![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
An operating system is |
A program that manages the computer hardware. It provides an intermediary between the computer user and the computer hardware |
|
|
Picture example 1 |
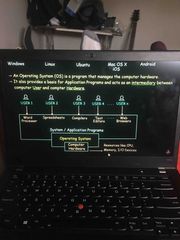
Back (Definition) |
|
|
If we didn’t have OS would computers still be effective? |
No the OS does all the minute scale processes so we don’t have to tell the hardware to do things like open an app, we just click it. |
|
|
Types of OS |
Batch Time Sharing Distributed Network Real Time Multi Programming/processing/tasking |
|
|
Goals of OS |
Convenience Efficiency |
|
|
Functions of OS |
Interface between user and hardware Allocation of resources Management of memory, security, etc. |
|
|
What are resources allocated in an OS? |
Memory, CPU and I/O Devices |
|
|
What is a CPU? What does it do? Where is it? |
Central Processing Unit It is the brain of the computer hardware, does all of the calculations. In the motherboard. |
|
|
Bootstrap Program |
The first program that runs when a computer is powered up. Stored in ROM (Read only memory) It loads the OS and the OS Kernel |
|
|
Interrupt |
Signalled from hardware triggered when the hardware sends a signal to the CPU |
|
|
System call (monitor call) |
Software may trigger an interrupt by using the operation system call. |
|
|
What happens when a CPU is interrupted? |
It stops what it is doing and immediately transfers execution to a fixed location (The IRS) The interior service routine executes. After completion the CPU resumes what it was doing before interrupted. |
|
|
Storage Structure |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Registers |
Holds little amount but is very fast. Volatile |
|
|
Cache |
Holds a little more than the register but is a little slower Volatile |
|
|
Main memory (RAM) |
Anything loaded in the computer is loaded to the main memory for execution Volatile |
|
|
Secondary storage |
Stores everything larger than the ram waiting to be loaded to the main memory. Electronic Disk Magnetic Disk Optical Disk Magnetic Tapes Non Volatile |
|
|
Volatile |
Loses its contents when power is removed. |
|
|
Non Volatile |
Retains its contents even when power is removed |
|
|
Types of Processor systems |
Single Processor Many processor Clustered processor |

