![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ANTERIOR chapman points related to the GU system
|
One inch lateral to and one inch superior to the umbilicus
|
|
|
POSTERIOR chapman reflex related to the GU system
|
T12/L1 intertransverse space midway b/t the spinous and tip of the transverse processes
|
|
|
Parasympathetic innvervation to the kidney from the VAGUS nerve
|
from C1 and C2 to the renal parenchyma
|
|
|
Parasympathetic innervation to the kidney from S2-S4
|
Renal Pelvis
Upper ureters |
|
|
Sympathetic innvervation to the kidney is from _____
|
T10 to L1
|
|
|
sympathetic effects upon the kidney include
|
Vasoconstriction of AFferent arterioles
decreased GFR decreased urine volume Elevation of systemic BP Increased renin release from juxtoglomerular apparatus Assists in regulation of Na retention |
|
|
Sympathetic effects upon the kidney are exaggerated by
|
emotional stress
|
|
|
Sympathetic hyperactivity to the kidney has been implicated as one cause of ....
|
HTN
|
|
|
Prolonged SNS stimulation to the kidney (weeks) results in ...
|
retention of Na and H2O with resultant arterial P
|
|
|
Vagal PSNS afferent fibers have both ______ and play a role in _____
|
mechanireceptors
chemoreceptors renorenal reflexes |
|
|
Vagal PSNS mechanoreceptors, besides renorenal reflexes, also play a role in _____
|
assist in regulating BP
|
|
|
Effects of hyperparasympatheticonia are ...
|
unknown
|
|
|
Normal venous and lymphatic drainage of the kidney depends primarily upon _______
|
the diaphragm
|
|
|
Diaphragmatic motion and, as a result renal function, can be impaired by what (3) things?
|
lower rib dysfunction
upper lumbar dysfunction Somatosomatic reflexes from C3-5 dysfunction |
|
|
All renal lymph drains into the _____
|
thoracic duct and then into left subclavian vein
|
|
|
Kyphotic posturing tenses the diaphragm, leading to _____ of the kidney due to ....
|
Ptosis
Loss of protective fat d/t the liver pushing on the right kidney |
|
|
Ptosis of the kidney results in
|
Chronic passive congestion
Kinked ureters Hydronephrosis Orthostatic albuminuria Urinary statis -> UTI, calculi |
|
|
SXS of renal ptosis include ...
|
LBP
Sciatica Inguinal pain Recurrent pyelonephritis Recurrent renal lithiasis |
|
|
Less common SXS of renal ptosis include ...
|
considerable morning thirst
LBP upon awakening coated tongue painful soles of the feet leg discomfort knee pain |
|
|
Step I of treating renal ptosis is ...
|
lifting the kidney via visceral technique and observe if kidney stays lifted
|
|
|
Step II of treating renal ptosis is ...
|
If kidney does not stay lifted from step I, use visceral technique to lift liver (may be holding kidney down)
|
|
|
Step III of tx renal ptosis is ...
|
Redome the diaphragm (lymphatic technique)
|
|
|
Step IV of tx renal ptosis is ...
|
Release the pelvic floor (lymphatic technique)
|
|
|
Step V of tx renal ptosis is ...
|
Release the ANTERIOR cervical fasciae (myofascial release)
|
|
|
Step VI of tx renal ptosis is ...
|
Balance the reciprocal tension membrane (Cranial technique)
|
|
|
Caution should be used in administering OMM to pts on corticosteroids for antirejection therapy d/t ...
|
presence of severe osteoporosis
|
|
|
Psoas
|
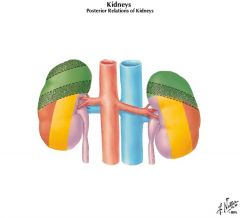
Somatic effects of dysfunction in the LAVENDER area
|
|
|
quadratus lumborum
|
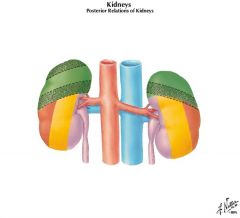
Somatic effects of dysfunction at the YELLOW area
|
|
|
Transverse abdominus
|

SD of dysfunction of the RED area
|
|
|
diaphragm
|
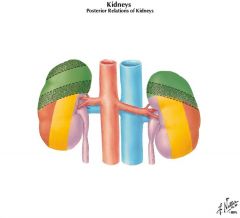
SD resulting from problems in the GREEN area
|
|
|
Polycystic kidneys
|

What is this?
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis
|
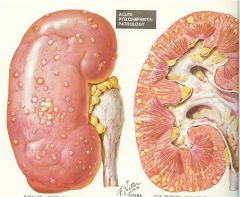
what is this?
|

