![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
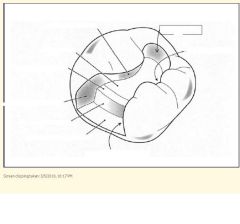
What kind of lesions are class II amalgams done on?
|
Posterior interproximal lesions
|
|
|
How do you identify where to put a class II amalgam?
|
Visual or touch
|
|
|
Proximal box of class II:
1) What degree cavosurface margin? 2) How much clearance should there be from the height of contour of the adjacent tooth? 3) What should you include in the proximal box? |
1) 90 degree (butte joint margin)
2) 0.5 mm clearance 3) All caries, existing restorations, faults |
|
|
Why should the angle formed at the cavosurface margin between the cavity prep and the external surface be 90 degrees?
|
To follow the enamel rods
|
|
|
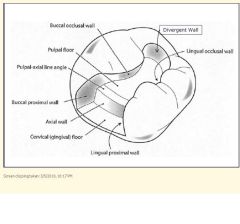
1) Occlusal table?
2) Proximal box mm depth/cavosurface to dentin floor? 3) Internal angles? 4) mm separation of box? 5) Which burs to use? 6) Facio/lingual convergence or divergence? 7) Axiopulpal line angle? 8) Proximal wall of dovetail area should converge or diverge? |
1) 1/3-1/2
2) 1.5-2.0 3) Rounded 4) 0.5 5) 330 O, 245 M,D 6) Convergence 7) Beveled 8) Diverge |
|
|
1) How much should contact be broken?
2) What is the depth of the gingival floor? |
1) 0.5 mm (width of explorer tip)
2) 1.0 mm depth axially |
|
|
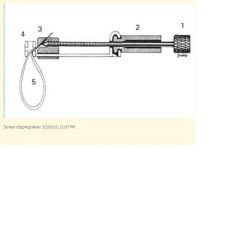
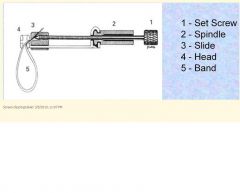
What are the five benefits of the matrix/wedge complex?
|
1) Provide rigidity to resist condensation forces
2) Template to re-establish proper anatomic contour 3) Template to re-establish proper proximal contact 4) Prevent gingival excess f restorative material 5) Ease of application/removal |
|
|
|
|
|
What are the eight steps in restoring an amalgam?
|
1) Condense/overfill occlusally
2) Rudimentary anatomy 3) Marginal ridge 4) Remove band 5) Interproximal margins 6) Carve occlusal anatomy 7) Articulating paper 8) Check interproximal contacts with floss |
|
|
What is the definition of adhesion?
|
State in which two surfaces are held together by interfacial forces which may consist of valence forces or interlocking forces or both
|
|
|
What is the definition of an adhesive?
|
Material, frequently a viscous fluid, that joints two substrates together and solidifies and is able to transfer a lod from one surface to another.
|
|
|
What are the 8 operative and preventative indications for adhesive dentistry?
|
1) Restore Class 1-6 carious/traumatic defects
2) Seal pits/fissures 3) Change shape/color of anterior teeth 4) Bond all-ceramic restorations 5) Bond indirect resin-based restorations 6) Desensitize exposed root surfaces 7) Seal beneath or bond amalgam to tooth structure 8) Impregnate dentin exposed to oral fluids, make it less susceptible to caries |
|
|
What are the two different types of adhesive dental materials?
|
1) Resin Based Composite (RBC) - chemical (auto cured or self cured) or visible light cured
2) Bonding Agents |
|
|
What is the main component of resin matrix materials?
|
Methacrylates
|
|
|
1) What is the job of filler particles in RBCs?
2) What kind of material is the filler? 3) What % filler are RBCs? 4) What is a mixture of different particle sizes called? |
1) Strength and wear resistance to restoration, b) Reduce shrinkage upon curing and polymerization
2) Quartz, silica, barium, strontium glass 3) 40-70% filler 4) Hybrid |
|
|
What do coupling agents in RBCs do?
|
Improves adherence of resin to filler, silane coats filler surfaces + increases strength by transferring stress to filler particles
|
|
|
What are the 4 components of RBCs?
|
Resin matrix (monomers), filler particles, coupling agents, polymerization activators and catalysts
|
|
|
What is the function of the catalyst in RBCs? What are the two types?
|
Initiates polymerization reaction. Chemical, visible light cured
|
|
|
Visible light cured catalyst:
1) What is activated in the catalyst by the blue light? 2) How many mm do you add resin in and why? |
1) Camphorquinone
2) Light can only penetrate 2 mm into resin, so add resin in 2 mm increments |
|
|
What are the two primary types of dental adhesion?
