![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why did the SELECT trial happen at all?
|
Essentially there were a few trials before it namely the Nutritional Prevention of Cancer (NPC) trial and the Alpha Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer Prevention study (ATBC) that showed prostate cancer risks were reduced by 63% for selenized yeast and 32% for a-tocopherol. There was also a large scale randomized controlled trial that showed that a combination of selenium, vitamin E, and beta carotene reduced overall cancer mortality. This was all epidemiological and preclinical data and therefore the SELECT trial.
|
|
|
What type of trial was the SELECT trial?
|
This was a phase III trial, which means that there is preliminary data that this drug may reduce the risk of prostate cancer in phase I & II trials and that it can go ahead with phase II or larger trials. It was a randomized, placebo controlled trial. Patients got either selenium, vitamin E, selenium + vitamin E, or placebo with the primary end point of prevention of prostate cancer. The trial took place between 2001 & 2008.
|
|
|
Were patients in the SELECT trial required to have annual PSA & DRE examinations?
|
No, no standardized across all study centers as this was a multi-instiution study, as there wasn't strong evidence at the time that this study was began for this practice patients were screened based on the practice pattern of the institution that they were at.
|
|
|
What is the social security death index?
|
This is part of the social security act that was initiated by FDR in which this contains the information of persons who have died, and their SSN, place of death, etc. It is not necessarily a complete file and therefore if a person's name is not in there it doesn't necessarily mean that they are alive.
It was put in place by FDR for the purpose of "social security" So if someone died then certain family members might be eligible for benefits if they paid into social security long enough. |
|
|
What was the basic design of the SELECT trial?
|
It was designed to be a 4 group trial with 5 prespecified comparisons. The groups were selenium vs placebo, vitamin E vs placebo, selenium + vitamin E vs placebo, selenium vs selenium + vitamine E, vitamin E vs selenium + vitamin E.
The really fascinating thing about this study is the assumptions that they had to make to determine how many patients would be needed for to power the study, these are listed in the study. |
|
|
What was the basic outcome of the SELECT trial?
|
The study ended early essentially because they determined that their alternative hypothesis was true that there no benefit from either study agent was identified and with the level that the study was powered continuing the study would be frutiless to determine a difference.
Essentially the hazard ratio was not increased and the precentage of patients in each trial group, including placebo that got prostate cancer was about 4%. |
|
|
What is Lupron? What are some typical side effects?
|
Lupron is a medication that we use for advanced prostate cancer. It is an analog of LH-RH that causes the release of LH or it is an LH agonist. This causes initially an increase in testosterone produciton which then will shut off testosterone production because the body typically produces LH in pulses and when this is shut off and the body gets a constant amount of LH without pulsatile nature then it becomes an antagonist.
When looking at research trials with this agent there was a surge in testosterone for the first week that may be associated with increased symptoms such as bone pain, UTIs, urinary obstruction, etc if not combined with an adrogen receptor antagonist. Levels go back to baseline around the second week and the decrease after that. Ginger's book states that typical side effects can include headaches, bloating, difficulty concentrating. |
|
|
Why had selenium possibly worked to prevent prostate cancer in some early preclinical studies but not shown to be benefit in the SELECT trial?
|
1.) Possible Selenium Format - They used L-selenomethionine as opposed to high-selenium yeast this is different format, but did for good reasons. Hard to get standardized form of the high selenium yeast, the active ingredient in that compound was thought to be the selenomethionine, there is potential toxicity with long term use of high selenium yeast, and in vitro data show that selenomethionine is affective in suppressing malignant prostate cells.
2.) Could have been chance finding in the previous NPC study because was small sample size and there was multiple testing done on that group 3.) The NPC trial was done in men deficient in selenium and the SELECT trial patients had normal baseline selenium. |
|
|
What is a possible reason why vitamin E was not affective in preveinting prostate cancer in the SELECT trial?
|
1.) Possible used to high of a dose, although the dose was chosen because the men in the ATBC study that had the highest reduction in prostate and lung cancer were those with the highest baseline vitamin E levels.
