![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
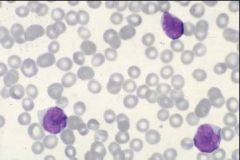
AML peripheral smear - The 3 blasts have a high N:C ratio and prominent nucleoli (pale area in nucleus)
|
a
|
|
|
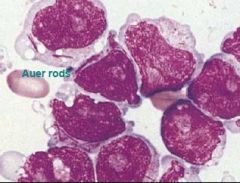
AML - blast cell w/ auer rod
|
a
|
|
|
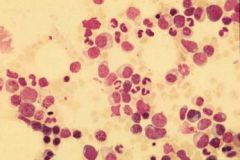
normal bone marrow - Heterogeneous mixture of myeloid and erythroid cells
|
a
|
|
|
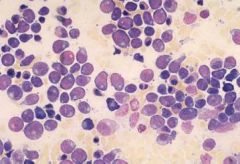
AML bone marrow - increased numbers of blasts (note prominent Golgi area in cytoplasm of blasts)
|
a
|
|
|
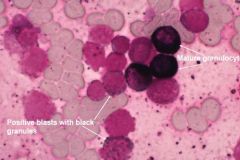
AML - MPO stain - MPO is present in immature and mature granulocytes and stains black
|
a
|
|
|
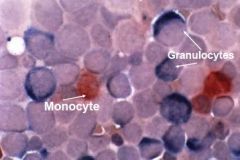
AML Esterase Stain - CAE & ANAE - granulocytes and monocytes - will stain mature and immature granulocytes blue
|
a
|
|
|
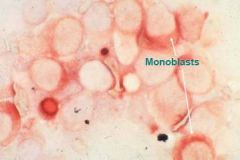
ANAE - Monoblasts/Monocytes - will stain mature and immature monocytes brown
|
a
|
|
|
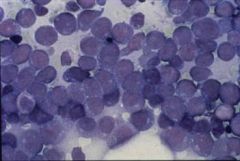
AML – note the absence of normal hematopoietic cells
|
a
|
|
|
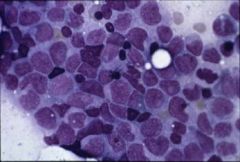
AML – some of the nuclei are folded - Consistent with monocytic differentiation
|
a
|
|
|
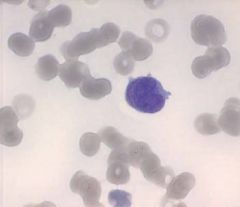
AML - Blast with folded nucleus
|
a
|
|
|
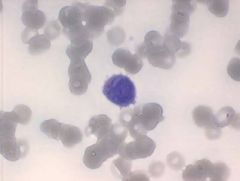
Blast with Auer rods
|
a
|
|
|
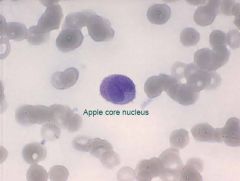
AML
|
a
|
|
|
AML - Bone marrow clot section - not a lot of megas, not a lot of diff – very bad
|
a
|
|
|
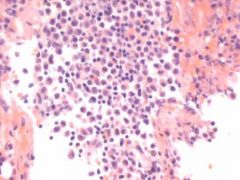
bone marrow in Lekukmia – sheets of blasts, maked reduction in normal hemapoitic cells
|
a
|
|
|
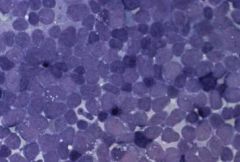
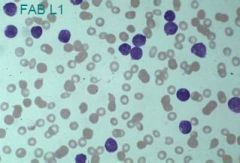
L1 - high N/C ratio
|
a
|
|
|
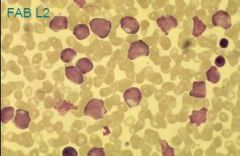
L2 – looks like myelobasts
|
a
|
|
|
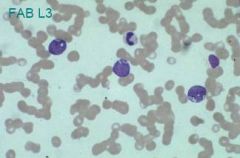
L3
|
a
|
|
|
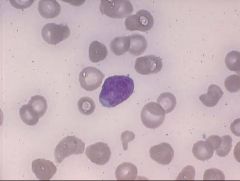
ALL smear
|
a
|
|
|
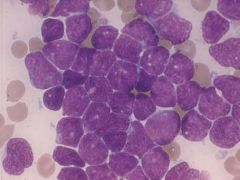
ALL - bone marrow aspirate
|
a
|
|
|
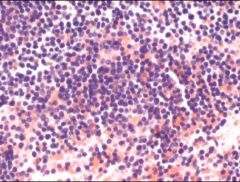
ALL Bone marrow clot section - too monotonous - Note the absence of normal hematopoietic precursors
|
a
|
|
|
ALL - Lymphoblast in CSF
|
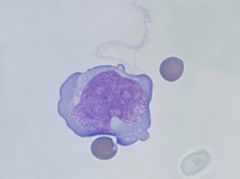
a
|
|
|
Leukemia - def
|
- cancer of BM progenitor cells
- malignant, monoclonal prolif of hematopoietic cells from the BM - abnormalities of cell prolif, diff, and termination |
|
|
Decreased apoptosis in leukemia
|
- common in lymphoid
- BCL2 overexpression in some NHL |
|
|
Blocked differentiation in leukemia
|
- common in myeloid
- t(15;17) is classic example |
|
|