|
1) Mechanical - macro level
2) Chemical - atomic level |
|
|
What is the main substrate for adhesion in:
1) Enamel? 2) Dentin? |
1) 88% mineral, 2% organic, 10% water
2) 50% mineral, 25% organic, 25% water |
|
|
Kerr Dentin/Enamel bonding:
1) What is the purpose of etch? What do you etch with? 2) When you apply the primer/adhesive, what happens? |
1) Creates micromechanical retention in enamel, removes smear layer and opens dentin tubules. 35% phosphoric acid
2) Deposits monomers in tubules, creates hybrid layer in dentin and enamel bond |
|
|
What does etched dentin display?
|
Demineralized surface and exposed collagen fibers
|
|
|
What is a hybrid layer?
|
5 micron layer of resin-infused collagen
|
|
|
Visible light cured catalyst:
1) What is activated in the catalyst by the blue light? 2) How many mm do you add resin in and why? |
1) Camphorquinone
2) Light can only penetrate 2 mm into resin, so add resin in 2 mm increments |
|
|
What are the two primary types of dental adhesion?
|
1) Mechanical - macro level
2) Chemical - atomic level |
|
|
What is the main substrate for adhesion in:
1) Enamel? 2) Dentin? |
1) 88% mineral, 2% organic, 10% water
2) 50% mineral, 25% organic, 25% water |
|
|
Kerr Dentin/Enamel bonding:
1) What is the purpose of etch? What do you etch with? 2) When you apply the primer/adhesive, what happens? |
1) Creates micromechanical retention in enamel, removes smear layer and opens dentin tubules. 35% phosphoric acid
2) Deposits monomers in tubules, creates hybrid layer in dentin and enamel bond |
|
|
What does etched dentin display?
|
Demineralized surface and exposed collagen fibers
|
|
|
What is a hybrid layer?
|
5 micron layer of resin-infused collagen
|
|
|
1) How much shrinkage is usually seen with polymerization?
2) What are the 6 main problems associated with shrinkage? |
1) 1.5-3.0%
2) Adaptation, marginal staining, microleakage, secondary caries, enamel micro-cracks, post-op sensitivity |
|
|
1) What is microleakage and when does it occur?
2) What is the pathological effect of microleakage? |
1) Leakage of ions, fluids, bacteria, bacterial byproducts through tooth-restoration interface. Occurs w/ poor seal and lack of effective contact between tooth cavity and restorative material
2) Bacterial infection of dentin and pulp resulting in secondary caries and pulp pathology |
|
|
What is a common source of post-op sensitivity from RBC based composite restorations?
|
Microleakage
|
|
|
What are the four layers in dentin bonding formation of a hybrid layer
|
Composite, adhesive (all resin), hybrid layer (resin and dentin), dentin
|
|
|
How do you minimize shrinkage problems?
|
2 coats of bonding agent cured properly - thick adhesive layer reduces stress of polymerization shrinkage on tooth/adhesive interface
|
|
|
What are the 7 main indications for composite restoration?
|
1) Small-moderate restoration, preferably w/ enamel margins
2) Premolar/first molar, aesthetics 3) Doesn't have all occlusal contacts 4) Doesn't have heavy occlusal contacts 5) Can be appropriately isolated 6) Some that serve as foundations for crowns 7) Some very large restorations to strengthen weakened tooth structure (interim, economics) |
|
|
What are the 4 contraindications for composite restoration?
|
1) Can't appropriately isolate operating site
2) Restoration with heavy occlusal stresses 3) Have occlusal contacts only on composite 4) Restorations that extend onto root surface |
|
|
What are the 4 advantages of composite over amalgam?
|
1) More esthetic
2) More conservative 3) Adhesive 4) May actually strengthen tooth |
|
|
What are the 4 disadvantages of composite vs. amalgam?
|
1) polymerization shrinkage
2) more susceptible to recurrent caries 3) post-op sensitivity 4) more technique sensitive - rubber dam necessary, must not dessicate tooth |
|
|
What are the 3 main ways in which composite differs from amalgam?
|
1) Extent of prep dictated by caries
2) May retain unsupported enamel, especially for aesthetics 3) Not necessary to penetrate DEJ |
|
|
How does the occlusal depth of a composite differ from amalgam?
|
Minimum 1 mm occlusal depth on composite, 1.5 on amalgam
|
|
|
What are the steps for applying composite?
|
1) Etch prep for 15 sec
2) Rinse well lots of water 3) Dry lightly 4) 2 layers of optibond with light air drying in between 5) Light cure 20 sec 6) Composite in 2 mm increments 7) Light cure each layer 20 sec 8) Finish/polish |
|
|
What is PRR?
|
Preventative resin restoration
|

