![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
what is six sigma? (draw a picture) |
six sigma is defined as the relentless and rigorous pursuit of the reduction of variation in all critical processes to achieve continuous and breakthrough improvements that impact the bottom line of the organization and increase customer satisfaction |
|
|
|
what is the definition of a process |
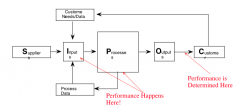
a collection of interacting components that transform inputs into outputs towards a common aim, called a mission statement. |
|
|
|
what are the three (3) types of processes |
- core processes: represent the core work of the organization (also called customer processes)
- support processes: enable core processes to be performed
- management processes: enable core and support processes to be performed (also called leadership processes) |
|
|
|
3. What are the six components of a project charter? |
- business case; - project obhective; - scope; - schedule and milestones - risks; - resources; - team roles & responsibilities |
|
|
|
What are the 7 QC Tools plus 1 (Flowchart)? Please list the tools and describe the purpose of each tool or what can be learned from each tool? |
- Check sheets - Flow chart - Cause and effect diagrams - Pareto analysis - Histograms - Scatter charts - Process control charts |
|
|
|
What are resolution methods?
|
- Do it project; - Rapid action; - Monitor project; - Standardization; - Design project; - Characterization; - Improvement |
|
|
|
Define PDCA (PDSA). (Please include a brief description of the output of each step.) |
Plan: team members develop a theory about the problem and plan change. They collect and study available data, determine if new data are necessary, and how to use these data;
Do: team members carry out the change, preferably on a small scale, to test their theory;
Check: team members study the effects of the change to determine if there was any improvement to confirm their theory. They also look for unanticipated side effects from the change;
Act: team members decide to take appropriate action and standardize the improvement based on results of the study. If the results from the study indicate that the proposed change did not result in improvement, the action taken might be to return to the plan and refine the theory |
|
|
|
What does DxVxF>R mean and how might you use it? |
this formula can be used to determine if a rapid action project should be undertaken.
Dissatisfaction*Vision*First Steps > Resistance to change |
This formula can be used to determine if a rapid action project should be undertaken. Guiding principle to rapid action design: DissatisfactionxVisionxFirststeps > ResistanceToChange
|
|
|
Briefly explain the three components of a good operational definition and also explain why operational definitions are important. |
Operational definition is one that people can do business with. It must be communicable with same meaning to all involved. 1) a statement of what is required by the customer or criteria to be measured;
2) a test - detailed process for measuring (CTQ's);
3) a decision that determines if a given output of VOC meets customer spec |
|
|
|
Define common cause variation and special cause variation. How would you work to improve a process that displays only common cause variation? What would be your action if there were evidence that a special cause may exist? |
- Special cause variation: something has changed, not inherent in the process. Responsibility of workers and engineers; if they cant fix it they ask for help from management -
- Common cause variation: inherent or built into the system (responsibility of management to change policies and procedures that define common causes) |
|
|
|
What problems could occur when you do not understand the difference between common and special cause variation? |
Confusing common cause variation with special cause (type I error) means that root cause wouldn’t be addressed, or misinterpretation of data causes more problems (wrong tool for the wrong kind of data).
Type II error is when special cause variation is confused with common cause variation. |
(hint: Type I and Type II Error)
|
|
|
What is process characterization? Why is characterizing a process important? What are the 8 Steps for Characterizing a Process?
|
Process characterization is following a series of 8 steps to get to root cause, and understanding the process. Characterizing a process is important because you want to fully understand a process to properly apply the 7 steps of problem solving.