2.) Again these patients weren't smokers and some research has shwon that it is more protective in men that are smokers, and only a small subset of the SELECT trial were smokers. |
|
|
What comments does the SELECT trial have on the high dose vitamin E being associated with increased all cause mortality and cardiovascular events?
|
This study basically tries to debunk that. They weren't powered to study that and it wasn't there primary end point but the point they make is that we had thousands of these guys on high dose vitamin E for a long period of time and there wasn't an increased risk of cardiovascular event or mortality. They point that in many of the studies that the meta-analysis show that result in were in pateints with significant comorbidiites.
|
|
|
What is the clinical TNM staging for prostate cancer?
|
pT0 - no tumor identified
pT1a - tumor found in <5% of TURP specimen & grade <7 pT1b - tumor found in >5% of TURP specimen &/or grade >7 pT1c - tumor identified based on screening PSA & then prostate biopsy. pT2 disease in general is organ confined disease pT2a- disease in less than one half of one lobe or less pT2b - tumor involves more than one half of one lobe but not both pT2c - tumor involves both sides pT3 - palpable tumor beyond prostate pT3a - extraprostatic extension unilateral or bilateral pT3b - tumor invvolves seminal vesicles pT4 - tumor is fixed or invades adjacent organs |
|
|
If a patient is s/p RALP for prostate cancer, what is Dr. Pruthi's cut-off value for evidence of biochemical recurrence & referral for a patient for radiation?
|
*0.4ng/dl. He states that there was research done here at UNC looking at the 0.2 levels and the 0.1 levels and there was a high percentage of those patients that returned back to undetectable levels and they weren't really real.
*0.4ng/dl is still early radiation, Dr. Pruthi was stating that they used to go to like 10 or 12 and still consider that early vs delayed radiation therapy for prostate cancer. |
|
|
What is Vantas?
|
Histrelin, which is a GnRH agonist (just like Lupron or Leuprolide). Used for treatment of advanced prostate cancer.
Hide It in the Skin for the first part of Histrelin....or Vantas....Annual Treatment of Advanced Symptoms Inserted once very year subcutaneously. |
|
|
What is the D'Amico criteria for high risk prostate cancer?
|
*this is based on the convential pre-op information that we have for patients w/ prostate cancer such as PSA, grade, biopsy results, & clinical T stage.
*Criteria state that men w/ PSA >20ng/dl, gleason grade 8-10, and or clinical stage greter than or equal to stage T2c, based on 92 system for TNM staging where this is bilateral palpable disease. |
|
|
What are the Partin Tables and when were they constructed? What parameters do they *****?
|
Partin tables were initially constructed in the 1990s and updated in 2001, assisting in the
preoperative prediction of final pathologic stage in men with clinically localized prostate cancer undergoing radical prostatectomy. These tables look at PSA, Gleason grade, and clinical stage. Pre-op assessment of Post-op Path after Prostatectomy! |
|
|
What is probably the most widely used tool to predict recurrence after local therapy for prostate cancer?
|
The most widely used tools to predict disease recurrence after local therapy are
the nomograms developed by Kattan and colleagues |
|
|
How many men needed to be screened to prevent one death from CaP in the european trilal? How does that compare with other things such as fecal occult blood tests or mammograms?
|
Notably, 1410 men
needed to be screened to prevent 1 prostate cancer death; however, the number of screenings to prevent 1 cancer death was similar to the numbers reported in studies of mammographic screening for breast cancer and fecal occult blood testing for colorectal cancer. |
|
|
Has neo-adjuvant hormone therapy proven to show a survival benefit for men with prostate cancer before prostatectomy, low, intermediate, or high risk patients?
|
Neoadjuvant androgen-suppressive
therapy prior to prostatectomy showed reduction in pathological stage after androgen suppression but showed no benefit in cancer-free survival. |
|
|
What is the lifetime risk of prostate cancer death from those patients that fit into the watchful waiting category, in other words those patients with low risk disease?
|
Among patients with low-risk prostate cancers, only a limited subset may harbor the potential for clinical metastasis. Without treatment, the long-term risk of cancer death from Gleason 6 cancers, like that of Mr D, is 27%.
|
|
|
What is conformal radiation treatment for prostate cancer? What is intensity modulated radiation?
|
Threedimensional conformal radiation uses images obtained from a computed tomographic scan to shape the radiation beams to the target tissue.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy is a form of conformal radiation in which the radiation energy of small areas in each beam is modulated, allowing refined shaping of the radiation dose around the target structure. |
|
|
If a patient is to undergo radiation for primary treatment of their CaP, and they are high risk, is there a benefit to getting pelvic radiation to the lymph nodes?
|
"The addition of radiation to the pelvis to treat pelvic lymph nodes has been evaluated in patients with high-risk cancers without a definitive survival benefit." This is the statement from the recent version of Campbell's, but there is a 2006 study of the RTOG 9413 that patients that got Neoadjuvant plus Adjuvant hormones as well as whole pelvic field radiation was better than prostate only radiation...review this study.
|
|
|
What are the acute symptoms of radiation as primary treatment for prostate cancer?
|
Acute toxic effects of radiotherapy include urinary frequency, urgency, or dysuria reported by 11% to 18% of patients (without such problems at baseline) and rectal urgency, frequency, or pain in 13% to 15%. By 1 to 2 years after treatment, urinary symptoms typically subside, but1 in 10 men report rectal symptoms as becoming a persistently moderate or big problem.
