision |
|
|
What does acetazolamide do ?
Side effects |
↓ aqueous production
(Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor)
Side effects: Parasthesia , renal calculi |
|
|
What surgical option is there for open angle glaucoma ? |
Trabeculectomy |
|
|
What surgical option is there for closed angle glaucoma |
Paracentesis
iridotomy |
|
|
Describe the stages of Diabetic retinopathy ? |
Background/nonproliferative ( Dot/Blot hemorrhages , Hard exudates, Microaneurysms)
Pre-proliferative ( Cotton wool spots)
proliferative ( Neovascularization) |
|
|
What are the other complications of diabetic retinopathy ? |
Maculopathy
Vitreous hemorrhage |
|
|
What are the characterstics of HTN retinopathy |
Hard exudates, cotton wool spots
Flame shaped retinal hemorrhages
Silver wiring/beading of vessels
Maculopathy |
|
|
What Rx is there for HTN/DM retinopathy ? |
Photocoagulation |
|
|
Name the thyroid eye diseases |
proptosis/exophthalmos
Chemosis
Lid retraction
lid lag
Diplopia - due to swelling of extraocular muscles |
|
|
What eye diseases are associated with RA/CT disease ? |
Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca
Scleritis |
|
|
What are the eye complications of SJS ? |
Symblepharon (adhesion of conjunctival to eyelid)
Corneal ulcers |
|
|
What organisms cause bacterial conjunctivitis ?
In Children Adults Teenagers + Follicles |
Children = HiB, Strep. pneumonia
Adults= Staph. aureus
teens + follicles = Chlamydia |
|
|
Cobblestone papillae in conjunctivae ? |
Allergic conjunctivitis |
|
|
What organisms cause viral conjunctivitis? |
Adenovirus ( commonest)
Herpetic --> dendritic ulcer |
|
|
What organisms cause conjunctivitis in contact lense wearers ? |
Pseudomonas
Acanthomeba |
|
|
What organisms of ophthalmia neonatorum ? |
Chlamydia /Gonorrhoea |
|
|
Bilateral conjunctivitis + teens + follicles |
Chlamydia |
|
|
What is hutchinson's sign |
VZV
Rash @ tip of nose --> herpetic eye infection |
|
|
Rx bacterial conjunctivitis ? |
Chloramphenicol |
|
|
Side effects of chloramphenicol |
Gray baby syndrome
Asplatic anemia |
|
|
Rx of pseudomonas conjunctivitis |
Gentamycin |
|
|
Rx of Chlamydial conjunctivitis |
Oxytetracycline (+PO azithromycin if genital infection) |
|
|
Rx of herpetic conjunctivitis |
Acyclovir + chloramphenicol |
|
|
Rx of allergic conjunctivitis |
Antazoline (antihistamine) |
|
|
What is keratitis ? |
inflammation + ulceration of cornea |