1. process owners/stakeholders 2. purpose & outputs 3. customer needs/requirements 4. suppliers & inputs 5. flowchart 6. baseline 7. current performance 8. sources of variation |
1) Process owners/stakeholders 2) Purpose (outputs) 3) Customer needs/requirements 4) Suppliers (inputs) 5) Flowchart 6) Baseline 7) Performance 8) Sources of variation
|
|
|
How would you coach a manager/leader who, through good intentions, wants to “tamper” with a process?
|
Explain how changing a process blindly often causes more problems than solutions. Can also make a process more complex and difficult to analyze.
|
|
|
|
What are the four different types of data? Please give an example of each type of data. Why is it important to know understand these different types of data? |
-Discrete: 1) verbatims - testimonies, opinions, textual 2) categorical - yes/no, unordered, ordered 3) count (#) -Continuous (measurement) |
Discrete: 1) Verbatims – testimonies, opinions, textual customer feedback. 2) Categorical – yes/no, unordered, ordered. 3) Count – number of instances of scrap. -- Continuous: 4) Continuous (measurement) – weight of part.; It is it important to know the type of data you have because many tools are data-type dependent
|
|
|
What is the key output of Improve? Step? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you. |
To identify performance issues. This step is important because it identifies the gaps between current and desired state. Identifies what obstacles are preventing the achievement of the target condition, and how to prioritize and attack the obstacles.
This can be achieved with relentless, systematic problem solving,
ie) pareto chart, run charts, control charts, PACE MATRIX |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Establish the Focus? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you. |
1. The purpose is to view the process flow, describe current situation with data, develop strategies and measure;
2. Output: knowledge from different perspectives, strategies and strategy measures;
3. It is important to identify X’s, narrow the focus (Baseline the process); 4. Tools used: Data collection stratification, run chart, flow chart, DPO, SPU, DPMO, process sigma, pareto diagram |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Examine the Current Situation? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you.
|
Key output is identifying the Y’s of the process.
This step is important because the process needs to be fully understood before trying to tackle a problem. Identify X variables and prioritize them.
tools: Flowcharts, value stream maps, check sheets are methods to help assist you. Flowcharts help visualize and narrow the focus/scope, value stream maps identify NVA and VA activities, and check sheets with pareto diagrams can be used to stratify the problem. |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Analyze the Causes? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you. |
1.Purpose is to find the root causes of the problem, refined with data and addressed
2. Output: theory of a Root cause of the problem
3.Why is it important: select the root causes and eliminate or minimize;
-- Tools: Cause and effect diagram, hypothesis testing |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Act on the Causes? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you.
|
The objective of this step is to develop and implement actions on a small scale to address root causes. This is done in four (4) steps:
1)brainstorm possible actions (tools: TRIZ for sorting through designs)
2) select actions to take (tools: PACE matrix to filter imminant actions to take first)
3) develop action plans
4) implement actions on small scale |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Study the Results? Why is this Step important? What tools might you use to assist you in this step? Please explain how the tools may help you.
|
The objective of this step is to determine whether the actions were successful and modify action plans as necessary. It is done in the following steps:
1) study the results and modify action plans [review the data from the implementation and change as necessary; maybe use hypothesis testing to see if there is a difference between the original state and implemented state]
2) implement actions on large scale (to meet the project objectives) |
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Standardize the changes? |
The purpose of Standardize the changes is to “lock-in” successful actions and develop a process management plan to roll the successful actions in a larger scale. |
|
|
|
What is a process management plan? Why is a process management plan important? |
A PMP is a system put in place to monitor and review the future performance of the process. It is important because it allows to make sure that the system is responding the actions that are standardized and allows to have time to react as soon as something goes wrong |
|
|
|
What is the key output of Draw Conclusions? Why is this Step important?
|
Draw Conclusions identifies benefits, difficulties and Lessons Learned and also discusses Future plans. It is important to identify what you would do differently in the future, this allows for continuity and puts the next team that will work on the project, equipment or area a much better shape and will make the organization get better results. Continuous improvement (Six Sigma) |
|
|
|
What does the term Y=f(X1, X2, X3,….Xn) mean? Why is this term important? |
The lagging measure Y, is a function of a number of leading measures, X1, X2, X3, X4. This is important because an undesirable output of a process might be the result of a number of issues upstream. Identifying each of the leading measures helps close the gap through rigorous problem solving. |
|