|
|
|
What is contained within the brachytherapy seeds?
|
These sealed sources contain radioactive iodine 125, palladium
103, or cesium 131 and emit low-energy radiation with doses limited to within millimeters of the seeds; none of these isotopes has been shown to be superior. |
|
|
What patients are bad candidates for brachytherapy?
|
Brachytherapy is contraindicated in prostates larger than
60 mL in size due to anatomic constraints of the pubic arch that preclude delivery of a sufficient distribution of seeds for adequate radiation dose.56 In addition, men with significant obstructive lower urinary tract symptoms prior to treatment may require long-term catheterization and are not optimal candidates for brachytherapy. Also brachytherapy alone not good idea in men with intermediate risk prostate cancer.... |
|
|
When was PSA approved?
|
by the FDA in 1986 to monitor men with prostate cancer for recurrent disease.
|
|
|
A patient has radiation therapy as primary therapy for their prostate cancer. After treatment they have a rising PSA, how long before they will have clinically detectable disease?
|
increasing PSA precedes clinically detectable recurrent disease by 3-5 years on average.
|
|
|
How does Wallen follow his patients post-prostatectomy that have a PSA that is undetectable post-op?
|
Wallen follow-up post-prostatectomy for prostate cancer is a PSA every 3 months for a year, every 6 months for a year, and then every year for 3 years for a total of 5 years of follow-up. If there PSA remains undetectable then they are done.
|
|
|
Is there a role for PLND in patients with low risk prostate cancer?
|
Well that is debatable. AUA Update '09 states that for patients with low risk prostate cancer, PSA<10, Gleason 6 disease, T1C clinical stage that many have shown the risk of LNI to be <5%, but these studies were using an obturator only sampling. The authors therefore conclude that if a more extensive node dissection was performed the rate of positive nodes would increase to about 11-17%.
*The drive home point for them was that men with low risk prostate cancer did not have a zero risk for LNI. *They also argue against the obturator only node dissection. Basically they state that several surgical studies have mapped out the LN drainage of the prostate and shown it to be variable and that for these patients you should do a more extensive dissection if you are going to do one. |
|
|
What are the complications of PLND?
|
*For men with RRP the risk of lymphocele is there and subsequent nerve compression and symptoms from the lymphocele. For robotic prostatectomy since you are intraperitoneal the risk of lymphocele is almost zero, but not zero and Wallen states that you can sometimes get them anyway.
|
|

|
in this case you would attempt a posterior sagital anal repair. An intra-abdominal repair would be difficult this far deep into the pelvis and so the first attempt would be from the perineum. The patient may ultimately need a urinary diversion but this can be attempted first.
|
|

|
Ketoconazole can get a patient to castrate levels within 48 hours and is the quickest way.
|
|
|
What is the role for the use of bisphosphonates in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer?
|

The answer to this question is now controversial however. There are several scenarios to consider this in:
1.) Delay skeletal progression 2.) Prevention of treatment related bone loss in men on ADT 3.) Palliation of bone pain. 4.) Prophylaxis against bone mets. |
|
|
What is Casodex?
|
Bicalutamide - Best tolerated. A nonsteroidal antiandrogen with a long serum half-life (6 days), bicalutamide has a once-per-day dosing schedule and therefore likely better compliance. It is the most potent of the nonsteroidal antiandrogens. These medications work on the androgen receptor.
|
|
|
What is Lupron?
|
*Leuprolide - it is a GnRH agonist, but given in a constant fashion will cause suppression of GnRH secretion and decrease testosterone levels. It works by desensitizing the receptors on the anterior pituitary and therefore you get no more secretion of LH and thus drop in testosterone.
|
|
|
What is trade name for Flutamide?
|
*Eulexin
|
|
|
A 69 year old pT2b Gleason 4 + 3 (7) adenocarcinoma of the prostate and a prostate volume of 30cc. PSA is 16.5ng/dl. CT scan of the abdomen & pelvis and bone scan are negative. He has radioactive seed implants. The most appropriate treatment regimen is what?
|
He should get external beam radiation, seed implants as well as hormone therapy as he has high risk prostate cancer with the PSA value and the fact that it is T2 disease.
|
|
|
The most substantial risk of mitoxantrone therapy is what?
|
*This is a chemotherapeutic that his used for hormone resistance prostate cancer. It has the risk of cardiotoxicity and patients who have symptoms at all should have a MUGA scan before initiation of therapy and be monitored closely during therapy.
|
|
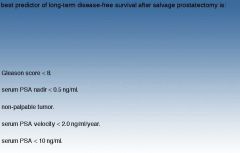
|
*PSA level being less than 10ng/dl. When thinking about radiation therapy as primary therapy a PSA nadir to less than 0.5 is a good prognostic indicatory but it has no value in predicting long term success for salvage prostatectomy.
|
|
|
You have a patient that has a history of prostate cancer s/p XRT for treatment with now recalcitrant hemorrhagic cystitis. You have decided to start him on po Amicar. What is the dosage for Amicar? What is the generic name and how does it work?
|
*Amicar is also known as Epsilon - Aminocaproic acid. It can be given either po/iv or intravesical as a solution.