Pancytopenia - definition and causes
|
- decreased production of BM cells
- if BM infiltrated, its probably leukemias, mets solid tumors, MF - If BM hypoplastic (decdevelopment), its prob aplastic anemias, infection, or metabolics |
|
|
AML - Histologic subtypes
|
M1 - M7 - just know that M3 is common and associated w/ DIC
|
|
|
AML - diagnosing BM failure
|
- Neutropenia
- Anemia - Thrombocytopenia |
|
|
AML - diagnosing
|
- Peripheral blood and BM - increased blasts (>20%) and auer rods
- Cytochemistry - MPO, SBB, or esterase stains |
|
|
AML - genetics
|
- t(15;17) - APL - good prog
- t(8;21), t(16;16) and inversion 16 - good prog - -7, -5 have poor prog |
|
|
AML - WHO classification
|
1) AML with recurrent genetic abnormalities
2) AML with multilineage dysplasia 3) AML therapy related 4) AML no otherwise specified (M0-M7) |
|
|
AML - treatment
|
- Allogenic transplantation > autologous trans > intensive chemo
- Drugs include all-trans-retinol, all-trans-retinoic acid, and #s w/ retinoic acid - 6 months in patient |
|
|
ALL - classifications
|
- L1 - Small cells, no granules TdT+ - most common
- L2 - larger cells w/ big nucleoli – common in adults - L3 (ass w/ EBV) - vacuolated cells – poor prognosis – t(8;14), t(8;22), t(2;8) |
|
|
ALL - diagnosing
|
- Flow cytometry!! - most kids have CD10 mophology – precursor B cell
- look for ITP, aplastic anemia, Reactive Lymphocytosis - In BM - inc blasts, (>30%) - decreased hematopoiesis |
|
|
ALL - causes
|
- almost always an unusual reaction to a common viral infection
- disease of childhood |
|
|
ALL - Immunophenotyping
|
- Low numbers - T-cell phenotype (CD 1-8)
- Midteens - Myelomonocytic 13 and 15 - Granulocyte, 14 - Monocytic - 19-23 - B-cell phenotype - 38 - B-cells/plasma cells - 34 - stem cell - 33 - myeloid |
|
|
ALL - Precursor B-cell flow cytometry
|
- + for CD10, CD19, CD34
- usually neg for k & l and B cell markers in mature B-cells (CD20, CD22) |
|
|
ALL - Mature B-cell flow cytometry
|
- + for CD10, 19, 20, 22
- + for either the k or l light chain - Negative for CD34 |
|
|
ALL - Precursor T-cell flow cytometry
|
- + for CD3, CD4 and CD8
|
|
|
ALL cytogenetics
|
- good prognosis - hyperdiploidy (50 or greater chromosomes)
- bad - Philadelphia chromosome (t(9;22)), t(4;11), t(8;14), hypodiploidy |
|
|
ALL - Treatment
|
- 2-3 years outpatient
– augmented therapy does better than standard therapy - do best if 2-10 – want WBC to be low |
|
|
ALL - 9-22 translocation
|
- mainly in adults – looks like CML – 3-5% - do horribly
|
|
|
ALL - 4-11 translocation
|
– babies and high WBC – do very bad
|
|
|
ALL - 8-14 translocation
|
- in c-myc
- burkitts lymphoma |

