![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain One Health |
Environment, animal, and human health inextricably linked |
|
|
What is health? |
A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity |
|
|
What is disease? |
Absence of health; a non-compensated perturbation of one or several functions of the host. |
|
|
What is epidemiology? |
The study of health status of populations |
|
|
What is a case definition? |
Set of uniform criteria used to define a disease for public health surveillance |
|
|
What is an epidemic? |
The occurrence of more cases of disease than expected in a given area or among a specific group of people over a particular period of time |
|
|
What is an outbreak? |
The occurrence of cases of disease in excess of what would normally be expected in a defined community, geographical area or season |
|
|
What is a pandemic? |
An epidemic that becomes very widespread and affects a whole region, a continent, or the world due to a susceptible population |
|
|
By definition, what does a true pandemic cause? |
A high degree of mortality |
|
|
What is attack rate? |
#new cases in population at risk/ #of people in population at risk |
|
|
Example of attack rate |
3 health care providers contracted Ebola virus; 100 health care providers treated Ebola patients 3/100=3% |
|
|
What is crude mortality rate? |
Mortality rate from all causes of death for a population during a specified time period |
|
|
What is case fatality rate? |
Proportion of animals/persons with a particular condition/case who die from that condition
|
|
|
Formula for case fatality rate |
number of cause-specific deaths among those cases/number of incident cases |
|
|
What is cause specific death rate? |
Number of deaths from a specified case per 100,000 person/animal-year |
|
|
What is the epidemiology triad? |
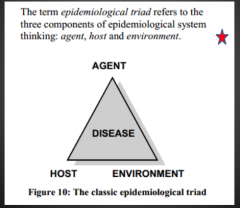
|
|
|
What is a ratio? |
Relationship between two observations |
|
|
What is a proportion? |
Fractions where numerator is in the denominator. Often expressed as a percentage or decimal. |
|
|
What is incidence? |
NEW cases |
|
|
What is prevalence? |
ALL cases |
|
|
What is incidence rate? |
new cases/population at risk in time |
|
|
What is cumulative incidence? |
The total number of new cases in a period of time |
|
|
What is prevalence rate? |
Total cases/population at risk in time |
|
|
What is risk factor? |
A characteristic of value in predicting risk |
|
|
What is absolute risk? |
The rate of occurrence and is the same as incidence |
|
|
What is relative risk? |
Incidence rate among exposed/incidence rate of among not exposed |
|
|
What is attributable risk? |
Incidence rate exposed-incident rate of unexposed |
|
|
Normal bell curve |
Mean, median, and mode are all the same; represents a perfectly symmetrical distribution |
|
|
Negatively skewed bell curve |
Mode>median>mean; negative direction
|
|
|
Positively skewed |
Mode |
|
|
What is probability? |
The numerical expression of the likelihood of occurrence |
|
|
What is conditional probability? |
The chances of A knowing B has occurred |
|
|
When is the multiplication rule used? |
Calculate probability of independent events both occurring (A and B) Pr (A and B)= Pr (A) x Pr (B) |
|
|
When is the addition rule used? |
Calculate the probability of independent events either occurring (A or B) Pr (A or B)=Pr (A) +/- Pr (B) |
|
|
What is a target population? |
The collection of individuals, items, or measurements that we want to study and make inferences about.
|
|
|
What is sampling error? |
The difference between the sample result and the population characteristic we seek to estimate |
|
|
What is random sampling? |
A selection process that gives each member of the population being studied an equal chance to be chosen; attempts to replicate the characteristics of the target population using a sample |
|
|
What is a standard error of measurement? |
The variability of a sample statistic |
|
|
What is confidence interval? |
The confidence that the tested sample result is within a range of the true number of the tested population |
|
|
What is nominal data? |
Refers to categorically discrete data such as name |
|
|
What is ordinal data? |
Data that has a discrete ranking |
|
|
What is interval data? |
Like ordinal except the intervals between each value are equally split. |
|
|
What is ratio data? |
Interval data with a natural zero |
|
|
What is statistical significance? |
The probability that an effect observed is occurring because of chance; expressed as p-value |
|
|
The smaller the p-value...... |
The less likely it is that the results are due to chance; the higher the confidence in the evidence |
|
|
What p-value is accepted as probably true? |
p<0.05 |
|
|
What is a null hypothesis? |
Statement that there is no difference between two events |
|
|
What are confounding factors? |
Additional variables that could influence results that are not considered in the subject population selection (unknown bias) |
|
|
What is standard variation? |
Amount of variation r dispersion from the average |
|
|
What is the percentage of 1 standard deviation? |
68.2% |
|
|
What is the percentage of 2 standard deviations? |
95.4% |
|
|
What is the percentage of 3 standard deviations? |
99.7% |
|
|
What is precision? |
The repeatability, or reproducibility of the measurement |
|
|
What is accuracy? |
The proximity of measurement results to the true (actual) value |
|
|
What is sensitivity? |
The ability of a test to give a positive finding on those with a disease (true positive) |
|
|
What is specificity? |
The ability to give a negative finding if there is no disease (true negative) |
|
|
What is the formula for sensitivity? |
TP/ (TP + FN) |
|
|
What is the formula for specificity? |
TN/ (FP + TN)
|
|
|
What is the formula for accuracy? |
(TP+TN)/(TP+FP+FN+TN) |
|
|
What is testing accuracy? |
The number of correct tests (true positive and true negative) out of the total tests |
|
|
What is the point of sampling? |
To infer results from the sample population to the target population |
|
|
What is sampling bias? |
A bias in which a sample is collected in such a way that some anials of the intended population are less likely to be included than others |
|
|
Is it okay to have sampling bias? |
Yes, it's very hard not to have some sampling bias. As long as you can look at how the samples were derived and understand the limitations |
|
|
What is random sampling? |
Each sample item has an equal chance of being selected |
|
|
What sampling error? |
The error that arises as a result of taking a sample from a population rather than using the whole population |