*Amicar works by inhibiting the activity of urokinase, which breaks plasminogen down into plasmin. Plasmin is a protein that works to break down fibrin clots. The po and IV doses are the same with the maximum dosage of 30 grams a day. Oral - give 5 grams during first hour, following by 1-1.25 grams/hour for approximately 8 hours or until bleeding stops. IV - Give 4-5 grams in 250ml of diluent during first hour followed by continuous infusion at the rate of 1-1.25gram/hour in 50ml of diluent, continue for 8 hours or until bleeding stops. |
|
|
A 55 year old man undergoes a difficult radical perineal prostatectomy that lasts six hours. Postop he has weakness of the left foot with inability to dorsiflex. The nerve most lkely injured is the what?
|
*Peroneal nerve. It leaves the popliteal fossa and crosses to the anterior part of the leg laterally around the bony prominence of the knee and can be exposed to compression and stretch injury in prolonged lithotomy cases. It supplies the tibialis anterior and patients can't dorsifelx.
|
|
|
A 55 year old man undergoes a difficult radical perineal prostatectomy that lasts six hours. Postop he has weakness of the left foot with inability to dorsiflex. The nerve most lkely injured is the what?
|
*Peroneal nerve. It leaves the popliteal fossa and crosses to the anterior part of the leg laterally around the bony prominence of the knee and can be exposed to compression and stretch injury in prolonged lithotomy cases. It supplies the tibialis anterior and patients can't dorsifelx.
|
|
|
What is Bicalutamide?
|
*Androgen receptor blocker also known as Casodex
|
|

|

|
|
|
People have looked at choline PET/CT scanning to help determine if post curative treatment (radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy) PSA rises represent local recurrent disease or metastatic disease. Why is it not a recommended modality in looking at post radiation recurrence?
|
*This is because benign prostatic tissue as well as tumoural prostate tissue presents a physiological uptake of choline and therefore some believe that PET/CT is not suitable for detection of local recurrences after EBRT as the remaining viable benign prostate tissue after treatment will also light up.
|
|
|
Is the prostate a prolate sphere and why or why not?
|
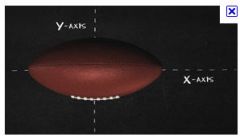
A prolate sphere is a sphere where the distance between the poles is larger than the equator.
|
|
|
What is the difference between 3D conformal radiation and old school radiation for prostate cancer?
|
*3D conformal radiation was the major advance of the 1990s and incorporated CT scans into radiation planning. This allowed direct visualization of the prostate as well as teh use of shaped beams and multiple beam angles that delivered less dose to the bladder and rectum. The old school radiation was simply based on xrays and bony landmarks.
*In a randomized trial 3D compared to 2D (old school) was associated with less acute and late radiation proctitis. |
|
|
What is IMRT?
|
This stands for intensity modulated radiation therapy which theoretically can spare more normal tissue than traditional 3D conformal therapy. IMRT improves upon 3D conformal therapy by subdividing each beam into tiny beamlets. The amount of radation passing through each beamlet can be controlled, therby allowing for greater degrees of freedom in radiation planning.
*The center with the greatest experience with IMRT is MSKCC. The patients get higher radiation instead of more traditional 64 Gy these patients are getting >75Gy or even higher dose at 81Gy. |
|
|
What are potential downsides of IMRT?
|
*While IMRT has many advantages it also has disadvantages. Treatment delivery takes 20 minutes a day versus 10 minutes a day for 3D conformal radiation and so fewer men can be treated on a machine each day. The cost to plan and deliver IMRT is significantly more than that of 3D conformal therapy (47,931 for IMRT vs 21,865 for 3D).
*In addition the multiple beam angles used and longer treatment times mean that more areas of non-target tissue will receive radiation during treatment. No one is for sure if this is associated with higher risk of long term radiation induced malignancies. |
|
|
What is a typical course of radiation therapy for prostate cancer as primary treatment?
|
*8 weeks
|
|
|
What does scintigraphy mean?
|
Scintigraphy ("scint," Latin scintilla, spark) is a form of diagnostic test used in nuclear medicine, wherein radioisotopes (here called radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally, and the emitted radiation is captured by external detectors (gamma cameras) to form two-dimensional[1] images
|

