![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
#1 cause of cancer death in the world (and canada? |
lung |
|
|
mortality? |
80% |
|
|
relationship of smoking and lung cancer? other causes? 4 |
90% of cases due to smoking other 10% 1. radon gas 2. workplace exposure (asbestos, argon, arsenic) 3. second hand smoke 4. RT |
|
|
Lung cancer screening? |
NOT currently done in canada |
|
|
Def'n of a SPN + features that suggest benign or malignant cause |

|
|
|
workup and management of SPN |
1. CT 2. needle biopsy/PET in selected cases 3. surgical removal unless clearly benign note: if cancer, proceed to lobectomy |
|
|
Paraneoplastic syndromes in NSCLC? 3 |
1. clubbing and hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (adeno > SCLC) 2. hpyercalcemia from PTH-rp (squamous cell) 3. gynecomastia (HCG (large cell)) |
|
|
paraneoplastic syndromes in SCLC 3 |
1. cushings from ectopic ACTH 2. Neuro: Eaton lambert, neuropathy, cerebellar degeneration 3. hyponatremia from SIADH (euvolemic hyponatremia) |
|
|
Suspected lung cancer.. need to get some tissue central vs peripheral sampling |
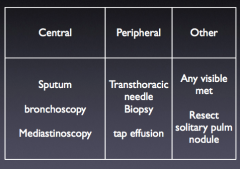
|
|
|
major distinction to make: in Lung Ca |
SCLC vs. NSCLC |
|
|
SCLC: 1. extent of spread at diagnosis 2. paraneoplastic syndromes.. 3. tx modalities? 4. resistance issues |

|
|
|
SCLC: how is limited disease defined? extensive disease? |
limited: tumor in one lung, mediastinum and LNs that can be radiated to an adequate dose to control the cancer with an ACCEPTABLE risk of toxicity extensive disease: has spread beyond one lung, the mediastinum, and local LNs |
|
|
Tx of SCLC: limited disease? 3 Extensive disease? 2 |

|
|
|
survival: benefits of treatment |
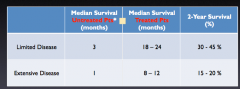
|
|
|
Histologic types of lung Ca 1. SC 2. NSC 3. other |
Small cell (10-15%) Non-small cell (85-90%): Squamous cell Adenocarcinoma Large cell Bronchoalveolar ..... etc. Other - metastases, carcinoid, lymphoma etc.. |
|
|
How to stage the lung Ca patient ? which indications are indicated |

|
|
|
TNM staging for NSCLC I through IV |

|
|
|
treatments corresponding to stages of NSCLC |

|
|
|
concept: resectable vs. Operable |

|
|
|
outcomes for early stage therapy |

|
|
|
role of adjuvant therapy in resected disease? |
no benefit from adjuvant radiation adjuvant chemo: 5-15% survival benefit 5 y overall survival |
|
|
tx for locally advanced NSCLC (no mets, but extensive tumor invasion or mediastinal adenopathy) |
Combination chemoradiotherapy 5yOS is about 10-15% , median survival 17 mo. |
|
|
complications of pancoast tumors? 2 |
1. frequent vertebral invasion
2. neurovascular invasion (shoulder/arm pain, horner's, arm weakness and mm atrophy |
|
|
tx pancoast tumors |

|
|
|
tx of early stage disease outcomes/cure rates |

|
|
|
RT for early stage disease |
radical radiothterapy in 30-33 daily treatments (fractions) |
|
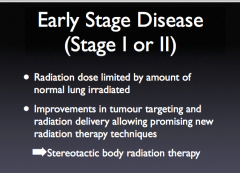
|

|
|
|
Tx of locally advanced NSCLC (stage III) |
RT and concurrent chemotherapy. RT over 6-7 weeks 30-33 daily treatments |
|
|
limiting factors for dose of deliverable radiation in Stage III NSCLC |

|
|
|
Solitary brain met when is tx surgical? |
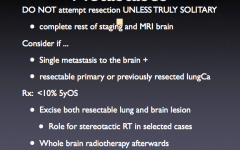
|
|
|
when is NSCLC incurable |
>99% of stage IV and most stage III |
|
|
Indications for palliative RT in NSCLC |
localized, symptomatic lesions Lung, brain, bone |
|
|
Palliative Chemotx in NSCLC |

|
|
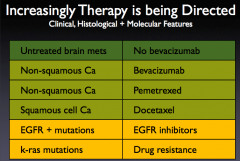
|
d |
|
|
Note: EGFR receptor inhibs in specific types of NSCLC |
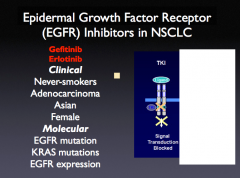
|
|
|
note: dramatic response to EGFR TKI therapy |
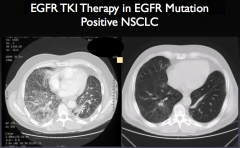
|

